|
Maxillopoda
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthropods including decapods (shrimps, prawns, crabs, lobsters and crayfish), seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, opossum shrimps, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods (insects and entognathans) emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed pan-group referred to as Pancrustacea. The three classes Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda and Remipedia are more closely related to the hexapods than they are to any of the other crustaceans ( oligostracans and multicrustaceans). The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thecostraca
Thecostraca is a class of marine invertebrates containing over 2,200 described species. Many species have planktonic larvae which become sessile or parasitic as adults. The most prevalent subgroup are the barnacles (subclass Cirripedia), constituting a little over 2,100 known species. The subgroup Facetotecta contains a single genus, ''Hansenocaris'', known only from the tiny planktonic nauplii called "y-larvae". These larvae have no known adult form, though it is suspected that they are parasites, and their affinity is uncertain. Some researchers believe that they may be larval tantulocaridans. No larval tantulocaridans are currently known. The group Ascothoracida contains about 110 species, all parasites of coelenterates and echinoderms. The nauplius larvae (sometimes absent) can be both lecithotrophic (non-feeding) and planktotrophic (feeding), and is followed by a larval stage called the cyprid, which is always lecithotrophic. The cypridoid larvae are referred to as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
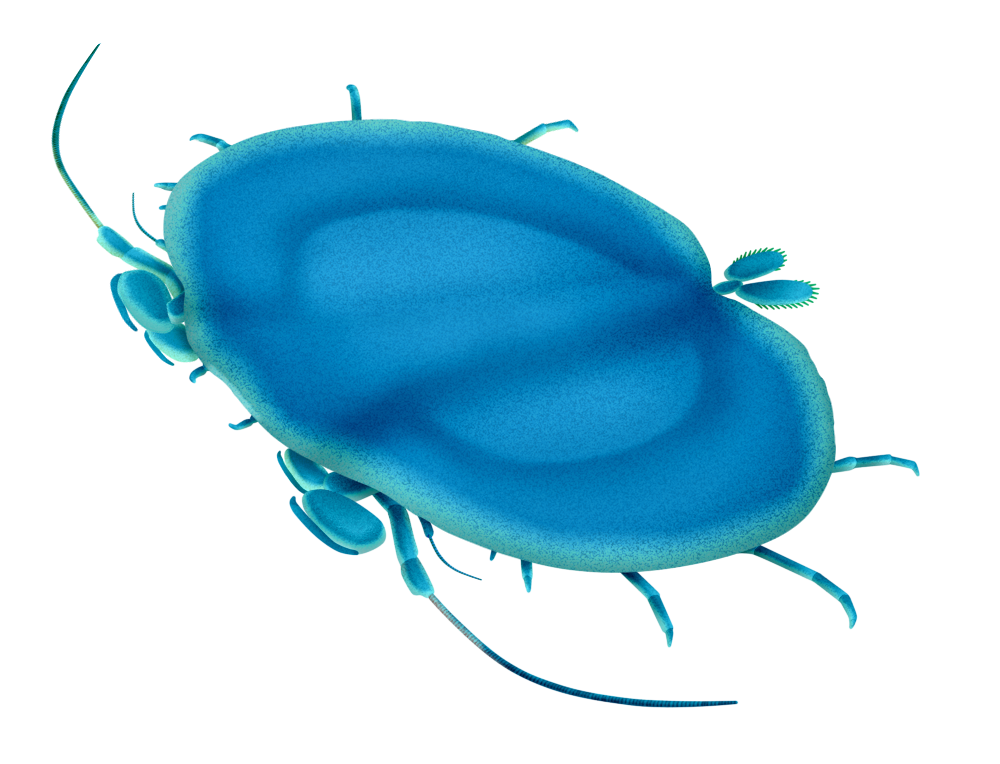
Tantulocarida
Tantulocarida is a highly specialised group of parasitic crustaceans that consists of about 33 species, treated as a class in superclass Multicrustacea. They are typically ectoparasites that infest copepods, isopods, tanaids, amphipods and ostracods. Description In the Tantulocarida, animals do not ever present eyes. The tantulus larvae has a head with a ventral oral disc but no appendages, a six-segmented thorax with six pairs of legs, and a limbless abdomen consisting of one to six segments in addition to a telson. The larvae also possesses a cuticular stylet on the cephalon through which they can push a rootlet system for extraction of nutrients from a host. The rootlet system itself is a direct extension of the gut. Body length Members of this subclass are minute – less than in length and have a dramatic reduction in body form compared to other crustaceans, with an unsegmented, sac-like thorax and a much reduced abdomen. One tantulocarid species, ''Tantulacus diet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclida
Cyclida (formerly Cycloidea, and so sometimes known as cycloids) is an extinct order of crab-like fossil arthropods that lived from the Carboniferous to the Jurassic and possibly Cretaceous. Their classification is uncertain, but they are generally interpreted as crustaceans, likely belonging to the superclass Multicrustacea. Description Cyclidans have a "striking" resemblance to crabs, with circular to ovoid carapaces, which vary from flat to domed. The carapace covers the entire body. The largest members are over across the carapace. Their gill plates are arranged in a horseshoe shape beneath the carapace in at least some species. The head and thorax were fused into a single unit, the cephalothorax. The eyes, when present, were stalked, with the head also bearing two pairs of antennae, the first of which (dubbed the antennulae), are significantly longer than the second. There are at least eight pairs of appendages excluding the antennae and antennulae. The anterior appendag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnacle
Barnacles are arthropods of the subclass (taxonomy), subclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacean, Crustacea. They are related to crabs and lobsters, with similar Nauplius (larva), nauplius larvae. Barnacles are exclusively marine invertebrates; many species live in shallow and tidal waters. Some 2,100 species have been described. Barnacle adults are Sessility (motility), sessile; most are Filter feeder, suspension feeders with hard calcareous shells, but the Rhizocephala are parasitic castration, specialized parasites of other crustaceans, with reduced bodies. Barnacles have existed since at least the mid-Carboniferous, some 325 million years ago. In folklore, barnacle geese were once held to emerge fully formed from goose barnacles. Both goose barnacles and the Austromegabalanus psittacus, Chilean giant barnacle are fished and eaten. Barnacles are economically significant as biofouling on ships, where they cause hydrodynamic Drag (physics), drag, reducing efficiency. Ety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copepod
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthos, benthic (living on the sediments), several species have Parasitism, parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants (phytotelmata) such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as Ecological indicator, biodiversity indicators. As with other crustaceans, copepods have a larval form. For copepods, the egg hatches into a Crustacean larvae#Nauplius, nauplius form, with a head and a tail but no true thorax or abdomen. The larva molts several times until it resembles the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyostraca
Ichthyostraca is a class of parasitic crustaceans. It is composed of two subclasses; Pentastomida The Pentastomida are an enigmatic group of parasitic arthropods commonly known as tongue worms due to the resemblance of the species of the genus ''Linguatula'' to a vertebrate tongue; molecular studies point to them being highly derived crust ... and Branchiura. They mainly parasitize various vertebrates and feed on their blood or mucus. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q22986461 Arthropod classes Maxillopoda Crustaceans Parasitic crustaceans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mystacocarida
Derocheilocarididae is a family of marine crustaceans that form part of the meiobenthos. It is the only family in the monotypic order Mystacocaridida, and the monotypic subclass Mystacocarida. These mystacocarids are less than long, and live interstitially in the intertidal zones of sandy beaches. Taxonomy The taxonomy of the mystacocarids is extremely conservative, since all mystacocarids look superficially alike. , the 13 described species are divided between two genera, ''Derocheilocaris'' (eight species) and ''Ctenocheilocaris'' (five species). The first mystacocarids to be found were discovered on a beach in southern New England in 1939. Distribution Mystacocarids occur along the coasts of South and North America, southern Africa, and the western Mediterranean. The lack of records from other parts of the world is "almost certainly" due to a lack of appropriate sampling, rather than a true absence. Description Mystacocarids are tiny pigmentless crustaceans, less than long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subphylum
In zoological nomenclature, a subphylum is a taxonomic rank below the rank of phylum. The taxonomic rank of " subdivision" in fungi and plant taxonomy is equivalent to "subphylum" in zoological taxonomy. Some plant taxonomists have also used the rank of subphylum, for instance monocotyledons as a subphylum of phylum Angiospermae and vertebrates as a subphylum of phylum Chordata. Taxonomic rank Subphylum is: #subordinate to the phylum #superordinate to the infraphylum, which is in turn superordinate to parvphylum. Where convenient, subphyla in turn can be divided into infraphyla; in turn such an infraphylum also would be superordinate to any classes or superclasses in the hierarchy. Examples Not all fauna phyla are divided into subphyla. Those that are include: *Arthropoda: divided into subphyla Trilobitomorpha, Chelicerata, Myriapoda, and Pancrustacea * Brachiopoda: divided into subphyla Linguliformea, Craniformea and Rhynchonelliformea * Chordata: divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metamerism (biology), metameric) Segmentation (biology), segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior Organ (anatomy), organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, ventral Ventral nerve cord, nerve cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate subphylum Vertebrata, i.e. vertebrates. Well-known Phylum, phyla of invertebrates include arthropods, molluscs, annelids, echinoderms, flatworms, cnidarians, and sponges. The majority of animal species are invertebrates; one estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxon, taxa have a greater number and diversity of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata. Invertebrates vary widely in size, from 10 Micrometre, μm (0.0004 in) myxozoans to the 9–10 m (30–33 ft) colossal squid. Some so-called invertebrates, such as the Tunicata and Cephalochordata, are actually sister chordate subphyla to Vertebrata, being more closely related to vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the "invertebrates" para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatic Animal
An aquatic animal is any animal, whether vertebrate or invertebrate, that lives in a body of water for all or most of its lifetime. Aquatic animals generally conduct gas exchange in water by extracting dissolved oxygen via specialised respiratory system, respiratory organ (biology), organs called gills, cutaneous respiration, through the skin or enteral respiration, across enteral mucosae, although some are evolution, evolved from terrestrial ancestors that re-adaptation, adapted to aquatic environments (e.g. marine reptiles and marine mammals), in which case they actually use lungs to breathing, breathe air and are essentially apnea, holding their breath when living in water. Some species of gastropod mollusc, such as the Elysia chlorotica, eastern emerald sea slug, are even capable of kleptoplastic photosynthesis via endosymbiosis with ingested yellow-green algae. Almost all aquatic animals reproduce in water, either oviparously or viviparously, and many species routinely fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |