|
Media Policy
Media policy or media politics refers to decisions regarding legislation and political actions that organize, support, or regulate the media, particularly mass media and the media industry. These actions are typically driven by pressures from public opinion, non-governmental organizations, or industry interest groups. In some cases, they are influenced by the demands of political leaders. Historically, distinct policies were applied to print media, radio, television, public broadcasting, and telecommunications. However, these have converged in the digital infrastructure, resulting in markets that are often insufficiently regulated. While regulations exist, technological innovations frequently outpace them, leading to issues such as copyright violations, the spread of misinformation and disinformation, online harassment, and hate speech. Such challenges necessitate legal action to protect intellectual property rights (e.g. the Digital Economy Act 2010), although emerging technol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Opinion
Public opinion, or popular opinion, is the collective opinion on a specific topic or voting intention relevant to society. It is the people's views on matters affecting them. In the 21st century, public opinion is widely thought to be heavily influenced by the media; many studies have been undertaken which look at the different factors which influence public opinion. Politicians and other people concerned with public opinion often attempt to influence it using advertising or rhetoric. Opinion plays a vital role in uncovering some critical decisions. Sentiment analysis or opinion mining is a method used to mine the thoughts or feelings of the general population. One of the struggles of public opinion is how it can be influenced by misinformation. Etymology The term "public opinion" was derived from the French ', which was first used in 1588 by Michel de Montaigne, one of the most significant philosophers of the French Renaissance, in the second edition of his famous '' Essays ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
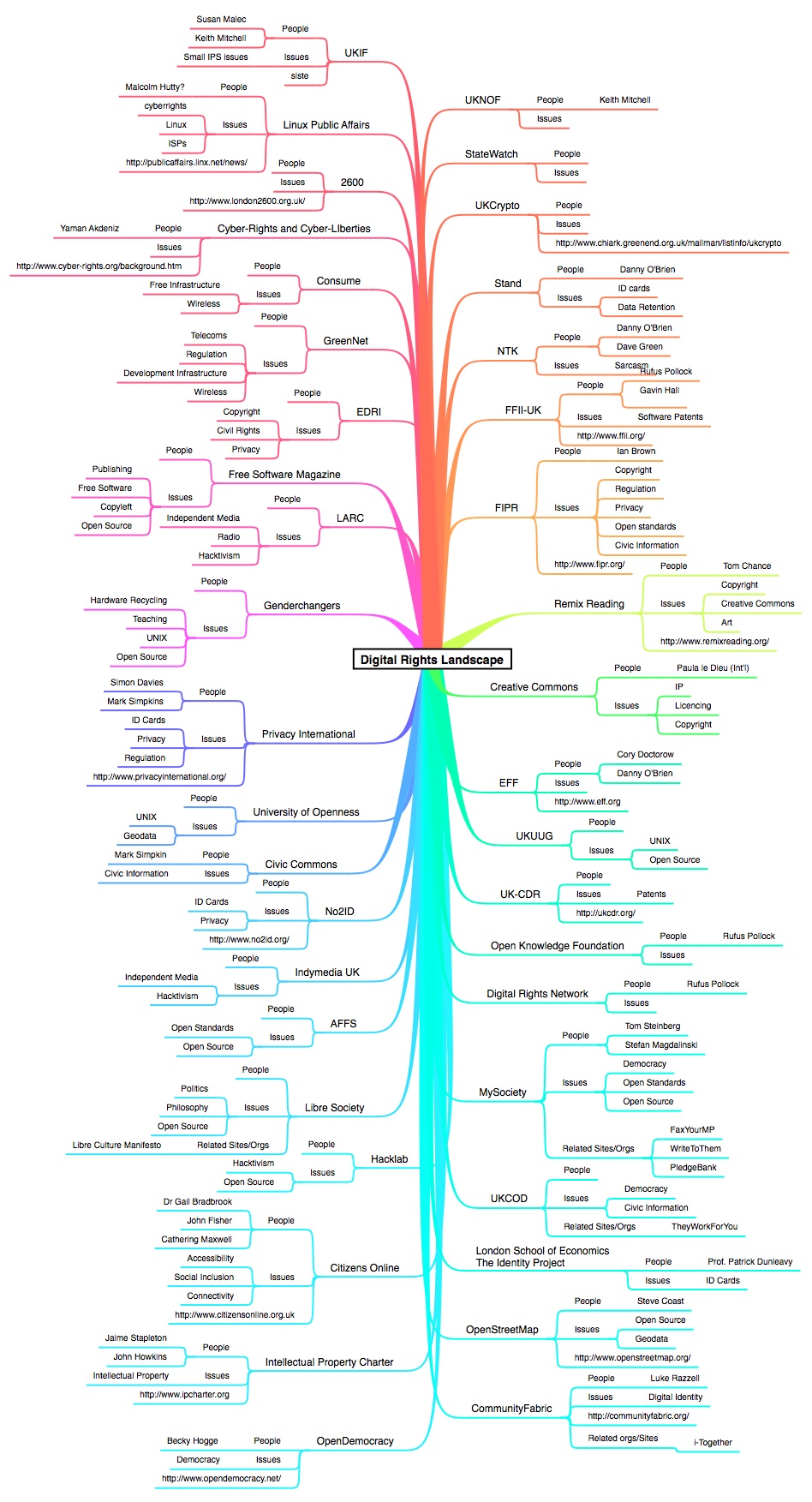
Digital Rights
Digital rights are those human rights and Natural and legal rights, legal rights that allow individuals to access, use, create, and publish digital media or to access and use computers, other Consumer electronics, electronic devices, and telecommunications networks. The concept is particularly related to the protection and realization of existing rights, such as the right to privacy and Freedom of speech, freedom of expression, in the context of digital technologies, especially the Internet. The laws of several countries recognize a right to Internet access. Human rights and the Internet A number of human rights have been identified as relevant with regard to the Internet. These include freedom of expression, privacy, and freedom of association. Furthermore, the right to education and multilingualism, consumer rights, and capacity building in the context of the right to development have also been identified. APC Internet Rights Charter (2001) The APC Internet Rights Charte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Editorial Independence
An editorial, or leading article (UK) or leader (UK), is an article or any other written document, often unsigned, written by the senior editorial people or publisher of a newspaper or magazine, that expresses the publication's opinion about a particular topic or issue. Australian and major United States newspapers, such as ''The New York Times'' and '' The Boston Globe'', often classify editorials under the heading " opinion". Examples Illustrated editorials may appear in the form of editorial cartoons. Typically, a newspaper's editorial board evaluates which issues are important for their readership to know the newspaper's opinion on. Editorials are typically published on a dedicated page, called the editorial page, which often features letters to the editor from members of the public; the page opposite this page is called the op-ed page and frequently contains opinion pieces (hence the name think pieces) by writers not directly affiliated with the publication. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute For Media And Communication Policy
The Institute for Media and Communication Policy (IfM) was founded in 2005 as an independent research institution that is exclusively dedicated to issues surrounding media and communication policies. It was established in February 2006 in Berlin-Charlottenburg, but in November 2014 it moved to Cologne. The institute is funded by leading German public and private media organizations. Benefactors The institute is financially supported by various media organizations including ARD, ZDF, RTL, Sky Germany, Axel Springer AG, the publishing groups Verlagsgruppe Georg von Holtzbrinck, Der Spiegel and the Medienboard Berlin-Brandenburg (the regional Berlin Media and Film funding organization) among others. The Institute’s scientific advisory council consists of 25 reputable scholars, all of whom gained recognition in the field through media and communication policy-related publications. Lutz Hachmeister, a journalist and media scholar, is the founding director of the Institute. The in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Media Legal Defence Initiative
Media Defence (or Media Legal Defence Initiative) is a non-governmental organization established in 2008 to provide legal assistance to journalists, citizen journalists and independent media institutions. It also supports training in media law and promotes the exchange of information, litigation tools and strategies for lawyers working on media freedom cases. It is based in London, England and has a global network of media lawyers and media freedom activists with whom it works on cases and projects. History The Media Defence was established as a not-for-profit company in June 2008 and registered as an independent charitable organization in 2009. It originated after the criminal defamation trial in 2004 of Indonesian newspaperman Bambang Harymurti, editor of ''Tempo'' magazine (Indonesia). The group that assisted the defense of Harymurti saw the need for an independent non-governmental organization that could provide legal support to journalists and media outlets worldwide to de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Media
State media are typically understood as media outlets that are owned, operated, or significantly influenced by the government. They are distinguished from public service media, which are designed to serve the public interest, operate independently of government control, and are financed through a combination of public funding, licensing fees, and sometimes advertising. The crucial difference lies in the level of independence from government influence and the commitment to serving a broad public interest rather than the interests of a specific political party or government agenda. State media serve as tools for public diplomacy and narrative shaping. These media outlets can broadcast via television, radio, print, and increasingly on social media, to convey government viewpoints to domestic and international audiences. The approach to using state media can vary, focusing on positive narratives, adjusting narratives retroactively, or spreading misinformation through sophisticated so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Democracy
E-democracy (a blend of the terms electronic and democracy), also known as digital democracy or Internet democracy, uses information and communication technology (ICT) in political and governance processes. The term is credited to digital activist Steven Clift. By using 21st-century ICT, e-democracy seeks to enhance democracy, including aspects like civic technology and E-government. Proponents argue that by promoting transparency in decision-making processes, e-democracy can empower all citizens to observe and understand the proceedings. Also, if they possess overlooked data, perspectives, or opinions, they can contribute meaningfully. This contribution extends beyond mere informal disconnected debate; it facilitates citizen engagement in the proposal, development, and actual creation of a country's laws. In this way, e-democracy has the potential to incorporate crowdsourced analysis more directly into the policy-making process. Electronic democracy incorporates a diverse ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Communication
Political communication is the study of political messaging that is communicated, usually to the public e.g. political campaigns, speeches and political advertising, often concerning the mass media. It is an interdisciplinary field that draws from communication studies and political science. Political communication is concerned with ideas such as information flow, political influence, policy making, news, and public opinion. The field also focuses on the study of political social media, propaganda, political economy of communication and non-profit organisations that communicate to affect political processes. Modern societal changes that have affected the field include the digitization of media, polarization and a movement towards a post-truth media environment. History Ancient History Political communication has existed since antiquity. During this era it was common for rulers to use symbols and monuments to communicate power and authority to the masses. In ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entertainment Law
Entertainment law, also known as media law, encompasses legal services provided to the entertainment industry. These services often overlap with intellectual property law, which includes key components such as trademarks, copyright, and the right of publicity. However, the practice of entertainment law frequently extends into other legal areas including employment law, contract law, torts, labor law, bankruptcy law, immigration, securities law, security interests, agency, right of privacy, defamation, advertising, criminal law, tax law, International law (especially private international law), and insurance law. Much of the work of an entertainment law practice is transaction based, i.e., drafting contracts, negotiation and mediation. Some situations may lead to litigation or arbitration. Overview Entertainment law covers an area of law that involves media of all different types (e.g. TV, film, music, publishing, advertising, Internet & news media, etc.) and stretche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentration Of Media Ownership
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', '' number concentration'', and '' volume concentration''. The concentration can refer to any kind of chemical mixture, but most frequently refers to solutes and solvents in solutions. The molar (amount) concentration has variants, such as normal concentration and osmotic concentration. Dilution is reduction of concentration, e.g. by adding solvent to a solution. The verb to concentrate means to increase concentration, the opposite of dilute. Etymology ''Concentration-'', ''concentratio'', action or an act of coming together at a single place, bringing to a common center, was used in post-classical Latin in 1550 or earlier, similar terms attested in Italian (1589), Spanish (1589), English (1606), French (1632). Qualitative description Often in informal, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interest Group
Advocacy groups, also known as lobby groups, interest groups, special interest groups, pressure groups, or public associations, use various forms of advocacy or lobbying to influence public opinion and ultimately public policy. They play an important role in the development of political and social systems. Motives for action may be based on political, economic, religious, moral, commercial or common good-based positions. Groups use varied methods to try to achieve their aims, including lobbying, media campaigns, awareness raising publicity stunts, polls, research, and policy briefings. Some groups are supported or backed by powerful business or political interests and exert considerable influence on the political process, while others have few or no such resources. Some have developed into important social, and political institutions or social movements. Some powerful advocacy groups have been accused of manipulating the democratic system for narrow commercial gain, and in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Media Regulation
Mass media regulations or simply media regulations are a form of media policy with rules enforced by the jurisdiction of law. Guidelines for mass media use differ across the world. This regulation, via law, rules or procedures, can have various goals, for example intervention to protect a stated "public interest", or encouraging competition and an effective media market, or establishing common technical standards. The principal targets of mass media regulation are the press, radio and television, but may also include film, recorded music, cable, satellite, storage and distribution technology (discs, tapes etc.), the internet, mobile phones etc. It includes the regulation of independent media. Content regulation The transmission of content and intellectual property have attracted attention and regulation from authorities worldwide, due to the memetic nature and possible social impact of content sharing. The regulation of content may take the form of selective censorship of work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |