Syzygy (astronomy) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In 
NASA's eclipse page
.
 On June 3, 2014, the ''Curiosity'' rover on Mars observed the planet Mercury transiting the Sun, marking the first time a planetary transit has been observed from a celestial body besides
On June 3, 2014, the ''Curiosity'' rover on Mars observed the planet Mercury transiting the Sun, marking the first time a planetary transit has been observed from a celestial body besides
 Because the orbits of all the planets in the Solar System (as well as the Moon) are inclined by only a few degrees, they always appear very near the
Because the orbits of all the planets in the Solar System (as well as the Moon) are inclined by only a few degrees, they always appear very near the
 In
In astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
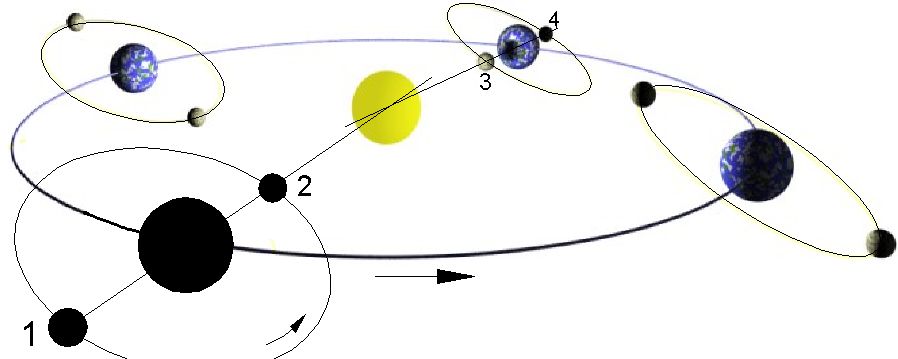
, a syzygy ( ; , expressing the sense of σύν ( "together") and ζυγ- ( "a yoke"))
is a roughly straight-line configuration of three or more celestial bodies
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists within the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are of ...
in a gravitational system.
The word is often used in reference to the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
, Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
, and either the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
or a planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
, where the latter is in ''conjunction'' or ''opposition''. Solar and lunar ''eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event which occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three ...
s'' occur at times of syzygy, as do ''transits'' and ''occultation
An occultation is an event that occurs when one object is hidden from the observer by another object that passes between them. The term is often used in astronomy, but can also refer to any situation in which an object in the foreground blocks f ...
s''.

Main types
A syzygy sometimes results in an occultation, transit, or an eclipse. * Anoccultation
An occultation is an event that occurs when one object is hidden from the observer by another object that passes between them. The term is often used in astronomy, but can also refer to any situation in which an object in the foreground blocks f ...
occurs when an apparently larger body passes in front of an apparently smaller one.
* A transit
Transit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Transit'' (1980 film), a 1980 Israeli film
* ''Transit'' (1986 film), a Canadian short film
* ''Transit'' (2005 film), a film produced by MTV and Staying-Alive about four people in countrie ...
occurs when a smaller body passes in front of a larger one.
** In the combined case where the smaller body regularly transits the larger, an occultation is also termed a secondary eclipse.
* An eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event which occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three ...
occurs when a body totally or partially disappears from view, either by an occultation, as with a solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season i ...
, or by passing into the shadow of another body, as with a lunar eclipse
A lunar eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, ...
(thus both are listed oNASA's eclipse page
.
Consequences
Einstein ring
As electromagnetic rays are affected by gravitation, when they pass by a heavy mass they are bent. As a result, the heavy mass acts as a form of gravitational lens. If the light source, the gravitating mass and the observer stand in a line, one sees what is termed an Einstein ring.Tidal variation
A syzygy causes the fortnightly phenomena ofspring tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ...
s. At the new and full moon, the Sun and Moon are in syzygy. Their tidal force
The tidal force or tide-generating force is the difference in gravitational attraction between different points in a gravitational field, causing bodies to be pulled unevenly and as a result are being stretched towards the attraction. It is the ...
s act to reinforce each other, and the ocean both rises higher and falls lower than the average. Tidal variations can also be measured in the Earth's crust
Earth's crust is its thick outer shell of rock, referring to less than one percent of the planet's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a solidified division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper ...
, and these ''Earth tide
Earth tide (also known as solid-Earth tide, crustal tide, body tide, bodily tide or land tide) is the displacement of the solid earth's surface caused by the gravity of the Moon and Sun. Its main component has meter-level amplitude at periods of a ...
'' influences may affect the frequency of earthquakes.
Extraterrestrial cases
The word ''syzygy'' is often used to describe interesting configurations of astronomical objects in general. For example, one such case occurred on March 21, 1894, around 23:00 GMT, when Mercury transited the Sun as would have been seen from Venus, and Mercury andVenus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
both simultaneously transited the Sun as seen from Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
.
 On June 3, 2014, the ''Curiosity'' rover on Mars observed the planet Mercury transiting the Sun, marking the first time a planetary transit has been observed from a celestial body besides
On June 3, 2014, the ''Curiosity'' rover on Mars observed the planet Mercury transiting the Sun, marking the first time a planetary transit has been observed from a celestial body besides Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
.
Other uses
The term is also used to describe situations when all the planets are on the same side of the Sun although they are not necessarily in a straight line, such as on March 10, 1982. Because the orbits of all the planets in the Solar System (as well as the Moon) are inclined by only a few degrees, they always appear very near the
Because the orbits of all the planets in the Solar System (as well as the Moon) are inclined by only a few degrees, they always appear very near the ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
in our sky. Therefore, although an apparent planetary alignment known as a planetary parade may appear as a line (actually, a great arc
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line, but that does not have to be straight.
Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point. This is the definition that ...
), the planets are not necessarily aligned in space.
References
{{Authority control Astrometry Eclipses Astronomical events