|
Mckelveyite-(Y)
Mckelveyite-(Y) is a hydrated sodium, barium, yttrium, and uranium–containing carbonate mineral, with the chemical formula Ba3Na(Ca,U)Y(CO3)6·3H2O. Occurrence It was first described in 1965 from deposits in the Green River Formation, Sweetwater County, Wyoming, and is named after Vincent Ellis McKelvey (1916–1985), a former director of the United States Geological Survey. It occurs associate with trona layers in the Green River Formation of Wyoming and has been reported from an alkalic intrusive, the Khibiny Massif in the Kola Peninsula of Russia. It occurs in association with ewaldite, acmite, biotite, quartz, labuntsovite, searlesite and leucosphenite in the Green River Formation. In the Khibiny Massif it occurs with ewaldite, belovite-(Ce), fluorite, nenadkevichite, ancylite-(Ce), synchysite-(Ce), kukharenkoite-(Y), burbankite, calcite, barite and orthoclase. In the Khanneshin complex, Afghanistan it occurs with dolomite, calkinsite-(Ce), carbocernaite, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate Mineral
Carbonate minerals are those minerals containing the carbonate ion, . Carbonate divisions Anhydrous carbonates *Calcite group: trigonal ** Calcite CaCO3 ** Gaspéite (Ni,Mg,Fe2+)CO3 **Magnesite MgCO3 ** Otavite CdCO3 ** Rhodochrosite MnCO3 ** Siderite FeCO3 ** Smithsonite ZnCO3 **Spherocobaltite CoCO3 *Aragonite group: orthorhombic ** Aragonite CaCO3 ** Cerussite PbCO3 ** Strontianite SrCO3 ** Witherite BaCO3 ** Rutherfordine UO2CO3 ** Natrite Na2CO3 Anhydrous carbonates with compound formulas *Dolomite group: trigonal ** Ankerite CaFe(CO3)2 ** Dolomite CaMg(CO3)2 ** Huntite Mg3Ca(CO3)4 ** Minrecordite CaZn(CO3)2 ** Barytocalcite BaCa(CO3)2 Carbonates with hydroxyl or halogen *Carbonate with hydroxide: monoclinic **Azurite Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2 ** Hydrocerussite Pb3(CO3)2(OH)2 ** Malachite Cu2CO3(OH)2 ** Rosasite (Cu,Zn)2CO3(OH)2 ** Phosgenite Pb2(CO3)Cl2 ** Hydrozincite Zn5(CO3)2(OH)6 ** Aurichalcite (Zn,Cu)5(CO3)2(OH)6 Hydrated carbonates * Hydromagnesite Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2.4H2O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acmite
List of mineral symbols, Aegirine is a member of the clinopyroxene group of Silicate minerals#Inosilicates, inosilicate minerals. Aegirine is the sodium endmember of the aegirine-augite series. Aegirine has the chemical formula sodium, Nairon, Fesilicon, Si2oxygen, O6 in which the iron is present as Fe3+. In the aegirine-augite series the sodium is variably replaced by calcium with iron(II) and magnesium replacing the iron(III) to balance the charge. Aluminium also substitutes for the iron(III). Acmite is a fibrous, green-colored variety. Aegirine occurs as dark green monoclinic prismatic crystals. It has a glassy luster and perfect cleavage. Its Mohs scale of mineral hardness, Mohs hardness varies from 5 to 6, and its specific gravity is between 3.2 and 3.4. This mineral commonly occurs in alkalic igneous rocks, nepheline syenites, carbonatites and pegmatites. It also appears in regionally Metamorphism, metamorphosed schists, gneisses, and iron formations; in blueschist facies r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcite
Calcite is a carbonate mineral and the most stable polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison. Large calcite crystals are used in optical equipment, and limestone composed mostly of calcite has numerous uses. Other polymorphs of calcium carbonate are the minerals aragonite and vaterite. Aragonite will change to calcite over timescales of days or less at temperatures exceeding 300 °C, and vaterite is even less stable. Etymology Calcite is derived from the German ''Calcit'', a term from the 19th century that came from the Latin word for lime, ''calx'' (genitive calcis) with the suffix "-ite" used to name minerals. It is thus etymologically related to chalk. When applied by archaeologists and stone trade professionals, the term alabaster is used not just as in geology and mineralogy, where it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchysite-(Ce) and carbonatite.
Synchysite-(Ce) is a carbonate mineral and an end member of the synchysite group. The general chemical formula is . Discovery and naming Synchysite-(Ce) was discovered in 1900 by Gustaf Flink. The name is derived from the Greek "σύγχΰσις", meaning "confounding", a reference to the possibility to confuse the mineral with Parisite-(Ce). Occurrences Synchysite-(Ce) is found in rare-earth element bearing pegmatites. It can also occur as a hydrothermal mineral in granite, alkalic syenite Syenite is a coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock with a general composition similar to that of granite, but deficient in quartz, which, if present at all, occurs in relatively small concentrations (< 5%). Some syenites contain larger proport ... References {{Reflist[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancylite-(Ce)
Ancylite is a group of hydrous strontium carbonate minerals containing cerium, lanthanum and minor amounts of other rare-earth elements. The chemical formula is with ancylite-Ce enriched in cerium and ancylite-La in lanthanum.http://webmineral.com/data/Ancylite-(Ce).shtml Webmineral data Ancylite-Ce.http://www.handbookofmineralogy.org/pdfs/ancylitela.pdf Handbook of Mineralogy. Ancylite was first described in 1899 for an occurrence in the Narsarsuk pegmatite in west Greenland Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is ... and named from the grc, αυκιλος for ''curved'' in reference to its rounded or distorted crystal form.http://www.mindat.org/min-216.html Mindat. References Carbonate minerals Strontium minerals Lanthanide minerals Orthorhombic minerals Minerals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nenadkevichite
Nenadkevichite is a rare silicate mineral containing niobium with the chemical formula . It forms brown to yellow to rose colored orthorhombic dipyramidal crystals with a dull to earthy luster. It has a Mohs hardness of 5 and a specific gravity of 2.86. It was first reported in 1955 from a nepheline syenite pegmatite in the Kola Peninsula. In addition it has been reported from Mont Saint-Hilaire, Canada; the Ilimaussaq complex, Greenland; Windhoek District, Namibia; and Zheltye Vody, Ukraine. It was named after Konstantin Avtonomovich Nenadkevich The first name Konstantin () is a derivation from the Latin name ''Constantinus'' (Constantine) in some European languages, such as Russian and German. As a Christian given name, it refers to the memory of the Roman emperor Constantine the Great. ... (1880–1963), Russian mineralogist and geochemist. ReferencesWebmineral data [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
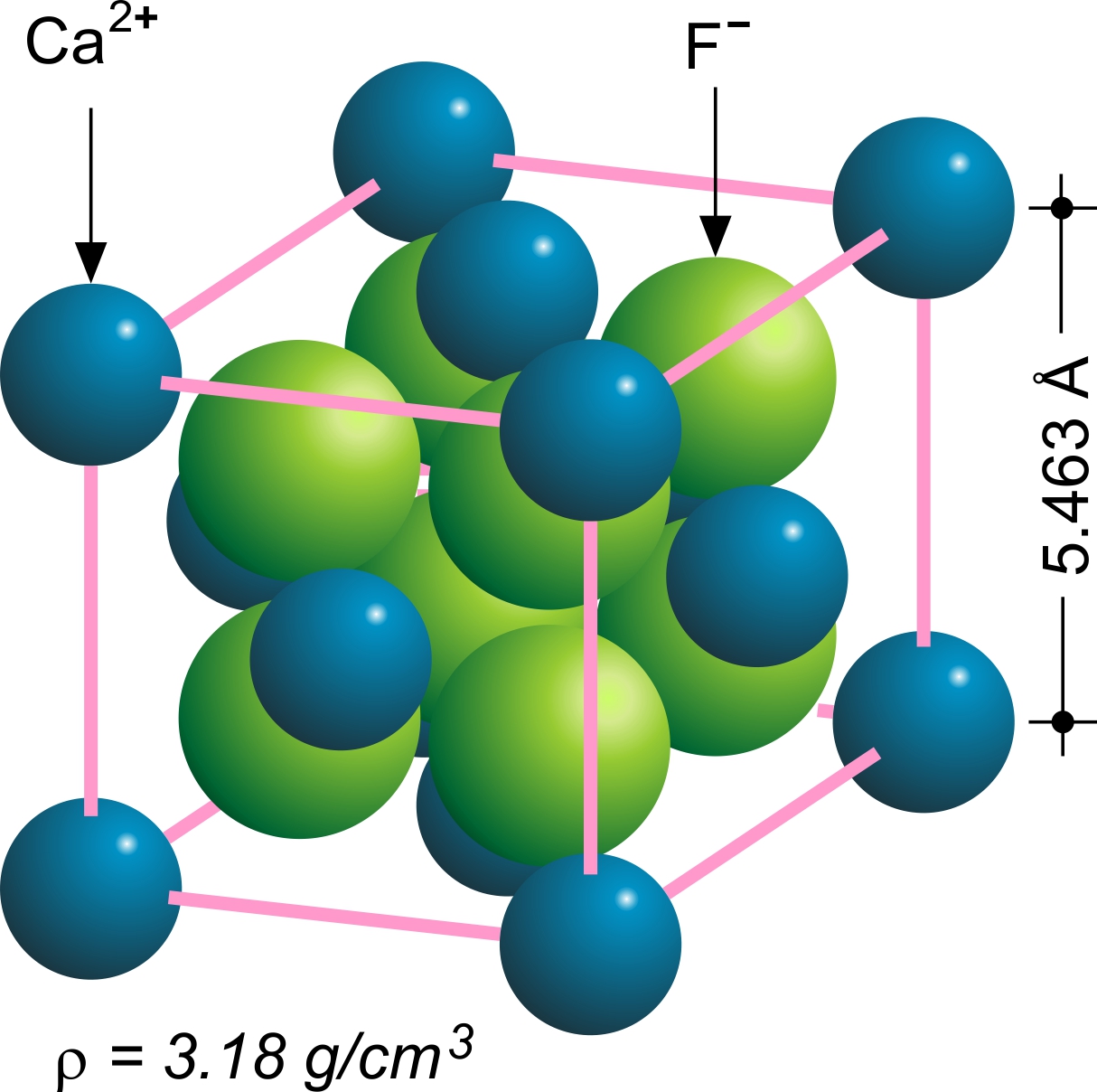
Fluorite
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon. The Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison, defines value 4 as fluorite. Pure fluorite is colourless and transparent, both in visible and ultraviolet light, but impurities usually make it a colorful mineral and the stone has ornamental and lapidary uses. Industrially, fluorite is used as a flux for smelting, and in the production of certain glasses and enamels. The purest grades of fluorite are a source of fluoride for hydrofluoric acid manufacture, which is the intermediate source of most fluorine-containing fine chemicals. Optically clear transparent fluorite lenses have low dispersion, so lenses made from it exhibit less chromatic aberration, making them valuable in microscopes and telescopes. Fluorite optics ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belovite-(Ce)
Belovite-(Ce) () is the cerium analogue of Belovite-(La). It is a member in the belovite group being a subgroup of the apatite group. Belovite-(Ce) was first described in 1954 and named for Nikolai Belov. Its type locality is Malyi Punkaruaiv mountain in Lovozersky District, Russia Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh .... References Sodium minerals Strontium minerals Cerium minerals Phosphate minerals Trigonal minerals Minerals in space group 147 Minerals described in 1953 {{mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |