Incremental launch on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
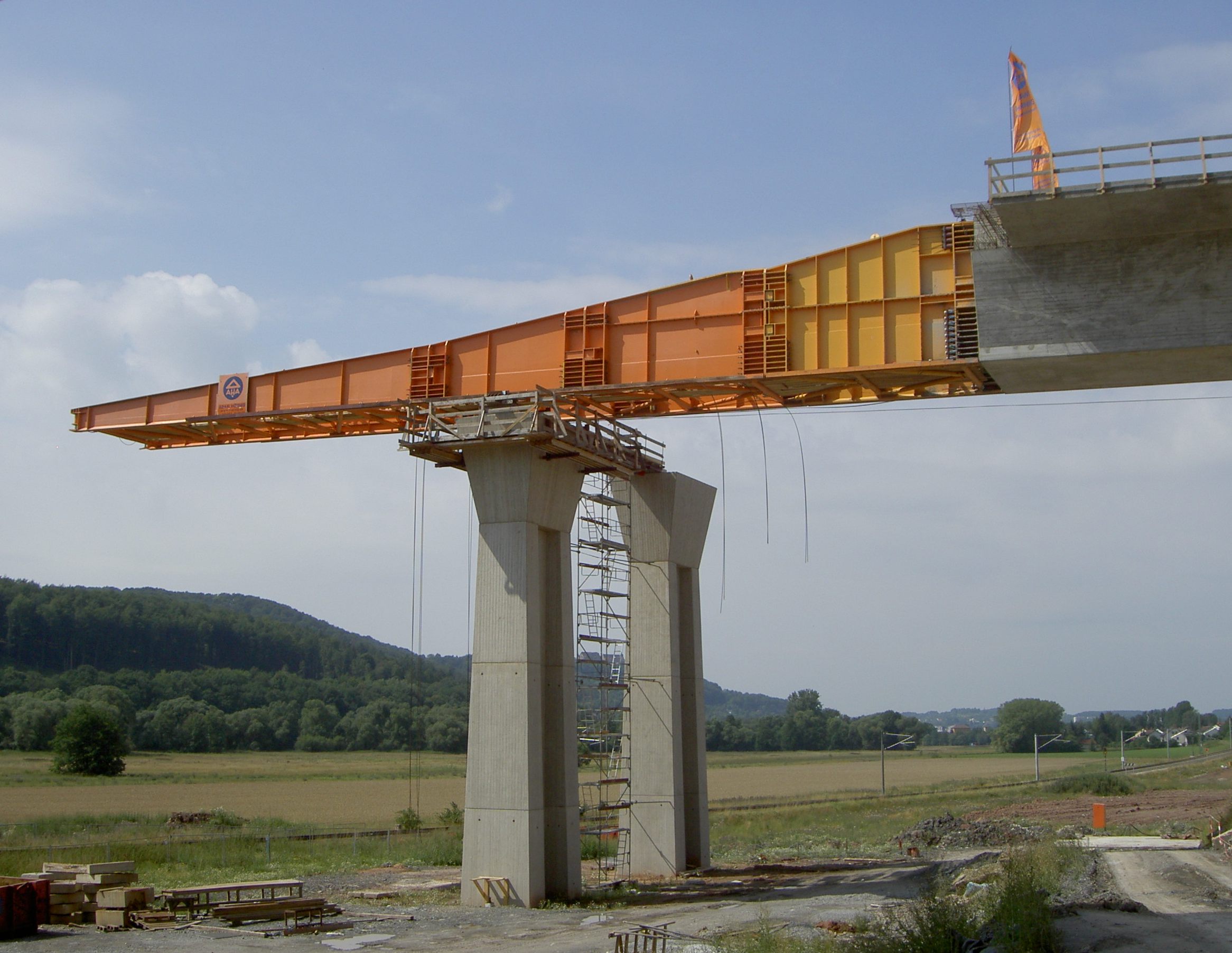
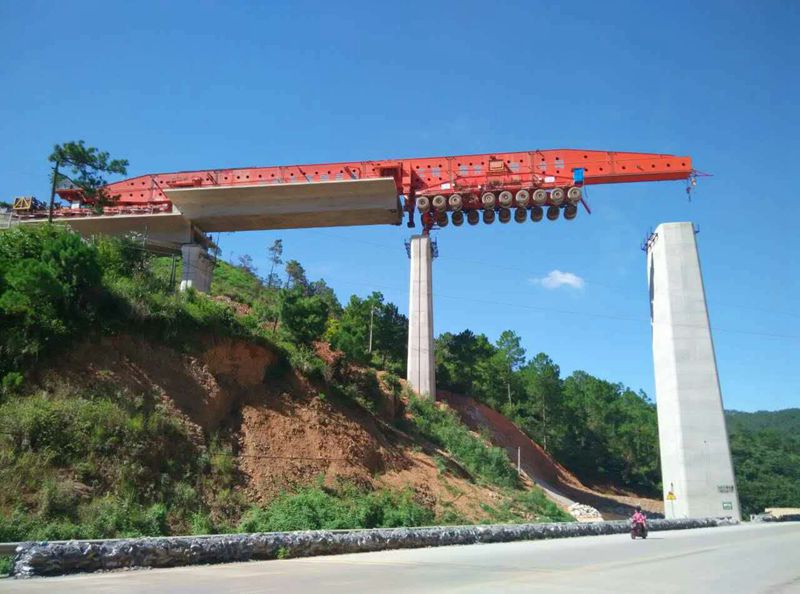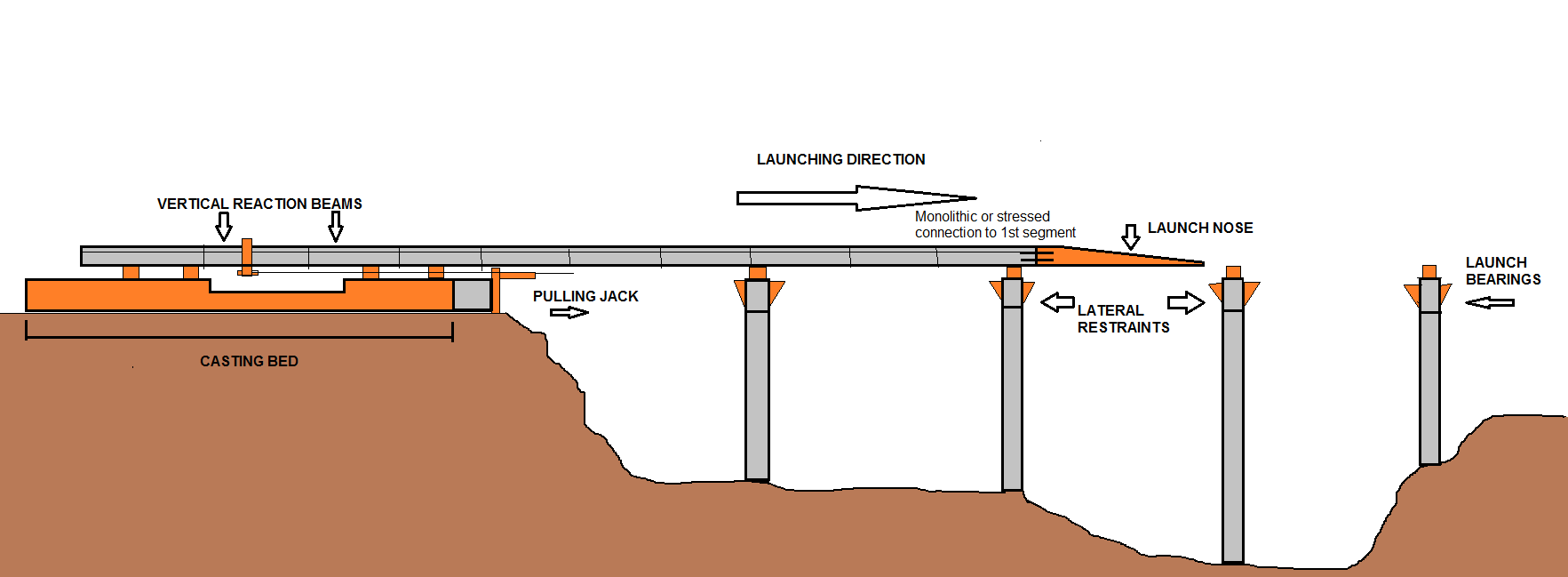

 Incremental launch is a method in
Incremental launch is a method in


civil engineering
Civil engineering is a regulation and licensure in engineering, professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads ...
of building a complete bridge deck
A deck is the surface of a bridge. A structural element of its superstructure
A superstructure is an upward extension of an existing structure above a baseline. This term is applied to various kinds of physical structures such as buildin ...
from one abutment
An abutment is the substructure at the ends of a bridge span or dam supporting its superstructure. Single-span bridges have abutments at each end that provide vertical and lateral support for the span, as well as acting as retaining walls ...
of the bridge only, manufacturing the superstructure
A superstructure is an upward extension of an existing structure above a baseline. This term is applied to various kinds of physical structures such as buildings, bridges, or ships.
Aboard ships and large boats
On water craft, the superstruct ...
of the bridge by sections to the other side. In current applications, the method is highly mechanised and uses pre-stressed concrete
Prestressed concrete is a form of concrete used in construction. It is substantially prestressed ( compressed) during production, in a manner that strengthens it against tensile forces which will exist when in service. Post-tensioned concreted is ...
.
History
The first bridge to have been incrementally launched appears to have been theWaldshut–Koblenz Rhine Bridge
The Waldshut–Koblenz Rhine Bridge is a single-track railway bridge on the Turgi–Koblenz–Waldshut railway, between Waldshut and Koblenz AG, crossing the Rhine and the border between Germany and Switzerland. It was the first railway bridge ...
, a wrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.05%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4.5%), or 0.25 for low carbon "mild" steel. Wrought iron is manufactured by heating and melting high carbon cast iron in an ...
lattice truss
A lattice truss bridge is a form of truss bridge that uses many small, closely spaced diagonal elements forming a lattice. The design was patented in 1820 by architect Ithiel Town.
Originally a means of erecting a substantial bridge from mere p ...
railway bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually somet ...
, completed in 1859. The second incrementally launched bridge was the Rhine Bridge, a railway bridge that spanned the Upper Rhine
Upper Rhine ( ; ; kilometres 167 to 529 of the Rhine) is the section of the Rhine between the Middle Bridge, Basel, Middle Bridge in Basel, Switzerland, and the Rhine knee in Bingen am Rhein, Bingen, Germany. It is surrounded by the Upper Rhine P ...
between Kehl
Kehl (; ) is a city with around 38,000 inhabitants in the southwestern Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg. It lies in the region of Baden on the Rhine River, at the confluence with the smaller Kinzig (Rhine), Kinzig River, directly oppo ...
, Germany and Strasbourg
Strasbourg ( , ; ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est Regions of France, region of Geography of France, eastern France, in the historic region of Alsace. It is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin Departmen ...
, France, completed in 1861 and subsequently destroyed and rebuilt on several occasions.
The first incrementally launched concrete bridge
Concrete bridges are a type of bridge, constructed out of concrete. They started to appear widely in the early 20th century.
History
file:First concrete bridge in Britain.jpg, Homersfield Bridge, England, cast iron reinforced, constructed 1869 ...
was the span box girder bridge
A box girder bridge, or box section bridge, is a bridge in which the main beam (structure), beams comprise girders in the shape of a hollow box. The box girder normally comprises prestressed concrete, structural steel, or a composite ma ...
over the Caroní River
The Caroní River is the second most important river of Venezuela, the second in flow, and one of the longest, from the Kukenan tepui through to its confluence with the Orinoco River. The name "Caroní" is applied starting from the confluenc ...
, completed in 1964. The second incrementally launched concrete bridge was over the Inn River
The Inn (; ; ) is a river in Switzerland, Austria and Germany. The long river is a right tributary of the Danube, being the third largest tributary of the Danube by discharge. The highest point of its drainage basin is the summit of Piz Berni ...
, Kufstein
Kufstein (; ) is a town in the Austrian state of Tyrol, the administrative seat of Kufstein District. With a population of about 20,000 it is the second largest Tyrolean town after the state capital Innsbruck. The greatest landmark is Kufstein For ...
in Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
, completed in 1965. The structural engineer
Structural engineers analyze, design, plan, and research List of structural elements, structural components and structural systems to achieve design goals and ensure the safety and comfort of users or occupants. Their work takes account mainly of ...
s for both bridges were Professor Dr Fritz Leonhardt
Fritz Leonhardt (12 July 1909 – 30 December 1999) was a German structural engineer who made major contributions to 20th-century bridge engineering, especially in the development of cable-stayed bridges. His book ''Bridges: Aesthetics and Design' ...
and his partner, Willi Baur.
The usual method of building concrete bridges is the segmental method, one span at a time.
Method
The bridges are mostly of thebox girder
A box girder or tubular girder (or box beam) is a girder that forms an enclosed tube with multiple walls, as opposed to an i-beam, - or H-beam. Originally constructed of wrought iron joined by riveting, they are now made of rolled steel, rolled ...
design and work with straight or constant curve shapes, with a constant radius. box girder sections of the bridge deck are fabricated at one end of the bridge in factory conditions. Each section is manufactured in around one week.
The first section of the launch, the launching nose, is not made of concrete, but is a stiffened steel plate girder
A plate girder bridge is a bridge supported by two or more plate girders.
Overview
In a plate girder bridge, the plate girders are typically I-beams made up from separate structural steel plates (rather than rolled as a single cross-section), w ...
and is around 60% of the length of a bridge span, and reduces the cantilever
A cantilever is a rigid structural element that extends horizontally and is unsupported at one end. Typically it extends from a flat vertical surface such as a wall, to which it must be firmly attached. Like other structural elements, a cantilev ...
moment. The sections of bridge deck slide over sliding bearings, which are concrete blocks covered with stainless steel
Stainless steel, also known as inox, corrosion-resistant steel (CRES), or rustless steel, is an iron-based alloy that contains chromium, making it resistant to rust and corrosion. Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion comes from its chromi ...
and reinforced elastomeric pads.
Notable examples
*Katima Mulilo Bridge
The Katima Mulilo Bridge (also known as ''Bridge 508'' in the Namibian Bridge Register) carries the TransCaprivi Highway over the Zambezi River between Katima Mulilo, Namibia and Sesheke, Zambia. It is a road bridge, completed in 2004, 900 metres ...
, 2004
* Redcliffe Bridge, 1986
* Woronora River Bridge, 2001, the largest incrementally-launched bridge when built
* Millau Viaduct
The Millau Viaduct (, ) is a multispan cable-stayed bridge completed in 2004 across the Canyon, gorge valley of the Tarn (river), Tarn near (west of) Millau in the Aveyron department in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Region, i ...
, 2004, an example of launching a curved road deck
References
External links
* {{YouTube, S3Kf9e6JgF4, Bridge construction - Incremental Launching - 3D Animation Bridges by structural type Civil engineering Hydraulics