|
Keloid Scar
Keloid, also known as keloid disorder and keloidal scar, is the formation of a type of scar which, depending on its maturity, is composed mainly of either type III (early) or type I (late) collagen. It is a result of an overgrowth of granulation tissue (collagen type III) at the site of a healed skin injury, which is then slowly replaced by collagen type I. Keloids are firm, rubbery lesions or shiny, fibrous nodules, and can vary from pink to the color of the person's skin or red to dark brown. A keloid scar is benign and not contagious, but sometimes accompanied by severe itchiness, pain, and changes in texture. In severe cases, it can affect the movement of the skin. In the United States, keloid scars are seen 15 times more frequently in people of sub-Saharan African descent than in people of European descent. There is a higher tendency to develop a keloid among those with a family history of keloids and people between the ages of 10 and 30 years. Keloids should not be confused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatology
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the Human skin, skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A List of dermatologists, dermatologist is a specialist medical doctor who manages diseases related to skin. Etymology Attested in English in 1819, the word "dermatology" derives from the Ancient Greek, Greek δέρματος (''dermatos''), genitive of δέρμα (''derma''), "skin" (itself from δέρω ''dero'', "to flay") and -λογία ''wikt:-logia, -logia''. Neo-Latin ''dermatologia'' was coined in 1630, an anatomical term with various French and German uses attested from the 1730s. History In 1708, the first great school of dermatology became a reality at the famous Hôpital Saint-Louis in Paris, and the first textbooks (Willan's, 1798–1808) and atlases (Jean-Louis-Marc Alibert, Alibert's, 1806–1816) appeared in print around the same time.Freedber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Surgical History Of The Naval War Between Japan And China - During 1894-95; Translated From The Original Japanese Report (1900) (14595050100)
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earlobe Piercing
Earrings are jewelry that can be worn on one's ears. Earrings are commonly worn in a piercing in the earlobe or another external part of the ear, or by some other means, such as stickers or clip-ons. Earrings have been worn across multiple civilizations and historic periods, often carrying a cultural significance. Locations for piercings other than the earlobe include the rook, tragus, and across the helix (see image in the infobox). The simple term "ear piercing" usually refers to an earlobe piercing, whereas piercings in the upper part of the external ear are often referred to as "cartilage piercings". Cartilage piercings are more complex to perform than earlobe piercings and take longer to heal. Earring components may be made of any number of materials, including metal, plastic, glass, precious stone, beads, wood, bone, and other materials. Designs range from small hoops and studs to large plates and dangling items. The size is ultimately limited by the physical capacity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pruritus
An itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes a strong desire or reflex to scratch. Itches have resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itches have many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant sensory experiences, their behavioral response patterns are different. Pain creates a withdrawal reflex, whereas itches leads to a scratch reflex. Unmyelinated nerve fibers for itches and pain both originate in the skin. Information for them is conveyed centrally in two distinct systems that both use the same nerve bundle and spinothalamic tract. Classification Most commonly, an itch is felt in one place. If it is felt all over the body, then it is called ''generalized itch'' or ''generalized pruritus''. Generalized itch is infrequently a symptom of a serious underlying condition, such as cholestatic liver disease. If the sensation of itching persists for six weeks or longer, then it is called ''chronic itch'' or ''ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage." Pain motivates organisms to withdraw from damaging situations, to protect a damaged body part while it heals, and to avoid similar experiences in the future. Congenital insensitivity to pain may result in reduced life expectancy. Most pain resolves once the noxious stimulus is removed and the body has healed, but it may persist despite removal of the stimulus and apparent healing of the body. Sometimes pain arises in the absence of any detectable stimulus, damage or disease. Pain is the most common reason for physician consultation in most developed countries. It is a major symptom in many medical conditions, and can interfere with a person's quality of life and general fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteoglycan
Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a "core protein" with one or more covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a serine (Ser) residue to which the glycosaminoglycan is joined through a tetrasaccharide bridge (e.g. chondroitin sulfate- GlcA- Gal-Gal- Xyl-PROTEIN). The Ser residue is generally in the sequence -Ser- Gly-X-Gly- (where X can be any amino acid residue but proline), although not every protein with this sequence has an attached glycosaminoglycan. The chains are long, linear carbohydrate polymers that are negatively charged under physiological conditions due to the occurrence of sulfate and uronic acid groups. Proteoglycans occur in connective tissue. Types Proteoglycans are categorized by their relative size (large and small) and the nature of their glycosaminoglycan chains. Types include: Certain members are considered members of the "small leucine-rich pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastin
Elastin is a protein encoded by the ''ELN'' gene in humans and several other animals. Elastin is a key component in the extracellular matrix of gnathostomes (jawed vertebrates). It is highly Elasticity (physics), elastic and present in connective tissue of the body to resume its shape after stretching or contracting. Elastin helps skin return to its original position whence poked or pinched. Elastin is also in important load-bearing tissue of vertebrates and used in places where storage of mechanical energy is required. Function The ''ELN'' gene encodes a protein that is one of the two components of elastic fibers. The encoded protein is rich in hydrophobic amino acids such as glycine and proline, which form mobile hydrophobic regions bounded by crosslinks between lysine residues. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Elastin's soluble precursor is tropoelastin. Mechanism of elastic recoil The characterization of disorder is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
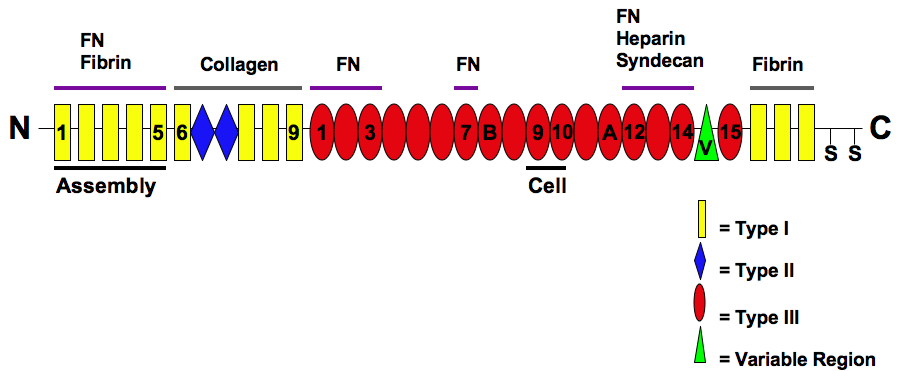
Fibronectin
Fibronectin is a high- molecular weight (~500-~600 kDa) glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that binds to membrane-spanning receptor proteins called integrins. Fibronectin also binds to other extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen, fibrin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (e.g. syndecans). Fibronectin exists as a protein dimer, consisting of two nearly identical monomers linked by a pair of disulfide bonds. The fibronectin protein is produced from a single gene, but alternative splicing of its pre-mRNA leads to the creation of several isoforms. Two types of fibronectin are present in vertebrates: * soluble plasma fibronectin (formerly called "cold-insoluble globulin", or CIg) is a major protein component of blood plasma (300 μg/ml) and is produced in the liver by hepatocytes. * insoluble cellular fibronectin is a major component of the extracellular matrix. It is secreted by various cells, primarily fibroblasts, as a soluble protein dimer and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix (ICM), is a network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest. Each type of connective tissue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell typically with a spindle shape that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of connective tissue in animals. Structure Fibroblasts have a branched cytoplasm surrounding an elliptical, speckled cell nucleus, nucleus having two or more nucleoli. Active fibroblasts can be recognized by their abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). Inactive fibroblasts, called 'fibrocytes', are smaller, spindle-shaped, and have less RER. Although disjointed and scattered when covering large spaces, fibroblasts often locally align in parallel clusters when crowded together. Unlike the epithelial cells lining the body structures, fibroblasts do not form flat monolayers and are not restricted by a polarizing attachment to a basal lamina on one side, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histologically
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissue (biology), tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cell (biology), cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keloid -1
Keloid, also known as keloid disorder and keloidal scar, is the formation of a type of scar which, depending on its maturity, is composed mainly of either type III (early) or type I (late) collagen. It is a result of an overgrowth of granulation tissue (collagen type III) at the site of a healed skin injury, which is then slowly replaced by collagen type I. Keloids are firm, rubbery lesions or shiny, fibrous nodules, and can vary from pink to the color of the person's skin or red to dark brown. A keloid scar is benign and not contagious, but sometimes accompanied by severe itchiness, pain, and changes in texture. In severe cases, it can affect the movement of the skin. In the United States, keloid scars are seen 15 times more frequently in people of sub-Saharan African descent than in people of European descent. There is a higher tendency to develop a keloid among those with a family history of keloids and people between the ages of 10 and 30 years. Keloids should not be confused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |