|
Kōtukutuku
''Fuchsia excorticata'', commonly known as tree fuchsia, New Zealand fuchsia and by its Māori name , is a New Zealand native tree belonging to the family Onagraceae. It is commonly found throughout New Zealand and as far south as the Auckland Islands. It grows from sea level up to about , particularly alongside creeks and rivers. It is easily recognised in its native environment by the characteristic appearance of its bark, which peels spontaneously, hanging in red papery strips to show a pale bark underneath. Its scientific name, ''excorticata'', reflects this distinctive property. ''Fuchsia excorticata'' is the largest member of the genus ''Fuchsia'', growing to a height of . It is unusual among New Zealand trees in being deciduous in the southern parts of its range. The introduction of the common brushtail possum to New Zealand precipitated a serious decline in this species, particularly where large concentrations of the possum are present. ''F. excorticata'' appears to be o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuchsia
''Fuchsia'' ( ) is a genus of flowering plants that consists mostly of shrubs or small trees. Almost 110 species of ''Fuchsia'' are recognized; the vast majority are native to South America, but a few occur north through Central America to Mexico, and also several from New Zealand to Tahiti. One species, ''Fuchsia magellanica, F. magellanica'', extends as far as the southern tip of South America, occurring on Tierra del Fuego in the cool temperateness, temperate zone, but the majority are tropical or subtropical. Taxonomy The first to be Species description, scientifically described, ''Fuchsia triphylla'', was discovered on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola (Haiti and the Dominican Republic) about 1696–1697 by the French Minim (religious order), Minim friar and botanist, Charles Plumier, during his third expedition to the Greater Antilles. He named the new genus after German botanist Leonhart Fuchs (1501–1566, ). The fuchsias are most closely related to the northern hem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Reinhold Forster
Johann Reinhold Forster (; 22 October 1729 – 9 December 1798) was a German Reformed pastor and naturalist. Born in Tczew, Dirschau, Pomeranian Voivodeship (1466–1772), Pomeranian Voivodeship, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (now Tczew, Poland), he attended school in Dirschau and Marienwerder before being admitted at the Joachimsthalsches Gymnasium in Berlin in 1745. Skilled in classical and biblical languages, he studied theology at the University of Halle. In 1753, he became a parson at a parish just south of Danzig. He married his cousin Justina Elisabeth Nicolai in 1754, and they had seven children; the oldest child was Georg Forster, George Forster, also known as Georg. In 1765, Forster was commissioned by the Russian government to inspect the new colonies on the Volga. Accompanied by George on the journey, he observed the conditions of the colonists and made scientific observations that were later read at the Russian Academy of Sciences. After making a report that wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynodioecious
Gynodioecy is a rare breeding system that is found in certain flowering plant species in which female and hermaphroditic plants coexist within a population. Gynodioecy is the evolutionary intermediate between hermaphroditism (exhibiting both female and male parts) and dioecy (having two distinct morphs: male and female). Gynodioecy is sometimes considered a mixed mating system comparable with trioecy and androdioecy. It is also considered a dimorphic sexual system alongside dioecy and androdioecy. Gynodioecy occurs as a result of transmission of nuclear (nuclear male sterility) or, more commonly, extra-nuclear (e.g. cytoplasmic male sterility) mutated alleles, which prevents pollen production, while keeping the female reproductive parts intact; other members of the species population don't inherit the mutated alleles, thus remaining hermaphrodites. In some cases, a combination of both nuclear and extra-nuclear mechanisms is observed in determining the sterile phenotype. Gynod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leather Tanning
Tanning may refer to: *Tanning (leather), treating animal skins to produce leather *Sun tanning, using the sun to darken pale skin **Indoor tanning, the use of artificial light in place of the sun **Sunless tanning, application of a stain or dye to the skin (active ingredient in tanning lotion products is dihydroxyacetone (DHA)). *Physical punishment, metaphorically, such as a severe spanking which leaves clear marks See also *Skin whitening *Tan (color) *Tan (other) *Tannery (other) A tannery is a facility where the tanning process is applied to hide to produce leather. Tannery may also refer to: Places * Tannery Road, a road in the Bangalore Cantonment, India * The Tannery, Ontario, a community in the town of Mississipp ... * Tannin (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddleia
''Buddleja'' (; ''Buddleia''; also historically given as ''Buddlea'') is a genus comprising over 140 species of flowering plants endemicity, endemic to Asia, Africa, and the Americas. The generic name bestowed by Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus posthumously honoured the Reverend Adam Buddle (1662–1715), an English botanist and Rector (ecclesiastical), rector, at the suggestion of William Houstoun (botanist), William Houstoun. Houstoun sent the first plants to become known to science as buddleja (Buddleja americana, ''B. americana'') to England from the Caribbean about 15 years after Buddle's death. ''Buddleja'' species, especially ''Buddleja davidii'' and interspecific hybrids, are commonly known as butterfly bushes and are frequently cultivated as garden shrubs. ''Buddleja davidii'' has become an invasive species in both Europe and North America. Nomenclature The botanic name has been the source of some confusion. By modern practice of botanical Latin, the spelling of a generic nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banana Passionfruit
Banana passionfruit (''Passiflora'' supersect. ''Tacsonia''), also known as taxo and curuba, is a group of around 64 ''Passiflora'' species found in South America. Most species in this section are found in high-elevation cloud forest habitats. Flowers have a cylindrical hypanthium. Species Invasive species ''P. tarminiana'' and ''P. tripartita'' thrive in the climate of New Zealand. They are invasive species since they can smother forest margins and forest regrowth. It is illegal to sell, cultivate, or distribute the plants. Banana passionfruit vines are now smothering more than of native forest on the islands of Hawaii and Kauai. Seeds are spread by feral pigs, birds and humans. The vine can also be found all across the highlands of New Guinea and in Tasmania Tasmania (; palawa kani: ''Lutruwita'') is an island States and territories of Australia, state of Australia. It is located to the south of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland, and is separated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silvereye
The silvereye or wax-eye (''Zosterops lateralis''), also known by its Māori name tauhou, is a very small omnivorous passerine bird of the south-west Pacific. In Australia and New Zealand its common name is sometimes white-eye, but this name is more commonly used to refer to all members of the genus ''Zosterops'', or the entire family Zosteropidae. In New Zealand, the silvereye was first recorded in 1832. It arrived in greater numbers in 1856, and it is assumed that a migrating flock was swept eastwards by a storm. As an apparently self-introduced bird it is protected as a native New Zealand species. Its Māori name, , means "stranger" or more literally, "new arrival". Taxonomy The silvereye was first described by the English ornithologist John Latham in 1801 under the binomial name ''Sylvia lateralis''. There are 17 subspecies: * ''Z. l. chlorocephalus'' A. J. Campbell & S. A. White, 1910 ( Capricorn silvereye)– Capricorn and Bunker Group, central Queensland, Australia * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kererū
The kererū (''Hemiphaga novaeseelandiae''), also known as kūkupa (Māori language#Northern dialects, northern Māori dialects), New Zealand pigeon or wood pigeon, is a species of pigeon native to New Zealand. Johann Friedrich Gmelin described the bird in 1789 as a large, conspicuous pigeon up to in length and in weight, with a white breast and iridescent green–blue plumage. Two subspecies have been recognised; the second—the Norfolk pigeon of Norfolk Island—became extinct in the early 20th century. Kererū pairs are Monogamy in animals, monogamous, breeding over successive seasons and remaining together when not breeding. They construct nests with twigs in trees, with a single egg clutch. Found in a variety of habitats across the country, the kererū feeds mainly on fruits, as well as leaves, buds and flowers. Although widespread in both forest and urban habitats, its numbers have declined significantly since European colonisation and the arrival of invasive mammals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Bellbird
The New Zealand bellbird (''Anthornis melanura''), also known by its Māori language names korimako, makomako and kōmako, is a medium-sized species of honeyeater Endemism in birds, endemic to New Zealand. It has been the only living member of the genus ''Anthornis'' since the Chatham bellbird went extinct in the early 20th century. The bellbird's closest living relative is the only other New Zealand honeyeater, the tūī (''Prosthemadera novaeseelandiae''). The bellbird forms a significant component of the famed New Zealand Dawn chorus (birds)#New Zealand, dawn chorus of bird vocalization, birdsong, which was much noted by early European settlers. Exceptional singing abilities were already observed by Captain James Cook, who described its song as "like small bells most exquisitely tuned". Bellbirds measure about in length, with females weighing approximately and males . Males are mostly olive-green with paler underparts, and bluish-black wings and tail. Females are paler and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tūī
The tūī (''Prosthemadera novaeseelandiae'') is a medium-sized bird native to New Zealand. It is blue, green, and bronze coloured with a distinctive white throat tuft (poi). It is an endemism, endemic passerine bird of New Zealand, and the only species in the genus ''Prosthemadera''. It is one of the largest species in the diverse Australasian honeyeater family Meliphagidae, and one of two living species of that family found in New Zealand, the other being the New Zealand bellbird (''Anthornis melanura''). The tūī has a wide distribution in the archipelago, ranging from the subtropical Kermadec Islands to the sub-Antarctic Auckland Islands, as well as the main islands. Taxonomy Europeans first encountered the tūī in 1770 at Queen Charlotte Sound / Tōtaranui, Queen Charlotte Sound on the north coast of New Zealand's South Island during James Cook, Captain James Cook's First voyage of James Cook, first voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Specimens were brought back to England an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
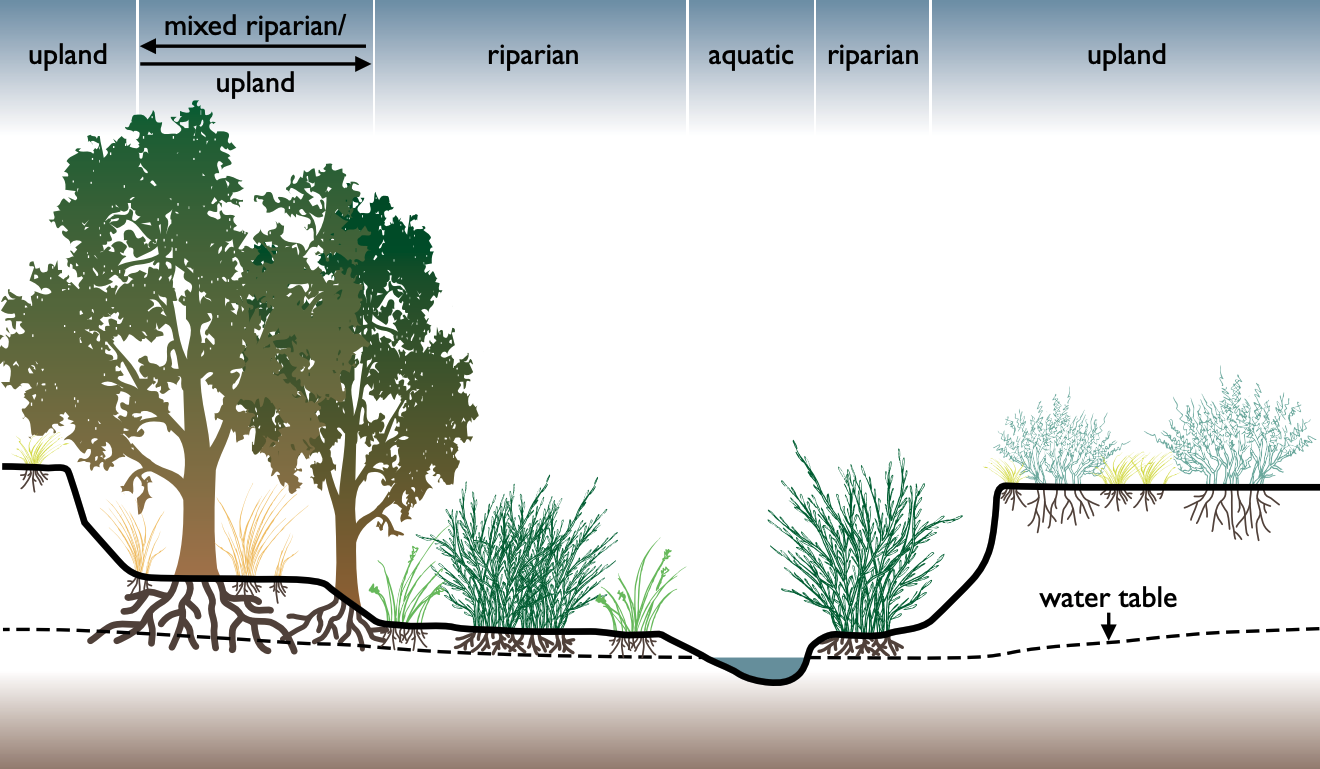
Riparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin '' ripa'', meaning " river bank". Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on terrestrial and semiaquatic fauna as well as aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, and even non-vegetative areas. Riparian zones may be natural or engineered for soil stabilization or restoration. These zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Island
The South Island ( , 'the waters of Pounamu, Greenstone') is the largest of the three major islands of New Zealand by surface area, the others being the smaller but more populous North Island and Stewart Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, to the south by the Foveaux Strait and Southern Ocean, and to the east by the Pacific Ocean. The South Island covers , making it the List of islands by area, world's 12th-largest island, constituting 56% of New Zealand's land area. At low altitudes, it has an oceanic climate. The most populous cities are Christchurch, Dunedin, Nelson, New Zealand, Nelson and Invercargill. Prior to European settlement, Te Waipounamu was sparsely populated by three major iwi – Kāi Tahu, Kāti Māmoe, and the historical Waitaha (South Island iwi), Waitaha – with major settlements including in Kaiapoi Pā near modern-day Christchurch. During the Musket Wars expanding iwi colonised Te Tau Ihu Māori, Te Tau Ihu, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |