|
Maritime Silk Road
The Maritime Silk Road or Maritime Silk Route is the maritime section of the historic Silk Road that connected Southeast Asia, East Asia, the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian Peninsula, eastern Africa, and Europe. It began by the 2nd century BCE and flourished until the 15th century CE. The Maritime Silk Road was primarily established and operated by Austronesian sailors in Southeast Asia who sailed large long-distance ocean-going sewn-plank and lashed-lug trade ships. The route was also utilized by the dhows of the Persian and Arab traders in the Arabian Sea and beyond, and the Tamil merchants in South Asia. China also started building their own trade ships ('' chuán'') and followed the routes in the later period, from the 10th to the 15th centuries CE. The network followed the footsteps of older Austronesian jade maritime networks in Southeast Asia, as well as the maritime spice networks between Southeast Asia and South Asia, and the West Asian maritime networks in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamils
The Tamils ( ), also known by their endonym Tamilar, are a Dravidian peoples, Dravidian ethnic group who natively speak the Tamil language and trace their ancestry mainly to the southern part of the Indian subcontinent. The Tamil language is one of the longest-surviving classical languages, with over two thousand years of Tamil literature, written history, dating back to the Sangam period (between 300 BCE and 300 CE). Tamils constitute about 5.7% of the Indian population and form the majority in the South Indian state of Tamil Nadu and the union territory of Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry. They also form significant proportions of the populations in Sri Lankan Tamils, Sri Lanka (15.3%), Tamil Malaysians, Malaysia (7%) and Indian Singaporeans, Singapore (5%). Tamils have migrated world-wide since the 19th century CE and a significant population exists in South Africa, Mauritius, Fiji, as well as other regions such as the Southeast Asia, Middle East, Caribbean and parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austronesians
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austronesian languages. They also include indigenous ethnic minorities in Vietnam, Cambodia, Myanmar, Thailand, Hainan, the Comoros, and the Torres Strait Islands. The nations and territories predominantly populated by Austronesian-speaking peoples are sometimes known collectively as Austronesia. The group originated from a Early human migrations, prehistoric seaborne migration, known as the Austronesian expansion, from Taiwan, circa 3000 to 1500 BCE. Austronesians reached the Batanes, Batanes Islands in the northernmost Philippines by around 2200 BCE. They used sails some time before 2000 BCE. In conjunction with their use of Austronesian vessels, other maritime technologies (notably catamarans, out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austronesian Maritime Trade Network
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over land or water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a single trade route contains long-distance arteries, which may further be connected to smaller networks of commercial and noncommercial transportation routes. Among notable trade routes was the Amber Road, which served as a dependable network for long-distance trade. Maritime trade along the Spice Route became prominent during the Middle Ages, when nations resorted to military means for control of this influential route. During the Middle Ages, organizations such as the Hanseatic League, aimed at protecting interests of the merchants and trade became increasingly prominent. In modern times, commercial activity shifted from the major trade routes of the Old World to newer routes between modern nation-states. This activity was sometimes carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jade
Jade is an umbrella term for two different types of decorative rocks used for jewelry or Ornament (art), ornaments. Jade is often referred to by either of two different silicate mineral names: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole group of minerals), or jadeite (a silicate of sodium and aluminum in the pyroxene group of minerals). Nephrite is typically green, although may be yellow, white or black. Jadeite varies from white or near-colorless, through various shades of green (including an emerald green, termed 'imperial'), to Lavender (color), lavender, yellow, orange, brown and black. Rarely it may be blue. Both of these names refer to their use as gemstones, and each has a mineralogically more specific name. Both the amphibole jade (nephrite) and pyroxene jade are mineral aggregates (rocks) rather than mineral species. Nephrite was deprecated by the International Mineralogical Association as a mineral species name in 1978 (replaced by tremolite). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingling-o
''Lingling-o'' or ''ling-ling-o'' are a type of penannular or double-headed pendant or amulet that have been associated with various Late Neolithic to late Iron Age Austronesian cultures. Most ''lingling-o'' were made in jade workshops in the Philippines, and to a lesser extent in the Sa Huỳnh culture of Vietnam, although the raw jade was mostly sourced from Taiwan. The earliest surviving examples of lingling-o, dating back to around 500 BC, were made out of nephrite jade, but many later examples were also made of shell, gold, copper, and wood; the different materials suggest differences in the wearer's social standing. The term lingling-o was first popularized by H. Otley Beyer, who adapted it from the Southern Ifugao name for such ornaments; it has since also come to be used as a blanket term for various metal age Austronesian ornaments found in the Philippines, Taiwan, and Vietnam. Although the earliest known lingling-o dates from 500 BC, the art of jade carving and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the History of agriculture, introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of sedentism, settlement. The term 'Neolithic' was coined by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury, Sir John Lubbock in 1865 as a refinement of the three-age system. The Neolithic began about 12,000 years ago, when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East and Mesopotamia, and later in other parts of the world. It lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BCE), marked by the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earings - Gem, Sa Huynh Culture
Earrings are jewelry that can be worn on one's ears. Earrings are commonly worn in a piercing in the earlobe or another external part of the ear, or by #Clip-on and other non-pierced earrings, some other means, such as stickers or clip-ons. Earrings have been worn across multiple civilizations and historic periods, often carrying a cultural significance. Locations for piercings other than the earlobe include the Rook (piercing), rook, Tragus piercing, tragus, and across the Helix (ear), helix (see image in the infobox). The simple term "ear piercing" usually refers to an earlobe piercing, whereas piercings in the upper part of the Pinna (anatomy), external ear are often referred to as "cartilage piercings". Cartilage piercings are more complex to perform than earlobe piercings and take longer to heal. Earring components may be made of any number of materials, including metal, plastic, glass, gemstone, precious stone, beads, wood, bone, and other materials. Designs range from sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-West Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth. In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the seas connecting the two. The term is especially useful in marine biology, ichthyology, and similar fields, since many marine habitats are continuously connected from Madagascar to Japan and Oceania, and a number of species occur over that range, but are not found in the Atlantic Ocean. As a distinct marine realm, the region has an exceptionally high species richness, with the world's highest species richness being found in at its heart in the Coral Triangle, and a remarkable gradient of decreasing species richness radiating outward in all directions. The region includes over 3,000 species of fish, compared with around 1,200 in the next richest marine region, the Western Atlantic, and around 500 species of reef building corals, compared w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
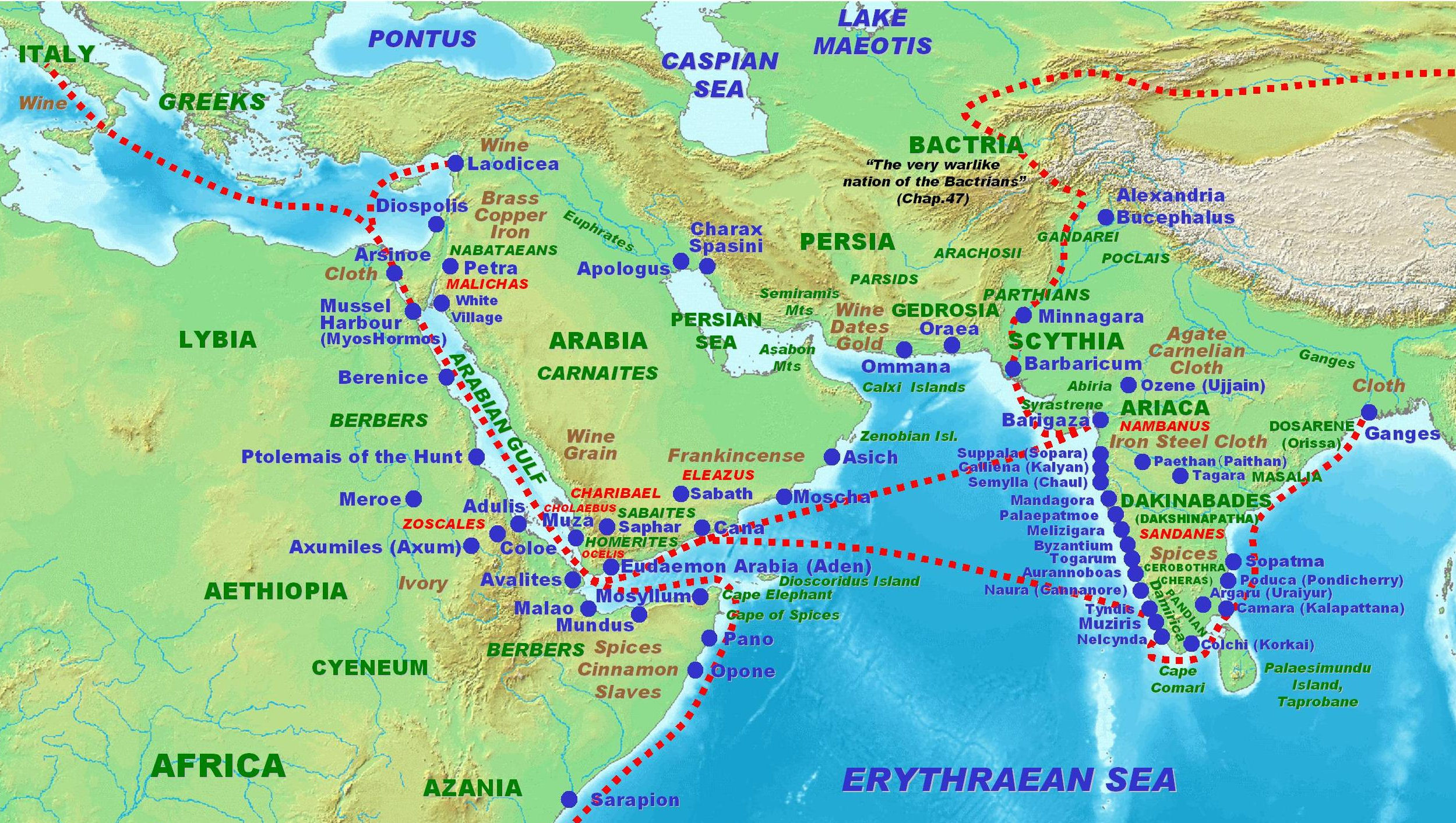
Indo-Roman Trade Relations
Indo-Roman trade relations (see also the spice trade and incense road) was trade between the Indian subcontinent and the Roman Empire in Europe and the Mediterranean Sea. Trade through the overland caravan routes via Asia Minor and the Middle East, though at a relative trickle compared to later times, preceded the southern trade route via the Red Sea, which started around the beginning of the Common Era (CE), following the reign of Augustus and his conquest of Egypt in 30 BCE. The southern route so helped enhance trade between the ancient Roman Empire and the Indian subcontinent, that Roman politicians and historians are on record decrying the loss of silver and gold to buy silk to pamper Roman wives, and the southern route grew to eclipse and then totally supplant the overland trade route. Roman and Greek traders frequented the ancient Tamil country, present day Southern India and Sri Lanka, securing trade with the seafaring Tamil states of the Pandyan, Chola and Chera d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spice Trade
The spice trade involved historical civilizations in Asia, Northeast Africa and Europe. Spices, such as cinnamon, cassia, cardamom, ginger, pepper, nutmeg, star anise, clove, and turmeric, were known and used in antiquity and traded in the Eastern World. These spices found their way into the Near East before the beginning of the Christian era, with fantastic tales hiding their true sources. The maritime aspect of the trade was dominated by the Austronesian peoples in Southeast Asia, namely the ancient Indonesian sailors who established routes from Southeast Asia to Sri Lanka and India (and later China) by 1500 BC. These goods were then transported by land toward the Mediterranean and the Greco-Roman world via the incense route and the Roman–India routes by Indian and Persian traders.Fage 1975: 164 The Austronesian maritime trade lanes later expanded into the Middle East and eastern Africa by the 1st millennium AD, resulting in the Austronesian colonization of Madagas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingling-o
''Lingling-o'' or ''ling-ling-o'' are a type of penannular or double-headed pendant or amulet that have been associated with various Late Neolithic to late Iron Age Austronesian cultures. Most ''lingling-o'' were made in jade workshops in the Philippines, and to a lesser extent in the Sa Huỳnh culture of Vietnam, although the raw jade was mostly sourced from Taiwan. The earliest surviving examples of lingling-o, dating back to around 500 BC, were made out of nephrite jade, but many later examples were also made of shell, gold, copper, and wood; the different materials suggest differences in the wearer's social standing. The term lingling-o was first popularized by H. Otley Beyer, who adapted it from the Southern Ifugao name for such ornaments; it has since also come to be used as a blanket term for various metal age Austronesian ornaments found in the Philippines, Taiwan, and Vietnam. Although the earliest known lingling-o dates from 500 BC, the art of jade carving and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |