|
Inflections
In linguistic morphology, inflection (less commonly, inflexion) is a process of word formation in which a word is modified to express different grammatical categories such as tense, case, voice, aspect, person, number, gender, mood, animacy, and definiteness. The inflection of verbs is called ''conjugation'', while the inflection of nouns, adjectives, adverbs, etc. can be called ''declension''. An inflection expresses grammatical categories with affixation (such as prefix, suffix, infix, circumfix, and transfix), apophony (as Indo-European ablaut), or other modifications. For example, the Latin verb ', meaning "I will lead", includes the suffix ', expressing person (first), number (singular), and tense-mood (future indicative or present subjunctive). The use of this suffix is an inflection. In contrast, in the English clause "I will lead", the word ''lead'' is not inflected for any of person, number, or tense; it is simply the bare form of a verb. The inflected form of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Gender
In linguistics, a grammatical gender system is a specific form of a noun class system, where nouns are assigned to gender categories that are often not related to the real-world qualities of the entities denoted by those nouns. In languages with grammatical gender, most or all nouns inherently carry one value of the grammatical category called ''gender''. The values present in a given language, of which there are usually two or three, are called the ''genders'' of that language. Some authors use the term "grammatical gender" as a synonym of "noun class", whereas others use different definitions for each. Many authors prefer "noun classes" when none of the inflections in a language relate to Sex–gender distinction, sex or gender. According to one estimate, gender is used in approximately half of the world's languages. According to one definition: "Genders are classes of nouns reflected in the behavior of associated words." Overview Languages with grammatical gender usually h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Number
In linguistics, grammatical number is a Feature (linguistics), feature of nouns, pronouns, adjectives and verb agreement (linguistics), agreement that expresses count distinctions (such as "one", "two" or "three or more"). English and many other languages present number categories of singular or plural. Some languages also have a Dual (grammatical number), dual, #Trial, trial and #Paucal, paucal number or other arrangements. The word "number" is also used in linguistics to describe the distinction between certain grammatical aspects that indicate the number of times an event occurs, such as the semelfactive aspect, the iterative aspect, etc. For that use of the term, see "Grammatical aspect". Overview Most languages of the world have formal means to express differences of number. One widespread distinction, found in English and many other languages, involves a simple two-way contrast between singular and plural number (''car''/''cars'', ''child''/''children'', etc.). Discussion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animacy
Animacy (antonym: inanimacy) is a grammatical and semantic feature, existing in some languages, expressing how sentient or alive the referent of a noun is. Widely expressed, animacy is one of the most elementary principles in languages around the globe and is a distinction acquired as early as six months of age. Concepts of animacy constantly vary beyond a simple animate and inanimate binary; many languages function off an hierarchical general animacy scale that ranks animacy as a "matter of gradience". Typically (with some variation of order and of where the cutoff for animacy occurs), the scale ranks humans above animals, then plants, natural forces, concrete objects, and abstract objects, in that order. In referring to humans, this scale contains a hierarchy of persons, ranking the first- and second-person pronouns above the third person, partly a product of empathy, involving the speaker and interlocutor. It is obvious that the ability to distinguish between animate and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Case
A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers (determiners, adjectives, participles, and Numeral (linguistics), numerals) that corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a Nominal group (functional grammar), nominal group in a wording. In various languages, nominal groups consisting of a noun and its modifiers belong to one of a few such categories. For instance, in English language, English, one says ''I see them'' and ''they see me'': the nominative case, nominative pronouns ''I/they'' represent the perceiver, and the accusative case, accusative pronouns ''me/them'' represent the phenomenon perceived. Here, nominative and accusative are cases, that is, categories of pronouns corresponding to the functions they have in representation. English has largely lost its inflected case system but personal pronouns still have three cases, which are simplified forms of the nominative, accusative (including functions formerly handled by the Dative case, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjective
An adjective (abbreviations, abbreviated ) is a word that describes or defines a noun or noun phrase. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun. Traditionally, adjectives are considered one of the main part of speech, parts of speech of the English language, although historically they were classed together with Noun, nouns. Nowadays, certain words that usually had been classified as adjectives, including ''the'', ''this'', ''my'', etc., typically are classed separately, as Determiner (class), determiners. Examples: * That's a ''funny'' idea. (Prepositive attributive) * That idea is ''funny''. (Predicate (grammar), Predicative) * * The ''good'', the ''bad'', and the ''funny''. (Substantive adjective, Substantive) * Clara Oswald, completely ''fictional'', died three times. (Apposition, Appositive) Etymology ''Adjective'' comes from Latin ', a calque of (whence also English ''epithet''). In the grammatical tradition of Latin and Greek, because adjectives were I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (Interlinear gloss, glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the part of speech, parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Sub-types include personal pronoun, personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive pronoun, reflexive and reciprocal pronoun, reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative pronoun, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora (linguistics), anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent (grammar), antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
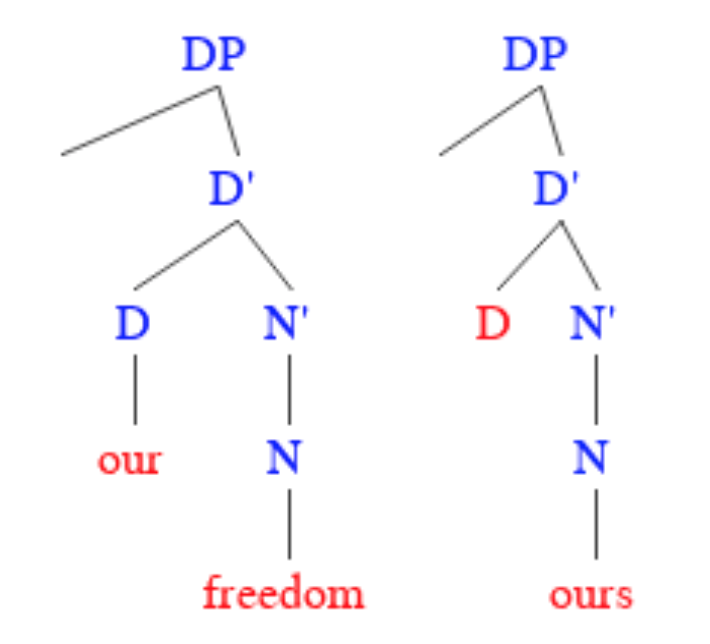
Determiners
Determiner, also called determinative (abbreviated ), is a term used in some models of grammatical description to describe a word or affix belonging to a class of noun modifiers. A determiner combines with a noun to express its reference. Examples in English include articles (''the'' and ''a''/''an''), demonstratives (''this'', ''that''), possessive determiners (''my,'' ''their''), and quantifiers (''many'', ''both''). Not all languages have determiners, and not all systems of grammatical description recognize them as a distinct category. Description The linguistics term "determiner" was coined by Leonard Bloomfield in 1933. Bloomfield observed that in English, nouns often require a qualifying word such as an article or adjective. He proposed that such words belong to a distinct class which he called "determiners". If a language is said to have determiners, any articles are normally included in the class. Other types of words often regarded as belonging to the determiner cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Participle
In linguistics, a participle (; abbr. ) is a nonfinite verb form that has some of the characteristics and functions of both verbs and adjectives. More narrowly, ''participle'' has been defined as "a word derived from a verb and used as an adjective, as in a ''laughing face''". "Participle" is a traditional grammatical term from Greek and Latin that is widely used for corresponding verb forms in European languages and analogous forms in Sanskrit and Arabic grammar. In particular, Greek and Latin participles are inflected for gender, number and case, but also conjugated for tense and voice and can take prepositional and adverbial modifiers. Cross-linguistically, participles may have a range of functions apart from adjectival modification. In European and Indian languages, the past participle is used to form the passive voice. In English, participles are also associated with periphrastic verb forms ( continuous and perfect) and are widely used in adverbial clauses. In non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflected Preposition
In linguistics, an inflected preposition is a type of word that occurs in some languages, that corresponds to the combination of a preposition and a personal pronoun. For instance, the Welsh word ' () is an inflected form of the preposition ''i'' meaning "to/for him"; it would not be grammatically correct to say *'. Terminology and analysis There are many different names for inflected prepositions, including conjugated preposition, pronominal preposition, prepositional pronoun, and suffixed pronoun. (But note that the term ''prepositional pronoun'' also has a different sense, for which see Prepositional pronoun.) Historically, inflected prepositions can develop from the contraction of a preposition with a personal pronoun; however, they are commonly reanalysed as inflected words by native speakers and by traditional grammar. Language change over time can obscure the similarity between the conjugated preposition and the preposition-pronoun combination. For example, in Scottish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preposition And Postposition
Adpositions are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositions (which precede their complement) and postpositions (which follow their complement). An adposition typically combines with a noun phrase, this being called its complement, or sometimes object. English generally has prepositions rather than postpositions – words such as ''in, under'' and ''of'' precede their objects, such as "in England", "under the table", "of Jane" – although there are a few exceptions including ''ago'' and ''notwithstanding'', as in "three days ago" and "financial limitations notwithstanding". Some languages that use a different word order have postpositions instead (like Turkic languages) or have both types (like Finnish). The phrase formed by an adposition together with its complement is called an adpositional phrase (or prepositional phras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numeral (linguistics)
In linguistics, a numeral in the broadest sense is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity. Some theories of grammar use the word "numeral" to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner that specify the quantity of a noun, for example the "two" in "two hats". Some theories of grammar do not include determiners as a part of speech and consider "two" in this example to be an adjective. Some theories consider "numeral" to be a synonym for "number" and assign all numbers (including ordinal numbers like "first") to a part of speech called "numerals". Numerals in the broad sense can also be analyzed as a noun ("three is a small number"), as a pronoun ("the two went to town"), or for a small number of words as an adverb ("I rode the slide twice"). Numerals can express relationships like quantity (cardinal numbers), sequence (ordinal numbers), frequency (once, twice), and part (fraction). Identifying numerals Numerals may be attributive, as in ''two dogs'', or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |