|
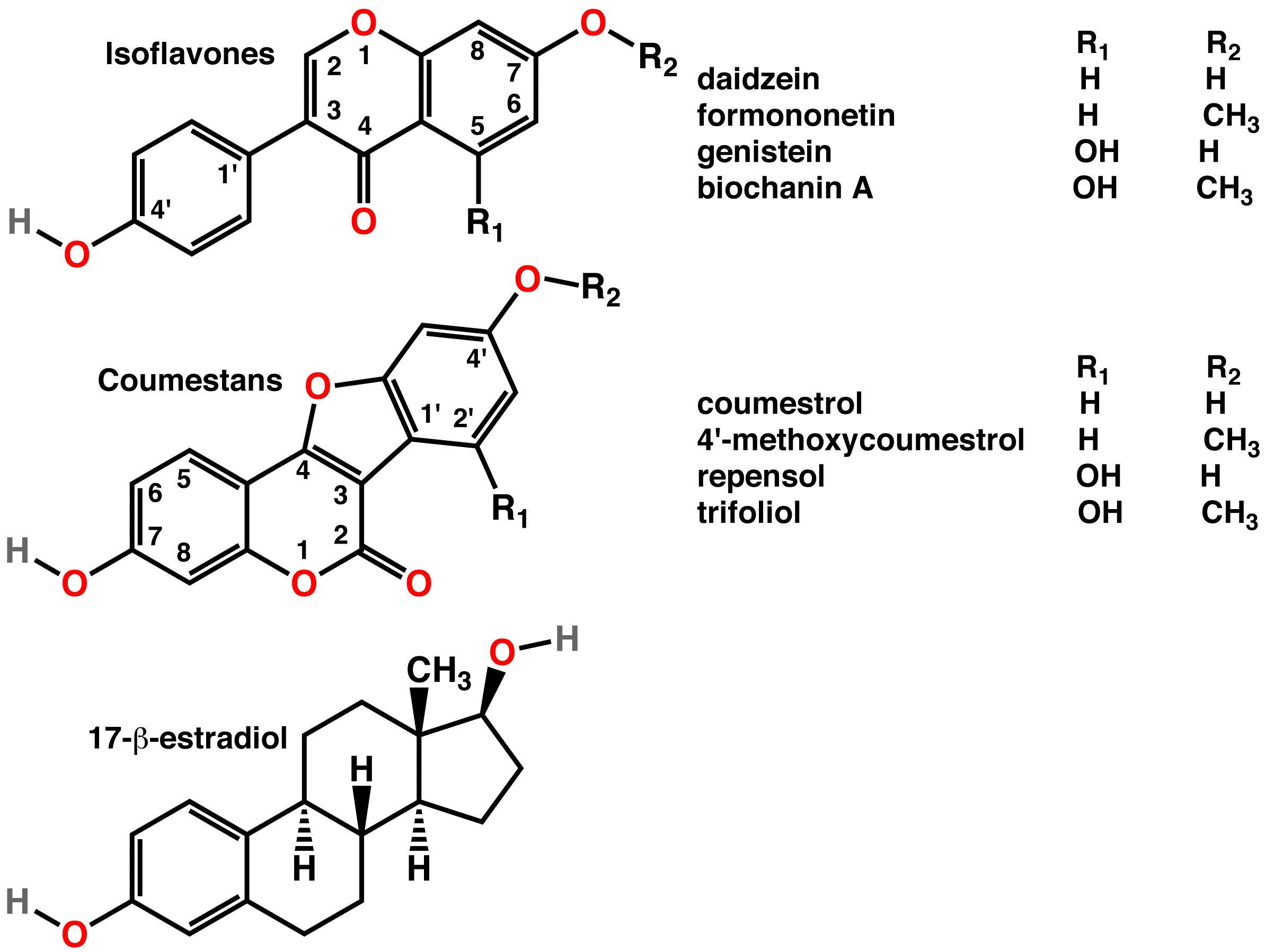
Isoflavones
Isoflavones are substituted derivatives of isoflavone, a type of naturally occurring isoflavonoids, many of which act as phytoestrogens in mammals. Isoflavones are produced almost exclusively by the members of the bean family, Fabaceae (Leguminosae). Although isoflavones and closely related phytoestrogens are sold as dietary supplements, there is little scientific evidence for either the safety of long-term supplementation or of health benefits from these compounds. Some studies have identified potential risks from high intake of isoflavones, such as in women with a history of breast cancer, but this concern has not been substantiated with high-quality clinical research. Organic chemistry and biosynthesis Isoflavone is an isomer of flavone, which is chromone substituted with a phenyl group in the 2-position. In isoflavone, the phenyl group is in the 4-position. Isoflavone is of liminted interest per se, but substituted derivatives are of nutritional interest. Substituted derivat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses. Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu and tofu skin are made. Fermented soy foods include soy sauce, fermented bean paste, nattō, and tempeh. Fat-free (defatted) soybean meal is a significant and cheap source of protein for animal feeds and many packaged meals. For example, soybean products, such as textured vegetable protein (TVP), are ingredients in many meat and dairy substitutes. Soybeans contain significant amounts of phytic acid, dietary minerals and B vitamins. Soy vegetable oil, used in food and industrial applications, is another product of processing the soybean crop. Soybean is the most important protein source for feed farm animals (that in turn yields animal protein for human consumption). Etymology The word "soy" originated as a corruption of the Cant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoestrogen
A phytoestrogen is a plant-derived xenoestrogen (see estrogen) not generated within the endocrine system, but consumed by eating plants or manufactured foods. Also called a "dietary estrogen", it is a diverse group of naturally occurring nonsteroidal plant compounds that, because of its structural similarity with estradiol (17-β-estradiol), have the ability to cause estrogenic or antiestrogenic effects. Phytoestrogens are not essential nutrients because their absence from the diet does not cause a disease, nor are they known to participate in any normal biological function. Common foods containing phytoestrogens are soy protein, beans, oats, barley, rice, coffee, apples, carrots (see Food Sources section below for bigger list). Its name comes from the Greek ''phyto'' ("plant") and ''estrogen'', the hormone which gives fertility to female mammals. The word "estrus" - Greek οίστρος - means "sexual desire", and "gene" - Greek γόνο - is "to generate". It has been hypot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daidzein
Daidzein (7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one) is a naturally occurring compound found exclusively in soybeans and other legumes and structurally belongs to a class of compounds known as isoflavones. Daidzein and other isoflavones are produced in plants through the phenylpropanoid pathway of secondary metabolism and are used as signal carriers, and defense responses to pathogenic attacks. In humans, recent research has shown the viability of using daidzein in medicine for menopausal relief, osteoporosis, blood cholesterol, and lowering the risk of some hormone-related cancers, and heart disease. Despite the known health benefits, the use of both puerarin and daidzein is limited by their poor bioavailability and low water solubility. Natural occurrence Daidzein and other isoflavone compounds, such as genistein, are present in a number of plants and herbs like kwao krua ('' Pueraria mirifica'') and kudzu. It can also be found in ''Maackia amurensis'' cell cultures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genistein
Genistein (C15H10O5) is a naturally occurring compound that structurally belongs to a class of compounds known as isoflavones. It is described as an angiogenesis inhibitor and a phytoestrogen. It was first isolated in 1899 from the dyer's broom, ''Genista tinctoria''; hence, the chemical name. The compound structure was established in 1926, when it was found to be identical with that of prunetol. It was chemically synthesized in 1928. It has been shown to be the primary secondary metabolite of the ''Trifolium'' species and ''Glycine max L''. Natural occurrences Isoflavones such as genistein and daidzein are found in a number of plants including lupin, fava beans, soybeans, kudzu, and psoralea being the primary food source, also in the medicinal plants, ''Flemingia vestita'' and '' F. macrophylla'', and coffee. It can also be found in ''Maackia amurensis'' cell cultures. Biological effects Besides functioning as an antioxidant and anthelmintic, many isoflavones have been s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoflavonoid
Isoflavonoids are a class of flavonoid phenolic compounds, many of which are biologically active. Isoflavonoids and their derivatives are sometimes referred to as phytoestrogens, as many isoflavonoid compounds have biological effects via the estrogen receptor. Medically, isoflavonoids and related compounds have been used in many dietary supplements but the medical and scientific community is generally skeptical of their use. Recently, some natural isoflavonoids have been identified as toxins, including biliatresone which may cause biliary atresia when infants are exposed to the plant product. The isoflavonoid group is broad, and includes many structurally similar groups, including: * isoflavones * isoflavanones * isoflavans * pterocarpans * rotenoids Isoflavonoids are derived from the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway via liquiritigenin or naringenin. Chemical makeup While flavonoids (in the narrow sense) have the 2-phenylchromen-4-one backbone, isoflavonoids have the 3-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavone
Flavone is an organic compound with the formula . A white solid, flavone is a derivative of chromone with a phenyl (Ph) substituent adjacent to the ether group. The compound is of little direct practical importance, but susbstituted derivatives, the flavones and flavonoids are a large class of nutritionally important natural products. Flavone can be prepared in the laboratory by cyclization of 2-hydroxacetophenone. Isomeric with flavone is isoflavone, where the phenyl group is adjacent to the ketone In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bon .... References {{Flavones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' Chemical specificity, specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psoralea
''Psoralea'' is a genus in the legume family ( Fabaceae) with over 60 closely related species native to southern Africa. In South Africa they are commonly referred to as fountainbush (English); fonteinbos, bloukeur, or penwortel (Afrikaans); and umHlonishwa (Zulu). Species * '' Psoralea abbottii'' C.H.Stirt. * ''Psoralea aculeata'' L. * '' Psoralea affinis'' Eckl. & Zeyh. * '' Psoralea alata'' (Thunb.) T.M.Salter * ''Psoralea angustifolia'' L'Hér. * ''Psoralea aphylla'' L. * '' Psoralea arborea'' Sims * '' Psoralea asarina'' (P.J.Bergius) T.M.Salter * ''Psoralea axillaris'' L.f. * '' Psoralea azuroides'' C.H.Stirt. * ''Psoralea brilliantissima'' C.H.Stirt., Muasya & A.Bello * ''Psoralea cataracta'' C.H.Stirt. * '' Psoralea congesta'' C.H.Stirt. & Muasya * '' Psoralea diturnerae'' A. Bello, C.H. Stirt. & Muasya * ''Psoralea elegans'' C.H.Stirt. * ''Psoralea ensifolia'' (Houtt.) Merr. * ''Psoralea fascicularis'' DC. , syn. ''Psoralea tenuifolia'' Thunb. , syn. ''Psoralea thunberg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Nodule
Root nodules are found on the roots of plants, primarily legumes, that form a symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Under nitrogen-limiting conditions, capable plants form a symbiotic relationship with a host-specific strain of bacteria known as rhizobia. This process has evolved multiple times within the legumes, as well as in other species found within the Rosid clade. Legume crops include beans, peas, and soybeans. Within legume root nodules, nitrogen gas (N2) from the atmosphere is converted into ammonia (NH3), which is then assimilated into amino acids (the building blocks of proteins), nucleotides (the building blocks of DNA and RNA as well as the important energy molecule ATP), and other cellular constituents such as vitamins, flavones, and hormones. Their ability to fix gaseous nitrogen makes legumes an ideal agricultural organism as their requirement for nitrogen fertilizer is reduced. Indeed, high nitrogen content blocks nodule development as there is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizobium
''Rhizobium'' is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria that fix nitrogen. ''Rhizobium'' species form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of (primarily) legumes and other flowering plants. The bacteria colonize plant cells within root nodules, where they convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia using the enzyme nitrogenase and then provide organic nitrogenous compounds such as glutamine or ureides to the plant. The plant, in turn, provides the bacteria with organic compounds made by photosynthesis. This mutually beneficial relationship is true of all of the rhizobia, of which the genus ''Rhizobium'' is a typical example. ''Rhizobium'' is also capable to solubilize phosphorus. History Martinus Beijerinck was the first to isolate and cultivate a microorganism from the nodules of legumes in 1888. He named it ''Bacillus radicicola'', which is now placed in '' Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology'' under the genus ''Rhizobium''. Research ''Rhizobi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |