|
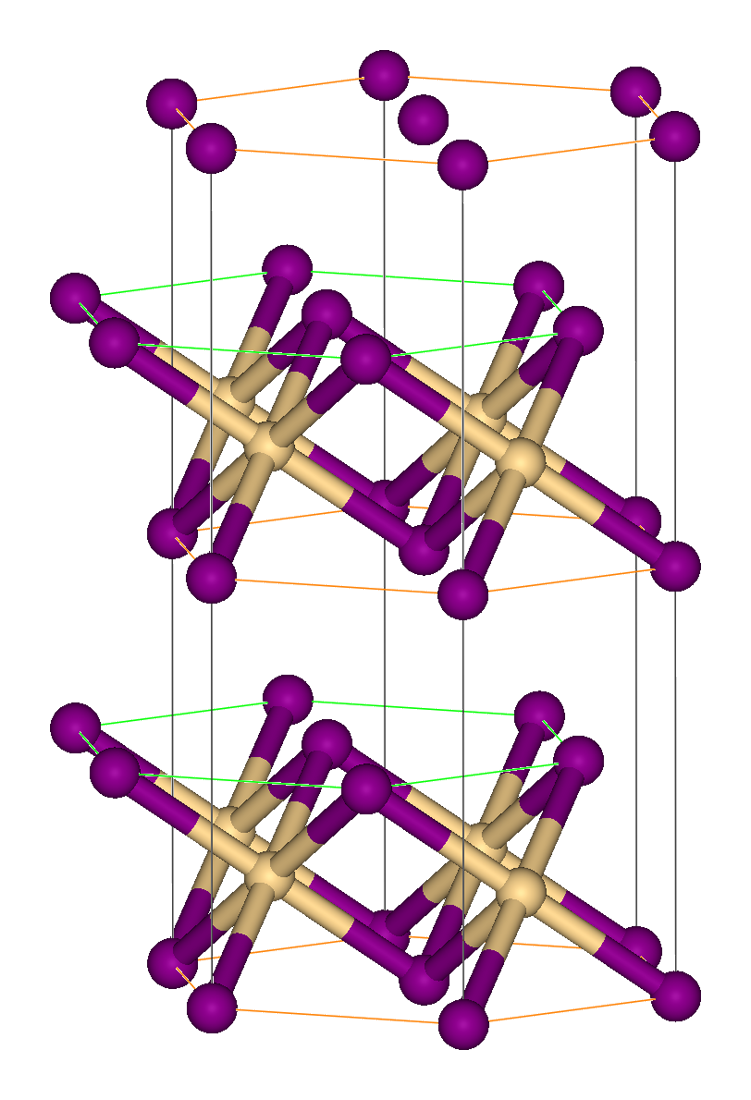
Manganese(II) Iodide
Manganese(II) iodide is the chemical compound composed of manganese and iodide with the formula MnI2. The anhydrous compound adopts the cadmium iodide Cadmium iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula CdI2. It is a white hygroscopic solid. It also can be obtained as a mono- and tetrahydrate. It has few applications. It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compound ... crystal structure. The pink tetrahydrate is known. Unlike MnX2(H2O)4, which are cis for X = Cl, Br, the iodides are trans in MnI2(H2O)4. It can be used as a pink pigment or as a source of the manganese ion or iodide ion. It is often used in the lighting industry. References Manganese(II) compounds Iodides Metal halides {{inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhombohedral
In geometry, a rhombohedron (also called a rhombic hexahedron or, inaccurately, a rhomboid) is a three-dimensional figure with six faces which are rhombi. It is a special case of a parallelepiped where all edges are the same length. It can be used to define the rhombohedral lattice system, a honeycomb with rhombohedral cells. A cube is a special case of a rhombohedron with all sides square. In general a ''rhombohedron'' can have up to three types of rhombic faces in congruent opposite pairs, ''C''''i'' symmetry, order 2. Four points forming non-adjacent vertices of a rhombohedron necessarily form the four vertices of an orthocentric tetrahedron, and all orthocentric tetrahedra can be formed in this way. Rhombohedral lattice system The rhombohedral lattice system has rhombohedral cells, with 6 congruent rhombic faces forming a trigonal trapezohedron: : Special cases by symmetry * Cube: with Oh symmetry, order 48. All faces are squares. * Trigonal trapezohedron (also cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearson Symbol
The Pearson symbol, or Pearson notation, is used in crystallography as a means of describing a crystal structure, and was originated by W. B. Pearson. The symbol is made up of two letters followed by a number. For example: * Diamond structure, ''cF''8 * Rutile structure, ''tP''6 The two (italicised) letters specify the Bravais lattice. The lower-case letter specifies the crystal family, and the upper-case letter the centering type. The number at the end of the Pearson symbol gives the number of the atoms in the conventional unit cell.Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry IUPAC Recommendations 2005 IR-3.4.4, pp. 49–51; IR-11.5, pp. 241–242. |
Manganese(II) Fluoride
Manganese(II) fluoride is the chemical compound composed of manganese and fluoride with the formula MnF2. It is a light pink solid, the light pink color being characteristic for manganese(II) compounds. It is made by treating manganese and diverse compounds of manganese(II) in hydrofluoric acid. Like some other metal difluorides, MnF2 crystallizes in the rutile structure, which features octahedral Mn centers. Uses MnF2 is used in the manufacture of special kinds of glass and laser A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The firs ...s. It is a canonical example of uniaxial antiferromagnet (with Neel temperature of 68 K) which has been experimentally studied since early on. References Manganese(II) compounds Fluorides Metal halides {{inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese(II) Chloride
Manganese(II) chloride is the dichloride salt of manganese, MnCl2. This inorganic chemical exists in the anhydrous form, as well as the di hydrate (MnCl2·2H2O) and tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O), with the tetrahydrate being the most common form. Like many Mn(II) species, these salts are pink, with the paleness of the color being characteristic of transition metal complexes with high spin d5 configurations. Preparation Manganese chloride is produced by treating manganese(IV) oxide with concentrated hydrochloric acid. :MnO2 + 4 HCl → MnCl2 + 2 H2O + Cl2 This reaction was once used for the manufacture of chlorine. By carefully neutralizing the resulting solution with MnCO3, one can selectively precipitate iron salts, which are common impurities in manganese dioxide.. In the laboratory, manganese chloride can be prepared by treating manganese metal or manganese(II) carbonate with hydrochloric acid: :Mn + 2 HCl + 4 H2O → MnCl2(H2O)4 + H2 :MnCO3 + 2 HCl + 3 H2O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese(II) Bromide
Manganese(II) bromide is the chemical compound composed of manganese and bromine with the formula MnBr2. It can be used in place of palladium in the Stille reaction, which couples two carbon atoms using an organotin compound Organotin compounds or stannanes are chemical compounds based on tin with hydrocarbon substituents. Organotin chemistry is part of the wider field of organometallic chemistry. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide (), discovered by .... References Manganese(II) compounds Bromides Metal halides {{inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron(II) Iodide
Iron(II) iodide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula FeI2. It is used as a catalyst in organic reactions. Preparation Iron(II) iodide can be synthesised from the elements, i.e. by the reaction of with . :Fe + I2 → FeI2 This is in contrast to the other iron(II) halides, which are best prepared by reaction of heated iron with the appropriate |
Cobalt(II) Iodide
Cobalt(II) iodide or cobaltous iodide are the inorganic compounds with the formula Co I2 and the hexahydrate CoI2(H2O)6. These salts are the principal iodides of cobalt. Synthesis Cobalt(II) iodide is prepared by treating cobalt powder with gaseous hydrogen iodide. The hydrated form CoI2.6H2O can be prepared by the reaction of cobalt(II) oxide (or related cobalt compounds) with hydroiodic acid. Cobalt(II) iodide crystallizes in two polymorphs, the α- and β-forms. The α-polymorph consists of black hexagonal crystals, which turn dark green when exposed to air. Under a vacuum at 500 °C, samples of α-CoI2 sublime, yielding the β-polymorph as a yellow crystals. β-CoI2 also readily absorbs moisture from the air, converting into green hydrate. At 400 °C, β-CoI2 reverts to the α-form.O. Glemser "Cobalt, Nickel" in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, NY. Vol. 1. p. 1518. Structures The anhydrous salts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, usi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent; as a rubber additive; and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide. Manganese is also an essential human dietary element, important in macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, and free radical defense systems. It is a critical component in dozens of proteins and enzymes. It is found mostly in the bones, but also the liver, kidneys, and brain. In the human brain, the manganese is bound to manganese metalloproteins, most notably glutamine synthetase in astrocytes. Manganese was first isolated in 1774. It is familiar in the laboratory in the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodide
An iodide ion is the ion I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt, which many governments mandate. Worldwide, iodine deficiency affects two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disability. Structure and characteristics of inorganic iodides Iodide is one of the largest monatomic anions. It is assigned a radius of around 206 picometers. For comparison, the lighter halides are considerably smaller: bromide (196 pm), chloride (181 pm), and fluoride (133 pm). In part because of its size, iodide forms relatively weak bonds with most elements. Most iodide salts are soluble in water, but often less so than the related chlorides and bromides. Iodide, being large, is less hydrophilic compared to the smaller anions. One consequence of this is that sodium iodide is highly soluble in acetone, whereas sodium chloride is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called '' empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of ato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Iodide
Cadmium iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula CdI2. It is a white hygroscopic solid. It also can be obtained as a mono- and tetrahydrate. It has few applications. It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compounds of the form MX2 with strong polarization effects. Preparation Cadmium iodide is prepared by the addition of cadmium metal, or its oxide, hydroxide or carbonate to hydroiodic acid. Also, the compound can be made by heating cadmium with iodine. Crystal structure In cadmium iodide the iodide anions form a hexagonal close packed arrangement while the cadmium cations fill all of the octahedral sites in alternate layers. The resultant structure consists of a layered lattice. This same basic structure is found in many other salts and minerals. Cadmium iodide is mostly ionically bonded but with partial covalent character. Cadmium iodide's crystal structure is the prototype on which the crystal structures many other compounds can be conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |