|
Junkun
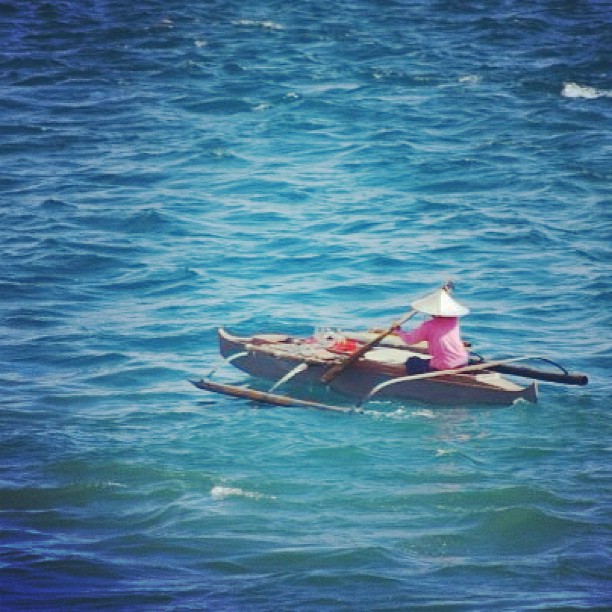
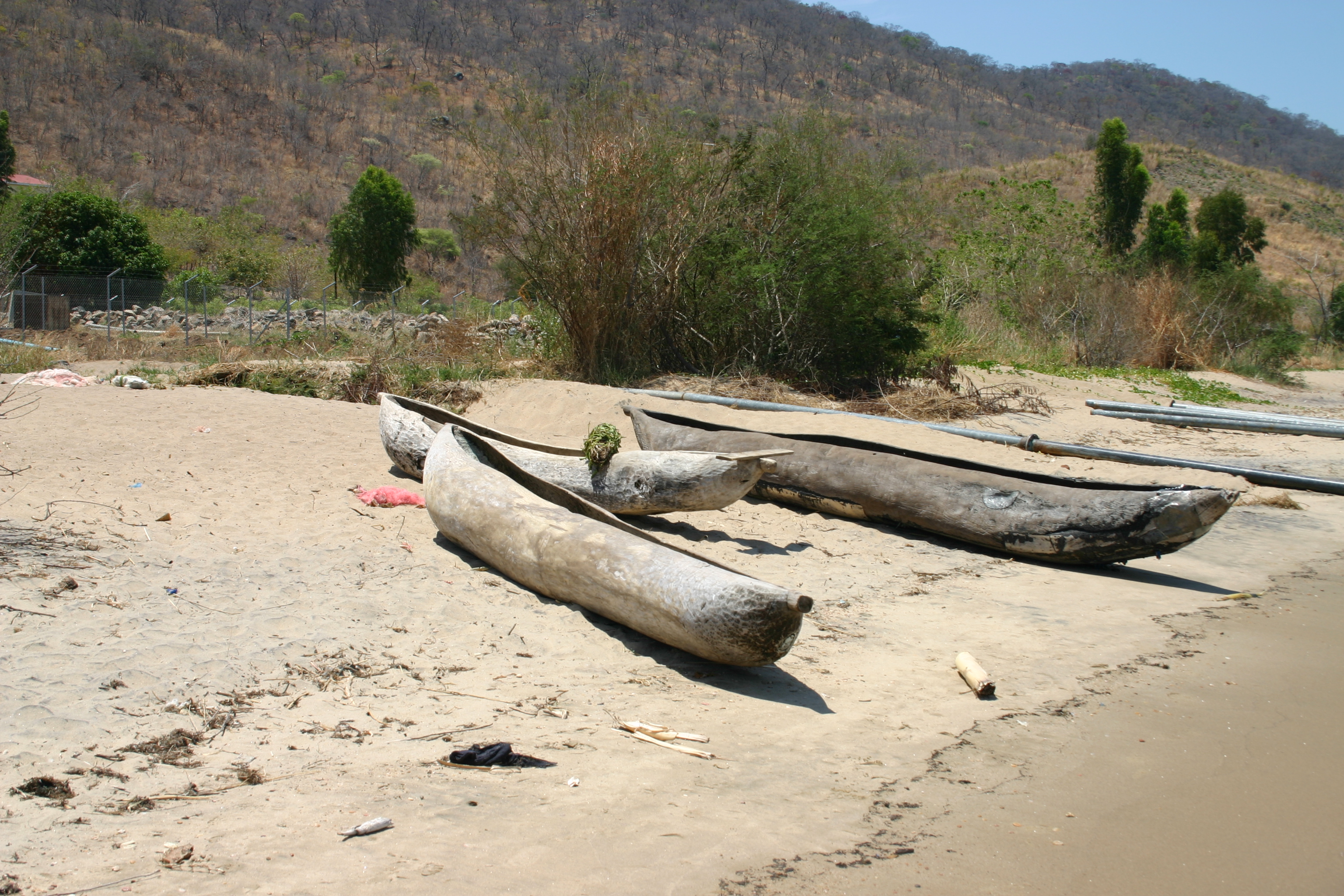
Junkun, is a type of small dugout canoe of the Sama-Bajau people of the Philippines. They are usually made from a single log, though a single plank can be added to the sides, and longer boats can include ribs that support a deck made of planks. They are around long. They have knob-like protrusions on the tip of the prow and the stern, which also sweep upwards from the waterline. They are sometimes equipped with double outriggers. They are used for fishing and short-distance travel. See also * Buggoh * Birau (boat) * Owong * Tiririt * Vinta * Djenging * Garay (ship) * Balangay A Balangay, or barangay is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines and were used largely as trading ships up until the colonial era. The ... References {{Fishing vessel topics Indigenous ships of the Philippines Canoes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buggoh
Buggoh is a type of small dugout canoe of the Sama-Bajau people of the Philippines. They are made from a single log hollowed into a canoe with a rounded bottom. It is equal-ended, with the prow and the stern dropping straight down or sloping outward. They are sometimes equipped with two outrigger floats. They are usually around long. It is also known by various other names, including boggo', buggoh jungalan, buggoh-buggoh, or beggong. Buggoh are commonly towed by larger houseboats like the lepa. They are used to ferry people and goods from the mothership to the coast or to other ships. They are also used to assist in fishing. Buggoh is very similar to the birau, but differs in the shape of the prow and the stern. See also * Junkun * Vinta * Owong * Awang (boat) * Djenging * Garay (ship) * Balangay A Balangay, or barangay is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birau (boat)
Birau, is a type of small dugout canoe of the Sama-Bajau people of the Philippines. They are made from a single log hollowed into a canoe with a rounded bottom. The prow and stern of the vessel usually has knob-like protrusions. A smaller wider variant without these knobs is known as bitok. Birau are usually around long. They are sometimes equipped with two outrigger floats. They are very similar to the buggoh, differing only in that the prow and the stern of the birau slope inward. See also * Junkun * Owong * Vinta * Djenging * Garay (ship) * Balangay A Balangay, or barangay is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines and were used largely as trading ships up until the colonial era. The ... References {{Austronesian ships Indigenous ships of the Philippines Canoes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
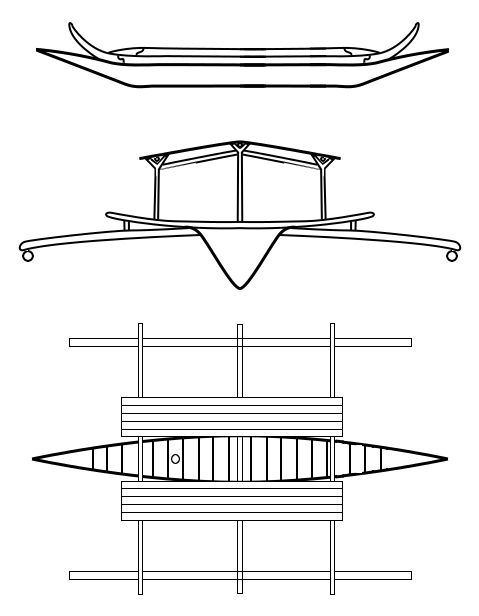
Owong
''Owong'', also spelled ''owung'', are traditional small dugout canoes of the T'boli people in the Philippines. It is traditionally made from the hollowed out trunks of ''lawaan'' (''Shorea'' spp.). It is propelled by paddling and can carry around three people. It is used by the T'boli people for fishing and transport in Lake Sebu, Lake Lahit, and Lake S'loton in their ancestral territory in southwestern Mindanao. See also * Awang (boat) * Buggoh * Birau (boat) * Junkun * Balangay A Balangay, or barangay is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines and were used largely as trading ships up until the colonial era. The ... References {{Fishing vessel topics Indigenous ships of the Philippines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiririt
Tiririt, also known as taririt or papet, is a type of small dinghy of the Sama-Bajau and Tausug people of the Philippines. It is commonly motorized. It is usually carried aboard larger motherships and assists in transporting passenger and cargo to the shore, as well as in towing the boat to port. However, it can also be used as a small inter-island transport. It is roughly leaf-shaped in outline with a distinctive hump-backed side-profile. The prow and stern can sometimes rise up into arcs. It normally has no outriggers. Larger independent versions of the tiririt reaching up to around long, are known as buti or buti-buti. They have upturned prows and sterns and can carry around a dozen people. Buti-buti are the subject of a Sama-Bajau folk dance also known as "buti-buti", which depicts everyday activities of fishing villages accompanied by a song (''leleng''). See also * Buggoh * Birau (boat) * Owong * Junkun * Vinta * Djenging * Garay (ship) * Balangay A Balangay, or baran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dugout Canoe
A dugout canoe or simply dugout is a boat made from a hollowed tree. Other names for this type of boat are logboat and monoxylon. ''Monoxylon'' (''μονόξυλον'') (pl: ''monoxyla'') is Greek – ''mono-'' (single) + '' ξύλον xylon'' (tree) – and is mostly used in classic Greek texts. In German, they are called Einbaum ("one tree" in English). Some, but not all, pirogues are also constructed in this manner. Dugouts are the oldest boat type archaeologists have found, dating back about 8,000 years to the Neolithic Stone Age. This is probably because they are made of massive pieces of wood, which tend to preserve better than others, such as bark canoes. Along with bark canoes and hide kayaks, dugouts were also used by Indigenous peoples of the Americas. Construction Construction of a dugout begins with the selection of a log of suitable dimensions. Sufficient wood must be removed to make the vessel relatively light in weight and buoyant, yet still strong enough ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sama-Bajau
The Sama-Bajau include several Austronesian ethnic groups of Maritime Southeast Asia. The name collectively refers to related people who usually call themselves the Sama or Samah (formally A'a Sama, "Sama people"); or are known by the exonym Bajau (, also spelled Badjao, Bajaw, Badjau, Badjaw, Bajo or Bayao). They usually live a seaborne lifestyle and use small wooden sailing vessels such as the ''perahu'' (''layag'' in Meranau), ''djenging'' (''balutu''), '' lepa'', and ''vinta'' (''pilang''). Some Sama-Bajau groups native to Sabah are also known for their traditional horse culture. The Sama-Bajau are the dominant ethnic group of the islands of Tawi-Tawi in the Philippines. They are also found in other islands of the Sulu Archipelago, coastal areas of Mindanao, northern and eastern Borneo, Sulawesi, and throughout the eastern Indonesian islands. In the Philippines, they are grouped with the religiously similar Moro people. Within the last fifty years, many of the Filipino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no), * bik, Republika kan Filipinas * ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas * cbk, República de Filipinas * hil, Republika sang Filipinas * ibg, Republika nat Filipinas * ilo, Republika ti Filipinas * ivv, Republika nu Filipinas * pam, Republika ning Filipinas * krj, Republika kang Pilipinas * mdh, Republika nu Pilipinas * mrw, Republika a Pilipinas * pag, Republika na Filipinas * xsb, Republika nin Pilipinas * sgd, Republika nan Pilipinas * tgl, Republika ng Pilipinas * tsg, Republika sin Pilipinas * war, Republika han Pilipinas * yka, Republika si Pilipinas In the recognized optional languages of the Philippines: * es, República de las Filipinas * ar, جمهورية الفلبين, Jumhūriyyat al-Filibbīn is an archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It is situated in the western Pacific Ocean and consists of aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Outrigger
A trimaran (or double-outrigger) is a multihull boat that comprises a main hull and two smaller outrigger hulls (or "floats") which are attached to the main hull with lateral beams. Most modern trimarans are sailing yachts designed for recreation or racing; others are ferries or warships. They originated from the traditional double-outrigger hulls of the Austronesian cultures of Maritime Southeast Asia; particularly in the Philippines and Eastern Indonesia, where it remains the dominant hull design of traditional fishing boats. Double-outriggers are derived from the older catamaran and single-outrigger boat designs. Terminology The word "trimaran" is a portmanteau of "tri" and "(cata)maran", a term that is thought to have been coined by Victor Tchetchet, a pioneering, Ukrainian-born modern multihull designer. Trimarans consist of a main hull connected to outrigger floats on either side by a crossbeam, wing, or other form of superstructure—the traditional Polynesian terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinta
The vinta is a traditional outrigger boat from the Philippine island of Mindanao. The boats are made by Sama-Bajau, Tausug and Yakan peoples living in the Sulu Archipelago, Zamboanga peninsula, and southern Mindanao. Vinta are characterized by their colorful rectangular lug sails (''bukay'') and bifurcated prows and sterns, which resemble the gaping mouth of a crocodile. Vinta are used as fishing vessels, cargo ships, and houseboats. Smaller undecorated versions of the vinta used for fishing are known as tondaan. The name "vinta" is predominantly used in Zamboanga, Basilan, and other parts of mainland Mindanao. It is also known as pilang or pelang among the Sama-Bajau of the Tawi-Tawi islands; dapang or depang among the Tausug in Sulu; and balanda or binta in Yakan in Basilan. It can also be generically referred to as '' lepa-lepa'', ''sakayan'', or '' bangka'', which are native names for small outrigger vessels. Description The vinta has a deep and narrow hull formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djenging
Djenging is a type of large double-outrigger plank boat built by the Sama-Bajau people of the Philippines. It is typically used as a houseboat, though it can be converted to a sailing ship. It was the original type of houseboat used by the Sama-Bajau before it was largely replaced by the lepa after World War II. Larger versions of djenging were also known as balutu or kubu, often elaborately carved with bifurcated extensions on the prow and stern. Description The djenging is made from a dugout keel (''baran balutu'') built up at the sides with two planks (''tapid'' and ''lingkam'') attached by dowels. It is usually around long, though it can commonly reach up to in length. It is usually equal-ended, with the prow and the stern indistinguishable from each other. It has two to four outrigger booms (''batangan'') attached to bamboo floats (''katig'') which are parallel to the main hull. The tips of the floats do not extend beyond the prow and stern. Secondary booms (''sa'am'') a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garay (ship)
''Garay'' were traditional native warships of the Banguingui people in the Philippines. In the 18th and 19th centuries, they were commonly used for piracy by the Banguingui and Iranun people against unarmed trading ships and raids on coastal settlements in the regions surrounding the Sulu Sea. History Most ''garay'' were built in the shipyards of Parang, Sulu in the late 18th century. During the early 19th century, Banguingui ''garay'' squadrons regularly plagued the straits of southern Palawan from the months of March to November each year. They raided coastal areas in northern Borneo for slaves as well as cut off trade into the Sultanate of Brunei. These attacks severely affected the economy of Brunei, leading to its decline. The Banguingui purportedly had a saying: "It is difficult to catch fish, but easy to catch Borneans." Description ''Garay'' were smaller, faster, and more maneuverable than the Iranun '' lanong'' warships. They had a much broader beam and a somewhat r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)