PRR FF1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The
The
 The
The Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad ( reporting mark PRR), legal name as the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy," was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At its ...
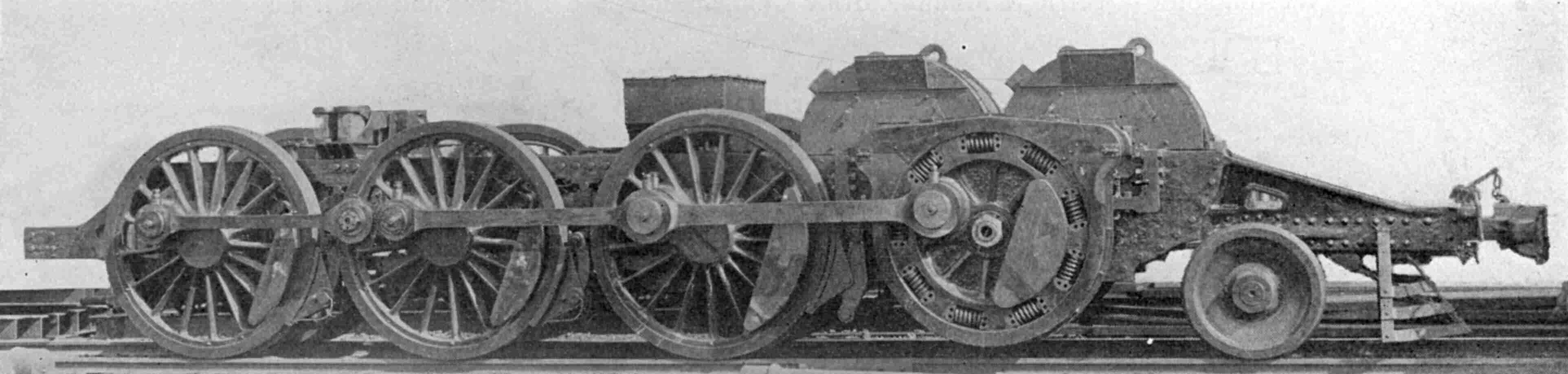
's class FF1 was an American electric locomotive
An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, a third rail or on-board energy storage such as a Battery (electricity), battery or a supercapacitor. Locomotives with on-board fuelled prime mover (locomotive), ...
, a prototype numbered #3931 and nicknamed "Big Liz". It was built in 1917 to haul freight trains across the Allegheny Mountains
The Allegheny Mountain Range ( ) — also spelled Alleghany or Allegany, less formally the Alleghenies — is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the Eastern United States and Canada. Historically it represented a significant barr ...
where the PRR planned to electrify. "Big Liz" proved workable but too powerful for the freight cars of the time with its and of tractive effort. Pulling the train it regularly snapped couplers and when moved to the rear as a pusher its force was sufficient to pop
Pop or POP may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Pop music, a musical genre
Artists
* POP, a Japanese idol group now known as Gang Parade
* Pop! (British group), a UK pop group
* Pop! featuring Angie Hart, an Australian band
Album ...
cars in the middle of the train off the tracks.
It had a 2-6-6-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, a is a locomotive with one pair of unpowered leading wheels, followed by two sets of three pairs of powered driving wheels and one pair of trailing wheels. ...
wheel arrangement in two half- frames, connected in the center. Each frame had a pair of three-phase AC induction motors driving a jackshaft through gearing and a spring drive; side rod
A coupling rod or side rod connects the driving wheels of a locomotive. Steam locomotives in particular usually have them, but some Diesel locomotive, diesel and Electric locomotive, electric locomotives, especially older ones and switcher locom ...
s then drove the wheels. The jackshafts can be mistaken for an additional fourth axle but the "wheels" are cogwheels to transfer power from the motors to the jackshaft. Three-phase
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3ϕ) is a common type of alternating current (AC) used in electricity generation, Electric power transmission, transmission, and Electric power distribution, distribution. It is a type of polyphase system ...
power for the four massive motors was supplied from the single phase overhead supply via a large rotary converter
A rotary converter is a type of electrical machine which acts as a mechanical rectifier, Power inverter, inverter or frequency converter.
Rotary converters were used to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), or DC to AC power, ...
housed in the body of the locomotive. Combined rated output of the motors was , but the converter could only supply a short term or a continuous . With three-phase induction motors there was no way to control the speed of the motors; changing the wiring of the motor poles allowed for two speed settings, , which were considered enough to drag heavy freight trains up and down steep grades.
Its intended use as an Allegheny climber was never realized and its power was too much for the rolling stock
The term rolling stock in the rail transport industry refers to railway vehicles, including both powered and unpowered vehicles: for example, locomotives, Railroad car#Freight cars, freight and Passenger railroad car, passenger cars (or coaches) ...
in service at the time. Big Liz was sidelined until being cut up for scrap
Scrap consists of recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap can have monetary value, especially recover ...
in 1940.
References
* * * 2-6-6-2 locomotives 11 kV AC locomotives FF1 1′C+C1′ locomotives Experimental locomotives Individual locomotives of the United States Electric locomotives of the United States Unique locomotives Scrapped locomotives Standard-gauge locomotives of the United States Westinghouse locomotives Railway locomotives introduced in 1917 {{US-train-stub