|
Invariant Plane
The invariable plane of a planetary system, also called Laplace's invariable plane, is the plane passing through its barycenter (center of mass) perpendicular to its angular momentum vector. Solar System In the Solar System, about 98% of this effect is contributed by the orbital angular momenta of the four giant planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune). The invariable plane is within 0.5° of the orbital plane of Jupiter, and may be regarded as the weighted average of all planetary orbital and rotational planes. Terminology and definition This plane is sometimes called the "Laplacian" or "Laplace plane" or the "invariable plane of Laplace", though it should not be confused with the Laplace plane, which is the plane about which the individual orbital planes of planetary satellites precess. Both derive from the work of (and are at least sometimes named for) the French astronomer Pierre-Simon Laplace. — English translation published in four volumes, 1829–1839; : origina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Planets
A giant planet, sometimes referred to as a jovian planet (''Jove'' being another name for the Roman god Jupiter), is a diverse type of planet much larger than Earth. Giant planets are usually primarily composed of low-boiling point materials ( volatiles), rather than rock or other solid matter, but massive solid planets can also exist. There are four such planets in the Solar System: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Many extrasolar giant planets have been identified. Giant planets are sometimes known as gas giants, but many astronomers now apply the term only to Jupiter and Saturn, classifying Uranus and Neptune, which have different compositions, as ice giants. Both names are potentially misleading; the Solar System's giant planets all consist primarily of fluids above their critical points, where distinct gas and liquid phases do not exist. Jupiter and Saturn are principally made of hydrogen and helium, whilst Uranus and Neptune consist of water, ammonia, and methane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamics Of The Solar System
Dynamics (from Greek δυναμικός ''dynamikos'' "powerful", from δύναμις ''dynamis'' " power") or dynamic may refer to: Physics and engineering * Dynamics (mechanics), the study of forces and their effect on motion Brands and enterprises * Dynamic (record label), an Italian record label in Genoa Mathematics * Dynamical system, a concept describing a point's time dependency ** Topological dynamics, the study of dynamical systems from the viewpoint of general topology * Symbolic dynamics, a method to model dynamical systems Social science * Group dynamics, the study of social group processes especially * Population dynamics, in life sciences, the changes in the composition of a population * Psychodynamics, the study of psychological forces driving human behavior * Social dynamics, the ability of a society to react to changes * Spiral Dynamics, a social development theory Other uses * Dynamics (music), the softness or loudness of a sound or note * DTA Dynamic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy And Astrophysics
''Astronomy & Astrophysics (A&A)'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering theoretical, observational, and instrumental astronomy and astrophysics. It is operated by an editorial team under the supervision of a board of directors representing 27 sponsoring countries plus a representative of the European Southern Observatory. The journal is published by EDP Sciences and the current editors-in-chief are Thierry Forveille and João Alves. History Origins ''Astronomy & Astrophysics'' was created as an answer to the publishing situation found in Europe in the 1960s. At that time, multiple journals were being published in several countries around the continent. These journals usually had a limited number of subscribers, and articles were written in languages other than English. They were less widely read than American and British journals and the research they reported had therefore less impact in the community. Starting in 1963, conversations between astronomers from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galaxy, which are so far away that they cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with a Galaxy#Isophotal diameter, D25 isophotal diameter estimated at , but only about 1,000 light-years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulge). Recent simulations suggest that a dark matter area, also containing some visible stars, may extend up to a diameter of almost 2 million light-years (613 kpc). The Milky Way has several List of Milky Way's satellite galaxies, satellite galaxies and is part of the Local Group of galaxies, forming part of the Virgo Supercluster which is itself a component of the Laniakea Supercluster. It is estimated to contain 100–400 billion stars and at least that number of pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newtonian Dynamics
In physics, Newtonian dynamics (also known as Newtonian mechanics) is the study of the dynamics of a particle or a small body according to Newton's laws of motion. Mathematical generalizations Typically, the Newtonian dynamics occurs in a three-dimensional Euclidean space, which is flat. However, in mathematics Newton's laws of motion can be generalized to multidimensional and curved spaces. Often the term Newtonian dynamics is narrowed to Newton's second law \displaystyle m\,\mathbf a=\mathbf F. Newton's second law in a multidimensional space Consider \displaystyle N particles with masses \displaystyle m_1,\,\ldots,\,m_N in the regular three-dimensional Euclidean space. Let \displaystyle \mathbf r_1,\,\ldots,\,\mathbf r_N be their radius-vectors in some inertial coordinate system. Then the motion of these particles is governed by Newton's second law applied to each of them The three-dimensional radius-vectors \displaystyle\mathbf r_1,\,\ldots,\,\mathbf r_N can be built into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way Galaxy
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galaxy, which are so far away that they cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with a D25 isophotal diameter estimated at , but only about 1,000 light-years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulge). Recent simulations suggest that a dark matter area, also containing some visible stars, may extend up to a diameter of almost 2 million light-years (613 kpc). The Milky Way has several satellite galaxies and is part of the Local Group of galaxies, forming part of the Virgo Supercluster which is itself a component of the Laniakea Supercluster. It is estimated to contain 100–400 billion stars and at least that number of planets. The Solar System is located at a radius of about 27,000 light-years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Solar System Body
A small Solar System body (SSSB) is an object in the Solar System that is neither a planet, a dwarf planet, nor a natural satellite. The term was first defined in 2006 by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) as follows: "All other objects, except satellites, orbiting the Sun shall be referred to collectively as 'Small Solar System Bodies. (IAU) This encompasses all s and all s other than those that are |
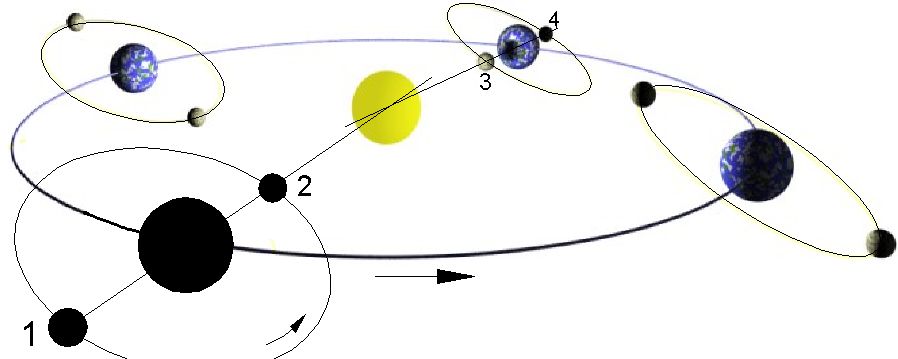
Syzygy (astronomy)
In astronomy, a syzygy ( ; , expressing the sense of σύν ( "together") and ζυγ- ( "a yoke")) is a roughly straight-line configuration of three or more celestial bodies in a gravitational system. The word is often used in reference to the Sun, Earth, and either the Moon or a planet, where the latter is in ''conjunction'' or ''opposition''. Solar and lunar ''eclipses'' occur at times of syzygy, as do ''transits'' and ''occultations''. Main types A syzygy sometimes results in an occultation, transit, or an eclipse. * An occultation occurs when an apparently larger body passes in front of an apparently smaller one. * A transit occurs when a smaller body passes in front of a larger one. ** In the combined case where the smaller body regularly transits the larger, an occultation is also termed a secondary eclipse. * An eclipse occurs when a body totally or partially disappears from view, either by an occultation, as with a solar eclipse, or by passing into the shadow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opposition (astronomy)
In positional astronomy, two astronomical objects are said to be in opposition when they are on antipodal point, opposite sides of the celestial sphere, as observed from a given body (usually Earth). A planet (or asteroid or comet) is said to be "in opposition" or "at opposition" when it is in opposition to the Sun. Because most orbits in the Solar System are nearly coplanar to the ecliptic, this occurs when the Sun, Earth, and the body are configured in an approximately straight line, or syzygy (astronomy), syzygy; that is, Earth and the body are in the same direction as seen from the Sun. Opposition occurs only for superior planets (see the diagram). The instant of opposition is defined as that when the apparent geocentric ecliptic coordinate system, celestial longitude of the body differs by 180° from the apparent geocentric longitude of the Sun. At that time, a body is: * in apparent retrograde motion * visible almost all night – rising around sunset, culmination, culmin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Resonance
In celestial mechanics, orbital resonance occurs when orbiting bodies exert regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods are related by a ratio of small integers. Most commonly, this relationship is found between a pair of objects (binary resonance). The physical principle behind orbital resonance is similar in concept to pushing a child on a swing, whereby the orbit and the swing both have a natural frequency, and the body doing the "pushing" will act in periodic repetition to have a cumulative effect on the motion. Orbital resonances greatly enhance the mutual gravitational influence of the bodies (i.e., their ability to alter or constrain each other's orbits). In most cases, this results in an ''unstable'' interaction, in which the bodies exchange momentum and shift orbits until the resonance no longer exists. Under some circumstances, a resonant system can be self-correcting and thus stable. Examples are the 1:2:4 resona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perturbation Theory
In mathematics and applied mathematics, perturbation theory comprises methods for finding an approximate solution to a problem, by starting from the exact solution of a related, simpler problem. A critical feature of the technique is a middle step that breaks the problem into "solvable" and "perturbative" parts. In regular perturbation theory, the solution is expressed as a power series in a small parameter The first term is the known solution to the solvable problem. Successive terms in the series at higher powers of \varepsilon usually become smaller. An approximate 'perturbation solution' is obtained by truncating the series, often keeping only the first two terms, the solution to the known problem and the 'first order' perturbation correction. Perturbation theory is used in a wide range of fields and reaches its most sophisticated and advanced forms in quantum field theory. Perturbation theory (quantum mechanics) describes the use of this method in quantum mechanics. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |