|
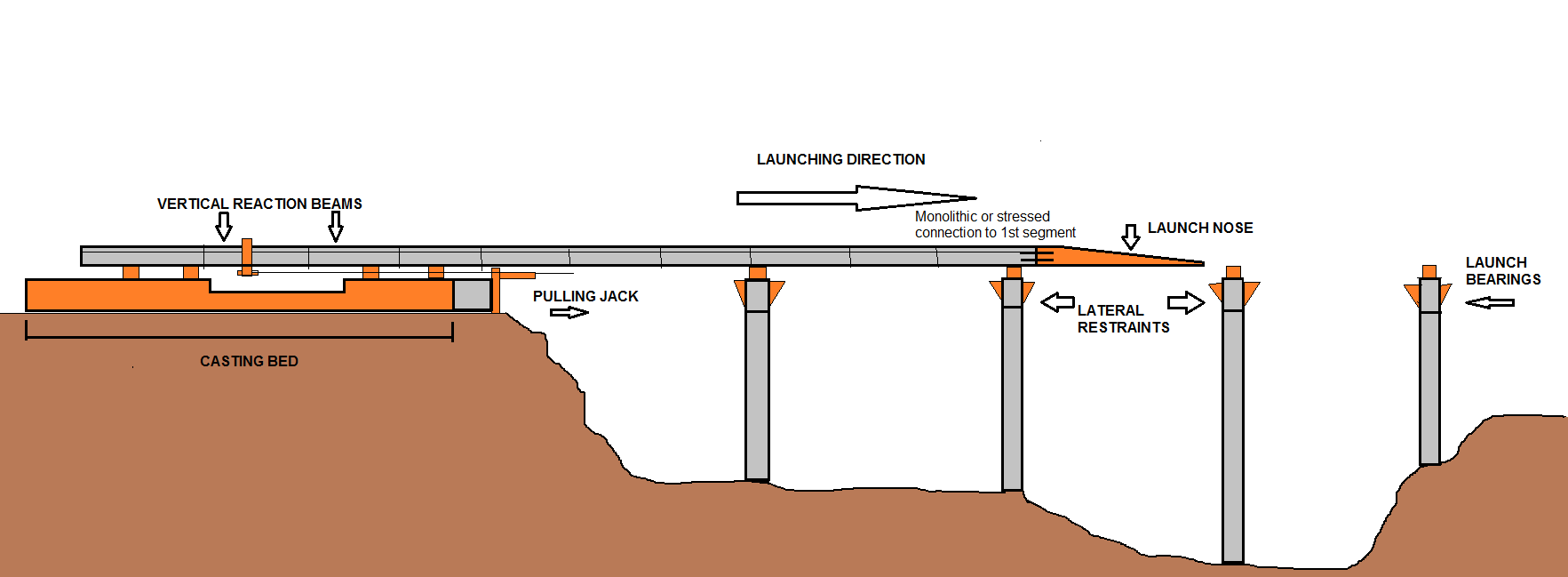
Incremental Launch
Incremental launch is a method in civil engineering of building a complete Deck (bridge), bridge deck from one abutment of the bridge only, manufacturing the Superstructure#Bridges, superstructure of the bridge by sections to the other side. In current applications, the method is highly mechanised and uses pre-stressed concrete. History The first bridge to have been incrementally launched appears to have been the Waldshut–Koblenz Rhine Bridge, a wrought iron lattice truss bridge, lattice truss railway bridge, completed in 1859. The second incrementally launched bridge was the Rhine Bridge, Kehl, Rhine Bridge, a railway bridge that spanned the Upper Rhine between Kehl, Germany and Strasbourg, France, completed in 1861 and subsequently destroyed and rebuilt on several occasions. The first incrementally launched concrete bridge was the Span (architecture), span box girder bridge over the Caroní River, completed in 1964. The second incrementally launched concrete bridge was ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incremental Bridge Launch Process
Increment or incremental may refer to: *Incrementalism, a theory (also used in politics as a synonym for gradualism) *Increment and decrement operators, the operators ++ and -- in computer programming *Incremental computing *Incremental backup, which contain only that portion that has changed since the preceding backup copy. *Increment, Glossary of chess#Increment, chess term for additional time a chess player receives on each move *Incremental games *Rounding#Rounding to a specified multiple, Increment in rounding See also * * *1+1 (other) *++ (other) {{Disambiguation da:Inkrementel fr:Incrémentation nl:Increment ja:インクリメント pl:Inkrementacja ru:Инкремент sr:Инкремент sv:++ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Span (architecture)
In engineering, span is the distance between two adjacent structural supports (e.g., two piers) of a structural member (e.g., a beam). Span is measured in the horizontal direction either between the faces of the supports (clear span) or between the centers of the bearing surfaces (effective span): A span can be closed by a solid beam or by a rope. The first kind is used for bridges, the second one for power lines, overhead telecommunication lines, some type of antennas or for aerial tramways. Span is a significant factor in finding the strength and size of a beam as it determines the maximum bending moment and deflection. The maximum bending moment M_ and deflection \delta_in the pictured beam is found using: :M_ = \frac :\delta_ = \frac = \frac where :q = Uniformly distributed load :L = Length of the beam between two supports (span) :E = Modulus of elasticity :I = Area moment of inertia The maximum bending moment and deflection occur midway between the two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantilever
A cantilever is a rigid structural element that extends horizontally and is unsupported at one end. Typically it extends from a flat vertical surface such as a wall, to which it must be firmly attached. Like other structural elements, a cantilever can be formed as a beam, plate, truss, or slab. When subjected to a structural load at its far, unsupported end, the cantilever carries the load to the support where it applies a shear stress and a bending moment. Cantilever construction allows overhanging structures without additional support. In bridges, towers, and buildings Cantilevers are widely found in construction, notably in cantilever bridges and balconies (see corbel). In cantilever bridges, the cantilevers are usually built as pairs, with each cantilever used to support one end of a central section. The Forth Bridge in Scotland is an example of a cantilever truss bridge. A cantilever in a traditionally timber framed building is called a jetty or forebay. In the sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Girder Bridge
A plate girder bridge is a bridge supported by two or more plate girders. Overview In a plate girder bridge, the plate girders are typically I-beams made up from separate structural steel plates (rather than rolled as a single cross-section), which are welded or, in older bridges, bolted or riveted together to form the vertical web and horizontal flanges of the beam. In some cases, the plate girders may be formed in a Z-shape rather than I-shape. The first tubular wrought iron plate girder bridge was built in 1846-47 by James Millholland for the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. Plate girder bridges are suitable for short to medium spans and may support railroads, highways, or other traffic. Plate girders are usually prefabricated and the length limit is frequently set by the mode of transportation used to move the girder from the bridge shop to the bridge site. Generally, the depth of the girder is no less than the span, and for a given load bearing capacity, a depth of arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stiffening
Stiffening is any process that increases the rigidity and structural integrity of objects. Stiffening is used in crafts, art, industry, architecture, sports, aerospace, object construction, bookbinding, etc. Mechanics In mechanics, "stiffening" beams brings anti-buckling, anti-wrinkling, desired shaping, reinforcement, repair, strength, enhanced function, extended utility, longer beam life, safety, etc. Stiffening of fluid or rigid beams is used in medical arts, aerospace, aviation, sports, bookbinding, art, architecture, natural plants and trees, construction industry, bridge building, and more. Mechanical methods for stiffening include tension stiffening, centrifugal stiffening, bracing, superstructure bracing, substructure bracing, straightening, strain stiffening, stress stiffening, damping vibrations, swelling, pressure increasing, drying, cooling, interior reinforcing, exterior reinforcing, wrapping, surface treating, or combinations of these and other methods. Beams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant Curvature
In mathematics, constant curvature is a concept from differential geometry. Here, curvature refers to the sectional curvature of a space (more precisely a manifold) and is a single number determining its local geometry. The sectional curvature is said to be constant if it has the same value at every point and for every two-dimensional tangent plane at that point. For example, a sphere is a surface of constant positive curvature. Classification The Riemannian manifolds of constant curvature can be classified into the following three cases: * Elliptic geometry – constant positive sectional curvature * Euclidean geometry – constant vanishing sectional curvature * Hyperbolic geometry – constant negative sectional curvature. Properties * Every space of constant curvature is locally symmetric, i.e. its curvature tensor is parallel \nabla \mathrm=0. * Every space of constant curvature is locally maximally symmetric, i.e. it has \frac n (n+1) number of local isometries, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Box Girder
A box girder or tubular girder (or box beam) is a girder that forms an enclosed tube with multiple walls, as opposed to an i-beam, - or H-beam. Originally constructed of wrought iron joined by riveting, they are now made of rolled steel, rolled or welded steel, aluminium extrusions or prestressed concrete. Compared to an i-beam, -beam, the advantage of a box girder is that it better resists Torsion (mechanics), torsion. Having multiple vertical Web (other)#Engineering, webs, it can also carry more load than an of equal height (although it will use more material than a taller -beam of equivalent capacity). The distinction in naming between a box girder and a tubular girder is imprecise. Generally the term ''box'' girder is used, especially if it is rectangular in section. Where the girder carries its "content" ''inside'' the "box", such as the Britannia Bridge, it is termed a ''tubular'' girder. ''Tubular'' girder is also used if the girder is round or oval in cross-sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segmental Bridge
A segmental bridge is a bridge built in short sections (called segments), i.e., one piece at a time, as opposed to traditional methods that build a bridge in very large sections. The bridge is made of concrete that is either cast-in-place (constructed fully in its final location) or precast concrete (built at another location and then transported to their final location for placement in the full structure). These bridges are very economical for long spans (more than ), especially when access to the construction site is restricted. They are also chosen for their aesthetic appeal. History The first cantilevered segmental cast-in-place concrete bridge, built in 1930, was across Rio do Peixe in the state of Santa Catarina of Brazil. It was followed in 1951 by the prestressed concrete bridge across the Lahn River in , the first of many cantilevered bridges designed by . The first prestressed concrete bridge, assembled by several precast elements, was the across the river Marne i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fritz Leonhardt
Fritz Leonhardt (12 July 1909 – 30 December 1999) was a German structural engineer who made major contributions to 20th-century bridge engineering, especially in the development of cable-stayed bridges. His book ''Bridges: Aesthetics and Design'' is well known throughout the bridge engineering community. Biography Born in Stuttgart in 1909, Leonhardt studied at Stuttgart University and Purdue University. In 1934 he joined the German Highway Administration, working with Paul Bonatz amongst others. He was appointed at the remarkably young age of 28 as the Chief Engineer for the Cologne Rodenkirchen Bridge, Cologne-Rodenkirchen Bridge. In 1954 he formed the consulting firm Leonhardt und Andrä, and from 1958 to 1974 taught the design of reinforced concrete and prestressed concrete at Stuttgart University. He was President of the University from 1967 to 1969. He received Honorary Doctorates from six universities, honorary membership of several important engineering universities, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Engineer
Structural engineers analyze, design, plan, and research List of structural elements, structural components and structural systems to achieve design goals and ensure the safety and comfort of users or occupants. Their work takes account mainly of safety, technical, economic, and environmental concerns, but they may also consider aesthetic and social factors. Structural engineering is usually considered a specialty discipline within civil engineering, but it can also be studied in its own right. In the United States, most practicing structural engineers are currently licensed as civil engineers, but the situation varies from state to state. Some states have a separate license for structural engineers who are required to design special or high-risk structures such as schools, hospitals, or skyscrapers. In the United Kingdom, most structural engineers in the building industry are members of the Institution of Structural Engineers or the Institution of Civil Engineers. Typical struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city and state. Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has Austrians, a population of around 9 million. The area of today's Austria has been inhabited since at least the Paleolithic, Paleolithic period. Around 400 BC, it was inhabited by the Celts and then annexed by the Roman Empire, Romans in the late 1st century BC. Christianization in the region began in the 4th and 5th centuries, during the late Western Roman Empire, Roman period, followed by the arrival of numerous Germanic tribes during the Migration Period. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kufstein
Kufstein (; ) is a town in the Austrian state of Tyrol, the administrative seat of Kufstein District. With a population of about 20,000 it is the second largest Tyrolean town after the state capital Innsbruck. The greatest landmark is Kufstein Fortress, first mentioned in the 13th century. The town was the place of origin of the Austrian noble family Kuefstein. Geography It is located in the Tyrolean Unterland region on the river Inn, at the confluence with its Weißache and Kaiserbach tributaries, near the border with Bavaria, Germany. The municipal area stretches along the Lower Inn Valley between the Brandenberg Alps in the northwest and the Kaiser Mountains in the southeast. The remote Kaisertal until recently was the last settled valley in Austria without transport connections, prior to the completion of a tunnel road from Kufstein to neighbouring Ebbs in 2008. North of the town, the Inn river leaves the Northern Limestone Alps and enters the Bavarian Alpine Forelan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |