|
Jackshaft (locomotive)
A jackshaft is an intermediate shaft used to transfer power from a powered shaft such as the output shaft of an engine or motor to driven shafts such as the drive axles of a locomotive. As applied to railroad locomotives in the 19th and 20th centuries, jackshafts were typically in line with the drive axles of locomotives and connected to them by side rods. In general, each drive axle on a locomotive is free to move about one inch (2.5 cm) vertically relative to the frame, with the locomotive weight carried on springs. This means that if the engine, motor or transmission is rigidly attached to the locomotive frame, it cannot be rigidly connected to the axle. This problem can be solved by mounting the jackshaft on unsprung bearings and using side-rods or (in some early examples) chain drives.General Construction, Baldwin Gasoline Industrial LocomotiveBaldwin Locomotive Works Record No. 74, 1913; pages 7-9. Jackshafts were first used in early steam locomotives, although the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB 14270-III
SBB may refer to: Arts and entertainment * SBB (band), a Polish progressive rock band, or their self-titled albums: ** ''SBB'' (1974 album) ** ''SBB'' (1978 album, Amiga) * Seán Bán Breathnach, also known as SBB, Irish TV personality * ''Saas Bahu aur Betiyaan'', a television programme on the Indian channel Aaj Tak * Soldier Boy#Television series, Soldier Boy Ben, a superhero in the third season of the television series ''The Boys'' Companies * Swiss Federal Railways () * Serbia Broadband (, ), a cable television and broadband internet service provider in Serbia Technology * Solid bleached board, a paperboard grade * Storage Building Block, an individual tape or disk drive component used in a computer data storage array or library * SwiftBroadband, a satellite-based communication network for aircraft * Screened Bottom Board, also known as Open Mesh Floor, a device used to protect beehives from ''Varroa destructor'' mites Others * Saxon Climbers' Federation (), now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driving Wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled together with side rods (also known as coupling rods); normally one pair is directly driven by the main rod (or connecting rod) which is connected to the end of the piston rod; power is transmitted to the others through the side rods. On diesel and electric locomotives, the driving wheels may be directly driven by the traction motors. Coupling rods are not usually used, and it is quite common for each axle to have its own motor. Jackshaft drive and coupling rods were used in the past (e.g. in the Swiss Crocodile locomotive) but their use is now confined to shunter locomotives. On an articulated locomotive or a duplex locomotive, driving wheels are grouped into sets with wheels within each set linked together. Diameter Drivin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Llewelyn D2302 (5588684248)
Hugh is the English-language variant of the masculine given name , itself the Old French variant of '' Hugo (name)">Hugo'', a short form of Continental Germanic Germanic name">given names beginning in the element "mind, spirit" (Old English ). The Germanic name is on record beginning in the 8th century, in variants ''Chugo, Hugo, Huc, Ucho, Ugu, Uogo, Ogo, Ougo,'' etc. The name's popularity in the Middle Ages ultimately derives from its use by Frankish nobility, beginning with Duke of the Franks and Count of Paris Hugh the Great (898–956). The Old French form was adopted into English from the Norman period (e.g. Hugh of Montgomery, 2nd Earl of Shrewsbury d. 1098; Hugh d'Avranches, 1st Earl of Chester, d. 1101). The spelling ''Hugh'' in English is from the Picard variant spelling '' Hughes'', where the orthography ''-gh-'' takes the role of ''-gu-'' in standard French, i.e. to express the phoneme /g/ as opposed to the affricate /ʒ/ taken by the grapheme ''g'' before front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
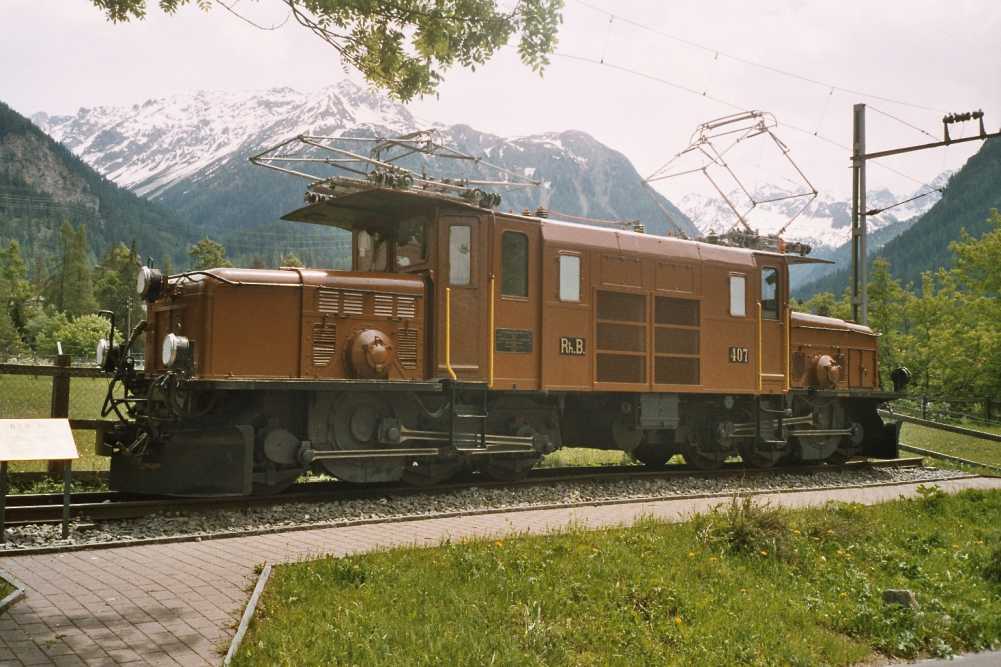
Rhaetian Railway Ge 6/6 I
The Rhaetian Railway Ge 6/6 I is a class of metre gauge Co-Co locomotives, C′C′ electric locomotives operated by the Rhaetian Railway (RhB), which is the main railway network in the Cantons of Switzerland, Canton of Graubünden, Switzerland. The class is so named because it was the first class of locomotives of the Swiss locomotive and railcar classification type ''Ge 6/6'' to be acquired by the Rhaetian Railway. According to that classification system, Ge 6/6 denotes a narrow gauge electric adhesion locomotive with a total of six axles, all of which are drive axles. Due to their shape – they are similar in form to the Swiss Federal Railways, SBB-CFF-FFS Crocodile (locomotive), Crocodiles of the Gotthard Railway – the Ge 6/6 I locomotives have also collectively been nicknamed the ''Rhaetian'' ''Crocodile (locomotive), Crocodiles'' by rail fans. Their internal working RhB designation is ''C-C''. As with its standard-gauge counterpar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodile (locomotive)
Crocodile (German ''Krokodil'') electric locomotives are so called because they have long "noses" at each end, reminiscent of the snout of a crocodile (see also Steeplecab). These contain the motors and drive axles, and are connected by an Articulated vehicle, articulated center section. The center section usually contains the crew compartments, pantograph (transport), pantographs and transformer. The first evidence of the nickname ''crocodile locomotive'' refers to the green Märklin Rail transport modelling, model railway locomotives in O gauge, gauge 0, item CCS 66/12920, as well as in gauge 1, item CCS 66/12921, which snake through the curves like a reptile when running through switch roads and counter curves, and are first referred to as such in the Märklin catalogue of 1933/1934. They are a reproduction of the Ce 6/8II and Ce 6/8III freight locomotives of the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB), which were put into service starting in 1919. Sometimes the term is also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
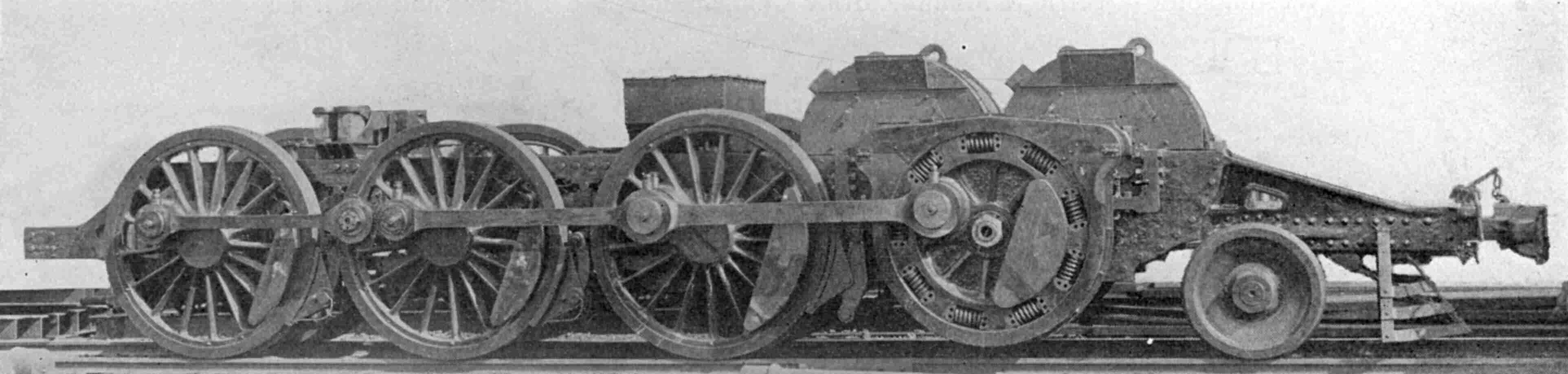
PRR FF1
The Pennsylvania Railroad's class FF1 was an American electric locomotive, a prototype numbered #3931 and nicknamed "Big Liz". It was built in 1917 to haul freight trains across the Allegheny Mountains where the PRR planned to electrify. "Big Liz" proved workable but too powerful for the freight cars of the time with its and of tractive effort. Pulling the train it regularly snapped couplers and when moved to the rear as a pusher its force was sufficient to pop cars in the middle of the train off the tracks. It had a 2-6-6-2 wheel arrangement in two half- frames, connected in the center. Each frame had a pair of three-phase AC induction motors driving a jackshaft through gearing and a spring drive; side rods then drove the wheels. The jackshafts can be mistaken for an additional fourth axle but the "wheels" are cogwheels to transfer power from the motors to the jackshaft. Three-phase power for the four massive motors was supplied from the single phase overhead supply via a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PRR DD1
The Pennsylvania Railroad DD1 was a class of boxcab electric locomotives built by the Pennsylvania Railroad. The locomotives were developed as part of the railroad's New York Tunnel Extension, which built the original Pennsylvania Station in New York City and linked it to New Jersey via the North River Tunnels. The Pennsylvania built a total of 66 locomotives in its Altoona Works; they operated in semi-permanently coupled pairs. Westinghouse supplied the electrical equipment. The first locomotives entered service in 1910, with the opening of Pennsylvania Station. They operated between Manhattan Transfer and Pennsylvania Station, and from there to the coach yards at Sunnyside Yard in Queens, New York. With the arrival of the Class L5 locomotives in 1924, some DD1s moved to the Pennsylvania-owned Long Island Rail Road (LIRR), which had substantial electrified commuter rail operations. The conversion of the New York–Philadelphia main line to alternating current in the 1930s s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westinghouse Electric (1886)
The Westinghouse Electric Corporation was an American manufacturing company founded in 1886 by George Westinghouse and headquartered in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was originally named "Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company" and was renamed "Westinghouse Electric Corporation" in 1945. Through the early and mid-20th century, Westinghouse Electric was a powerhouse in heavy industry, electrical production and distribution, consumer electronics, home appliances and a wide variety of other products. They were a major supplier of generators and steam turbines for most of their history, and was also a major player in the field of nuclear power, starting with the Westinghouse Atom Smasher in 1937. A series of downturns and management missteps in the 1970s and 80s combined with large cash balances led the company to enter the financial services business. Their focus was on mortgages, which suffered significant losses in the late 1980s. In 1992 they announced a major restruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown, Boveri & Cie
Brown, Boveri & Cie. (Brown, Boveri & Company; BBC) was a Swiss group of electrical engineering companies. It was founded in Baden bei Zürich, in 1891 by Charles Eugene Lancelot Brown and Walter Boveri who worked at the Maschinenfabrik Oerlikon. In 1988 BBC merged with ASEA to form ABB. Early history of BBC Brown Boveri BBC Brown Boveri was established in 1891. The company was one of only a few multinational corporations to operate subsidiaries that were larger than the parent company. Because of the limitations of the Swiss domestic market, Brown Boveri established subsidiaries throughout Europe relatively early in its history, and at times had difficulty maintaining managerial control over some of its larger operating units. The merger with ASEA, a company which was praised for its strong management, was expected to help Brown Boveri reorganize and reassert control over its vast international network. Activity in Britain Brown Boveri's early activities included manufac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maschinenfabrik Oerlikon
Maschinenfabrik Oerlikon was a Swiss engineering company based in the Zürich district of Oerlikon (Zürich), Oerlikon known for the early development of electric locomotives. It was founded in 1876 as the ''Werkzeug- und Maschinen-Fabrik Oerlikon'' by the industrialist Peter Emil Huber-Werdmüller, and occupied a large site immediately to the west of Zürich Oerlikon railway station, Oerlikon railway station. In 1906, the armaments business was demerged to form ', which evolved into the technology company OC Oerlikon and the armaments company Rheinmetall Air Defence (formerly ''Oerlikon Contraves''). In 1967, Maschinenfabrik Oerlikon was taken over by Brown, Boveri & Cie, which merged with ASEA in 1988 to form ABB Group. The site of the company's works has been redeveloped, including the innovative public MFO-Park. In the second decade of the 21st century, a project was initiated to expand Oerlikon railway station, with the provision of two additional platform tracks on n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traction Motor
A traction motor is an electric motor used for propulsion of a vehicle, such as locomotives, electric vehicle, electric or hydrogen vehicles, or electric multiple unit trains. Traction (engineering), Traction motors are used in electrically powered railway vehicles (electric multiple units) and other electric vehicles including electric milk floats, trolleybuses, elevators, roller coasters, and conveyor systems, as well as vehicles with electrical transmission systems (Diesel locomotive#Transmission types, diesel–electric locomotives, electric hybrid vehicles), and battery electric vehicles. Traction motor companies The word ''traction'' from Latin, being the Agent (grammar), agent noun of ''trahere'' "to pull" in the sense of "drawn" was used for the naming of traction engines developed circa 1870. The first experimental electric traction motor tramway of 1875 was rapidly developed internationally for city use. In the 19th century traction motor passenger car companies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Locomotive
An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, a third rail or on-board energy storage such as a Battery (electricity), battery or a supercapacitor. Locomotives with on-board fuelled prime mover (locomotive), prime movers, such as diesel engines or gas turbines, are classed as Diesel–electric powertrain, diesel–electric or turbine–electric powertrain, gas turbine–electric and not as electric locomotives, because the electric generator/motor combination serves only as a Transmission (mechanics), power transmission system. Electric locomotives benefit from the high efficiency of electric motors, often above 90% (not including the inefficiency of generating the electricity). Additional efficiency can be gained from regenerative braking, which allows kinetic energy to be recovered during braking to put power back on the line. Newer electric locomotives use AC motor-inverter drive systems that provide for regenerative braking. Electric loco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |