|
Incremental Cost
In economics, the marginal cost is the change in the total cost that arises when the quantity produced is increased, i.e. the cost of producing additional quantity. In some contexts, it refers to an increment of one unit of output, and in others it refers to the rate of change of total cost as output is increased by an infinitesimal amount. As Figure 1 shows, the marginal cost is measured in dollars per unit, whereas total cost is in dollars, and the marginal cost is the slope of the total cost, the rate at which it increases with output. Marginal cost is different from average cost, which is the total cost divided by the number of units produced. At each level of production and time period being considered, marginal cost includes all costs that vary with the level of production, whereas costs that do not vary with production are fixed. For example, the marginal cost of producing an automobile will include the costs of labor and parts needed for the additional automobile but not t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economy, economies, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and Expenditure, investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: Labour (human activity), labour, Capital (economics), capital, Land (economics), land, and Entrepreneurship, enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact gloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of financial panics (particularly the panic of 1907) led to the desire for central control of the monetary system in order to alleviate financial crises. Although an instrument of the U.S. government, the Federal Reserve System considers itself "an independent central bank because its monetary policy decisions do not have to be approved by the president or by anyone else in the executive or legislative branches of government, it does not receive funding appropriated by Congress, and the terms of the members of the board of governors span multiple presidential and congressional terms." Over the years, events such as the Great Depression in the 1930s and the Great Recession during the 2000s have led to the expansion of the roles and responsibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
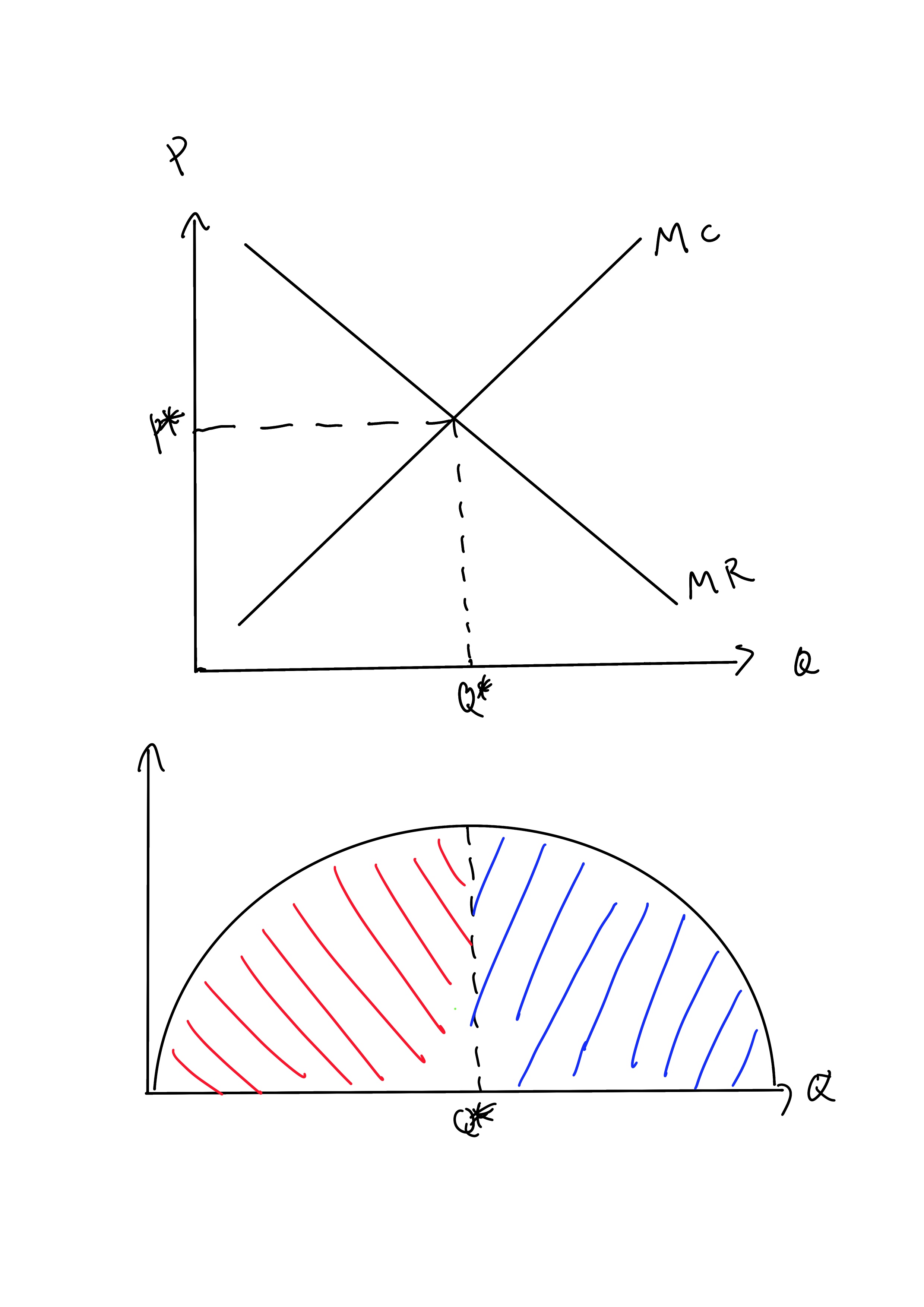
Negative Externality
In economics, an externality is an indirect cost (external cost) or indirect benefit (external benefit) to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party's (or parties') activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced components that are involved in either consumer or producer consumption. Air pollution from motor vehicles is one example. The cost of air pollution to society is not paid by either the producers or users of motorized transport. Water pollution from mills and factories are another example. All (water) consumers are made worse off by pollution but are not compensated by the market for this damage. The concept of externality was first developed by Alfred Marshall in the 1890s and achieved broader attention in the works of economist Arthur Pigou in the 1920s. The prototypical example of a negative externality is environmental pollution. Pigou argued that a tax, equal to the marginal damage or marginal external cost, (later called a "Pigou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the components of pollution, can be either foreign substances/energies or naturally occurring contaminants. Although environmental pollution can be caused by natural events, the word pollution generally implies that the contaminants Human impact on the environment, have a human source, such as manufacturing, Extractivism, extractive industries, poor waste management, transportation or Agricultural pollution, agriculture. Pollution is often classed as point source pollution, point source (coming from a highly concentrated specific site, such as a factory, Environmental effects of mining, mine, construction site), or nonpoint source pollution (coming from a widespread distributed sources, such as microplastics or agricultural runoff). Many sources of po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Financial Transaction
A financial transaction is an Contract, agreement, or communication, between a buyer and seller to exchange goods, Service (economics), services, or assets for payment. Any transaction involves a change in the status of the finances of two or more businesses or individuals. A financial transaction always involves one or more financial asset, most commonly money or another valuable item such as gold or silver. There are many types of financial transactions. The most common type, purchases, occur when a good, service, or other commodity is sold to a consumer in exchange for money. Most purchases are made with cash payments, including Cash, physical currency, debit cards, or cheques. The other main form of payment is credit, which gives immediate access to funds in exchange for repayment at a later date. History There is no evidence to support the theory that ancient civilizations worked on systems of barter. Instead, most historians believe that ancient cultures worked on princi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Externalities
In economics, an externality is an indirect cost (external cost) or indirect benefit (external benefit) to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party's (or parties') activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced components that are involved in either consumer or producer consumption. Air pollution from motor vehicles is one example. The cost of air pollution to society is not paid by either the producers or users of motorized transport. Water pollution from mills and factories are another example. All (water) consumers are made worse off by pollution but are not compensated by the market for this damage. The concept of externality was first developed by Alfred Marshall in the 1890s and achieved broader attention in the works of economist Arthur Pigou in the 1920s. The prototypical example of a negative externality is environmental pollution. Pigou argued that a tax, equal to the marginal damage or marginal external cost, (later called a "Pigou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Profit Maximization
In economics, profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm may determine the price, input and output levels that will lead to the highest possible total profit (or just profit in short). In neoclassical economics, which is currently the mainstream approach to microeconomics, the firm is assumed to be a " rational agent" (whether operating in a perfectly competitive market or otherwise) which wants to maximize its total profit, which is the difference between its total revenue and its total cost. Measuring the total cost and total revenue is often impractical, as the firms do not have the necessary reliable information to determine costs at all levels of production. Instead, they take more practical approach by examining how small changes in production influence revenues and costs. When a firm produces an extra unit of product, the additional revenue gained from selling it is called the marginal revenue (\text), and the additional cost to produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Perfect Competition
In economics, specifically general equilibrium theory, a perfect market, also known as an atomistic market, is defined by several idealizing conditions, collectively called perfect competition, or atomistic competition. In Economic model, theoretical models where conditions of perfect competition hold, it has been demonstrated that a Market (economics), market will reach an Economic equilibrium, equilibrium in which the quantity supplied for every Goods and services, product or service, including Workforce, labor, equals the quantity demanded at the current price. This equilibrium would be a Pareto optimum. Perfect competition provides both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency: * Such markets are ''allocatively efficient'', as output will always occur where marginal cost is equal to average revenue i.e. price (MC = AR). In perfect competition, any Profit maximization, profit-maximizing producer faces a market price equal to its marginal cost (P = MC). This implies that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
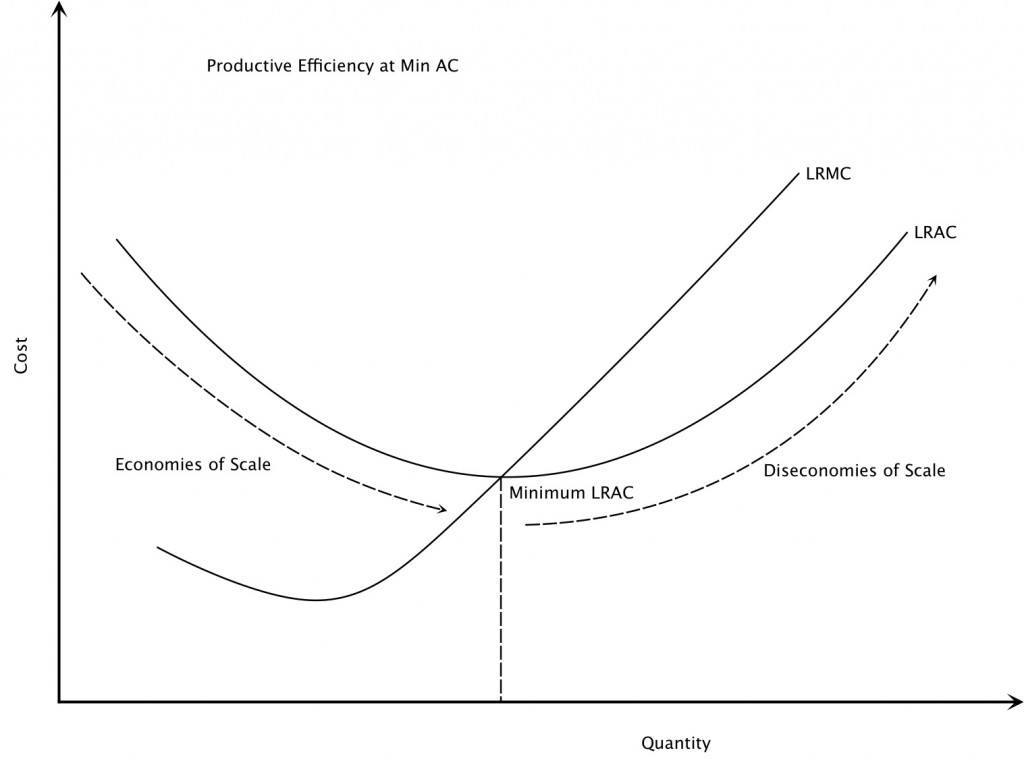
Diseconomies Of Scale
In microeconomics, diseconomies of scale are the cost disadvantages that economic actors accrue due to an increase in organizational size or in output, resulting in production of Product (business), goods and Service (economics), services at increased average cost, per-unit costs. The concept of diseconomies of scale is the opposite of economies of scale. It occurs when economies of scale become dysfunctional for a firm. In business, diseconomies of scale are the features that lead to an increase in average costs as a business grows beyond a certain size. Causes Communication costs Ideally, all employees of a firm would have one-on-one communication with each other so they know exactly what the other workers are doing. A firm with a single worker does not require any communication between employees. A firm with two workers requires one communication channel, directly between those two workers. A firm with three workers requires three communication channels between employees (betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Economies Of Scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of Productivity, output produced per unit of cost (production cost). A decrease in unit cost, cost per unit of output enables an increase in scale that is, increased production with lowered cost. At the basis of economies of scale, there may be technical, statistical, organizational or related factors to the degree of Market (economics), market control. Economies of scale arise in a variety of organizational and business situations and at various levels, such as a production, plant or an entire enterprise. When average costs start falling as output increases, then economies of scale occur. Some economies of scale, such as capital cost of manufacturing facilities and friction loss of transportation and industrial equipment, have a physical or engineering basis. The economic concept dates back to Adam Smith and the idea o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |