|
IPad Mini (1st Generation)
The iPad Mini (stylized as iPad mini), known retrospectively as the iPad Mini 1, is the first generation of the mini tablet computer developed and marketed by Apple Inc. It was announced on October 23, 2012, as the fourth major product in the iPad line and the first of the iPad Mini line. It features a reduced screen size of , compared to the display on standard iPads at that time. The first generation iPad Mini received positive reviews, with reviewers praising the device's size, design, and availability of applications. However, reviewers criticized its use of a proprietary power connector, its lack of expandable storage, its under-powered Apple A5 chip with 512 MB RAM, and the lack of a Retina display. The first generation iPad Mini was succeeded by the iPad Mini 2. History On October 16, 2012, Apple announced a media event scheduled for October 23 at the California Theatre in San Jose, California. The company did not predisclose the subject of the event, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
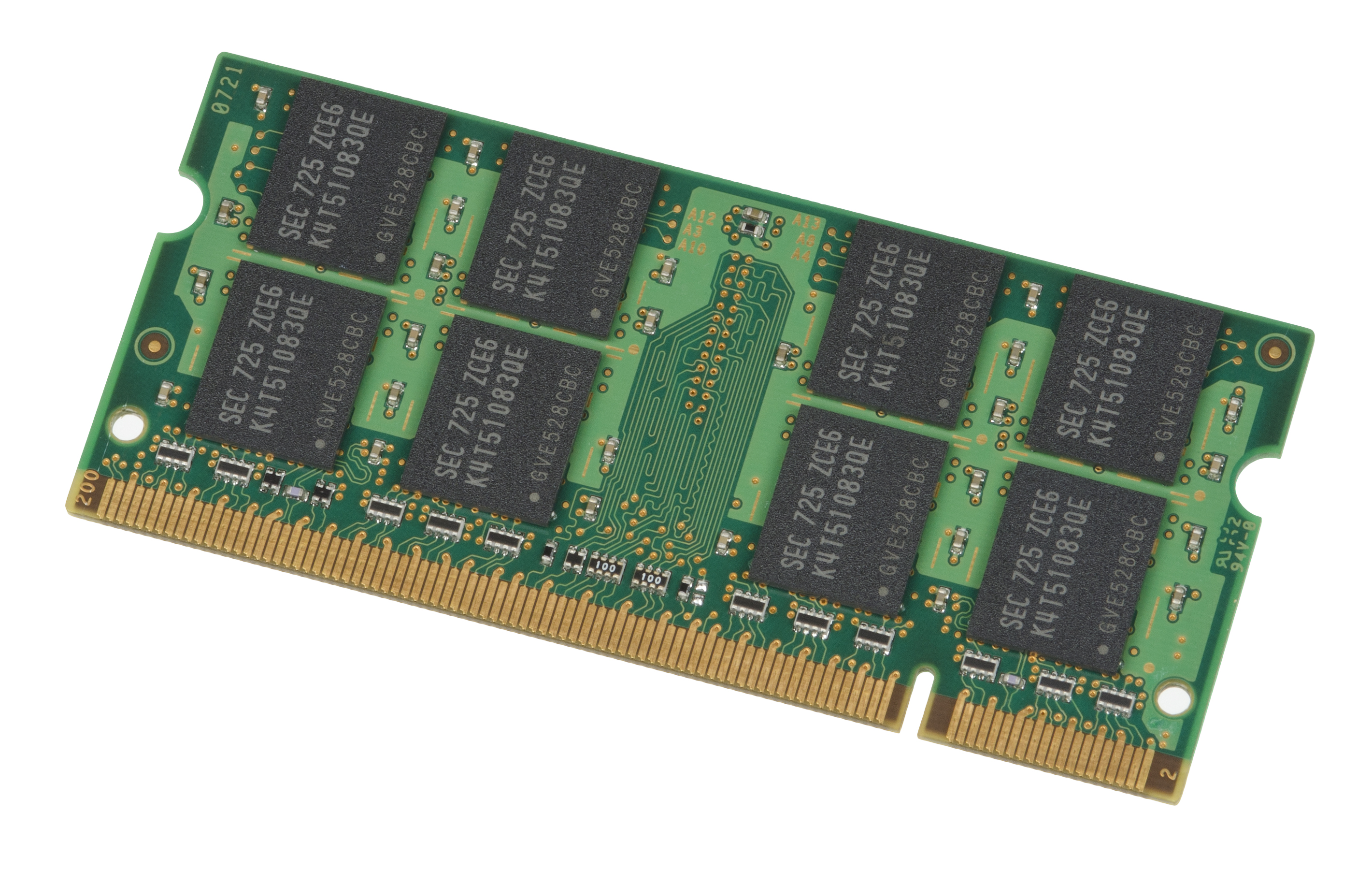
DDR2 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR2 SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It is a JEDEC standard (JESD79-2); first published in September 2003. DDR2 succeeded the original DDR SDRAM specification, and was itself succeeded by DDR3 SDRAM in 2007. DDR2 DIMMs are neither forward compatible with DDR3 nor backward compatible with DDR. In addition to double pumping the data bus as in DDR SDRAM (transferring data on the rising and falling edges of the bus clock signal), DDR2 allows higher bus speed and requires lower power by running the internal clock at half the speed of the data bus. The two factors combine to produce a total of four data transfers per internal clock cycle. Since the DDR2 internal clock runs at half the DDR external clock rate, DDR2 memory operating at the same external data bus clock rate as DDR results in DDR2 being able to provide the same bandwidth but with better la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining Orientation (geometry), orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rotation (spin axis) is free to assume any orientation by itself. When rotating, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotation of the mounting, due to the angular momentum#Conservation of angular momentum, conservation of angular momentum. Gyroscopes based on other operating principles also exist, such as the microchip-packaged Vibrating structure gyroscope#MEMS gyroscopes, MEMS gyroscopes found in electronic devices (sometimes called gyrometers), solid-state ring laser gyroscope, ring lasers, fibre optic gyroscopes, and the extremely sensitive quantum gyroscope. Applications of gyroscopes include inertial navigation systems, such as in the Hubble Space Telescope, or inside the steel hull of a submer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a device that measures the proper acceleration of an object. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change (mathematics), rate of change of velocity) of the object relative to an observer who is in free fall (that is, relative to an inertial frame of reference). Proper acceleration is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration with respect to a given coordinate system, which may or may not be accelerating. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an Gravitational acceleration, acceleration due to Earth's gravity straight upwards of about Standard gravity, ''g'' ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, an accelerometer that is in free fall will measure zero acceleration. Accelerometers have many uses in industry, consumer products, and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-key Lighting
Low-key lighting is a style of lighting for photography, film or television. It is a necessary element in creating a chiaroscuro effect. Traditional photographic lighting ( three-point lighting) uses a key light, a fill light and a back light for illumination. Low-key lighting often uses only a key light, optionally controlled with a fill light or a simple reflector. Low key light accentuates the contours of the subject by throwing areas into shade while a fill light or reflector may illuminate the shadow areas to control contrast. The relative strength of key-to-fill, known as the lighting ratio, can be measured using a light meter. Low key lighting has a higher lighting ratio, e.g., 8:1, than high-key lighting, which can approach 1:1. Examples in film The term "low key" is also used in cinematography and photography to refer to any scene with a high lighting ratio, especially if there is a predominance of shadowy areas. It tends to heighten the sense of alienation felt b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proximity Sensor
A proximity sensor (often simply prox) is a sensor able to detect the presence of nearby objects without any physical contact. A proximity sensor often emits an Electromagnetic field, electromagnetic field or a beam of electromagnetic radiation (infrared, for instance), and looks for changes in the electric field, field or return signal. The object being sensed is often referred to as the proximity sensor's target. Different proximity sensor targets demand different sensors. For example, a capacitive proximity sensor or photoelectric sensor might be suitable for a plastic target; an inductive sensor, inductive proximity sensor always requires a metal target. Proximity sensors can have a high reliability and long functional life because of the absence of mechanical parts and lack of physical contact between the sensor and the sensed object. Proximity sensors are also used in machine vibration monitoring to measure the variation in distance between a shaft and its support beari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audio
Audio most commonly refers to sound, as it is transmitted in signal form. It may also refer to: Sound *Audio signal, an electrical representation of sound *Audio frequency, a frequency in the audio spectrum *Digital audio, representation of sound in a form processed and/or stored by computers or digital electronics *Audio, audible content (media) in audio production and publishing * Semantic audio, extraction of symbols or meaning from audio * Stereophonic audio, method of sound reproduction that creates an illusion of multi-directional audible perspective * Audio equipment Entertainment * AUDIO (group), an American R&B band of 5 brothers formerly known as TNT Boyz and as B5 * ''Audio'' (album), an album by the Blue Man Group * ''Audio'' (magazine), a magazine published from 1947 to 2000 *Audio (musician), British drum and bass artist * "Audio" (song), a song by LSD *"Audios", a song by Black Eyed Peas from ''Elevation'' Computing *HTML audio, identified by the tag See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Touchscreen
A touchscreen (or touch screen) is a type of electronic visual display, display that can detect touch input from a user. It consists of both an input device (a touch panel) and an output device (a visual display). The touch panel is typically layered on the top of the electronic visual display of a device. Touchscreens are commonly found in smartphones, tablet computer, tablets, laptops, and other electronic devices. The display is often an Liquid-crystal display, LCD, AMOLED or OLED display. A user can give input or control the information processing system through simple or multi-touch gestures by touching the screen with a special Stylus (computing), stylus or one or more fingers. Some touchscreens use ordinary or specially coated gloves to work, while others may only work using a special stylus or pen. The user can use the touchscreen to react to what is displayed and, if the software allows, to control how it is displayed; for example, Zooming user interface, zooming to inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
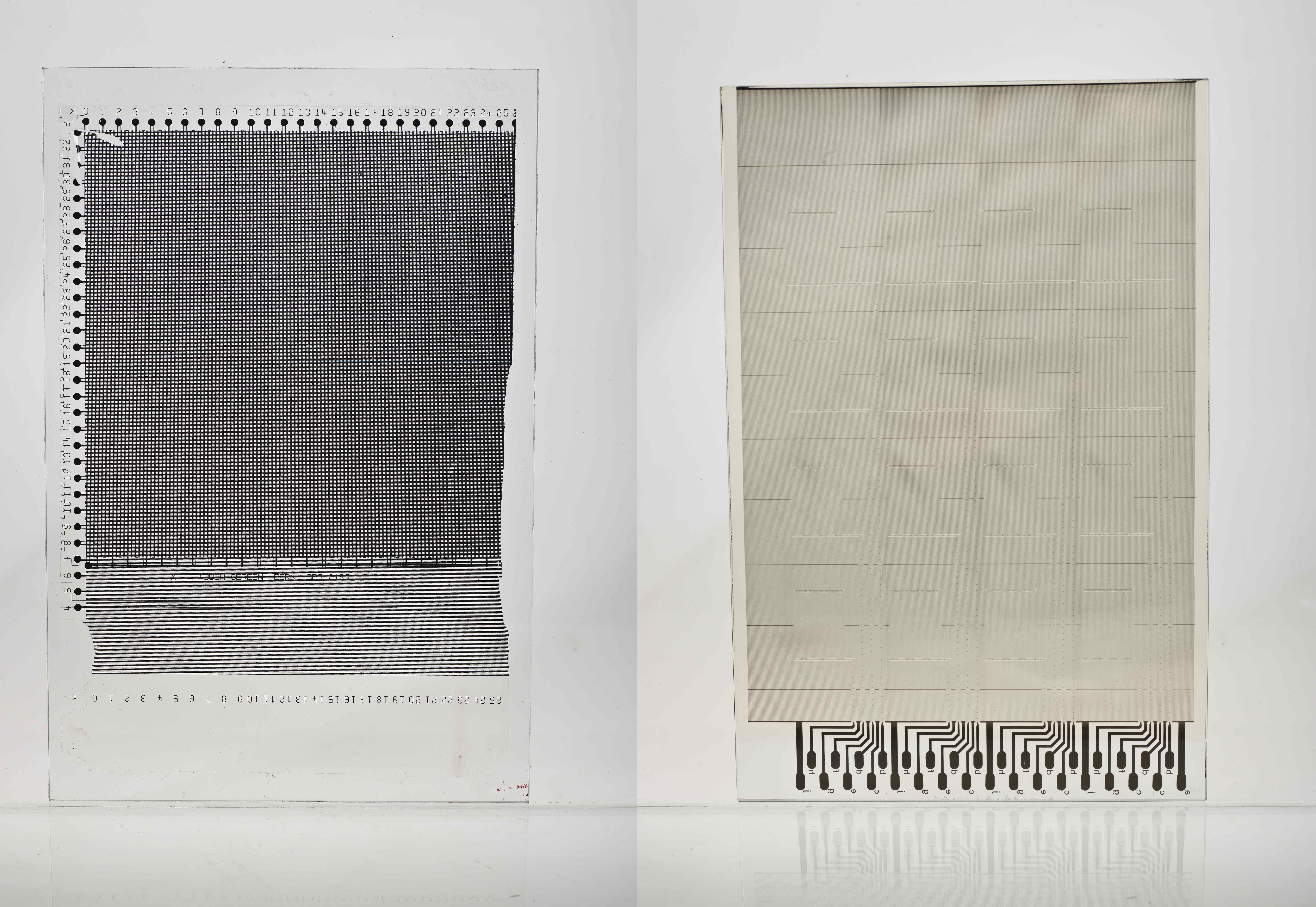
Multi-touch
In computing, multi-touch is technology that enables a surface (a touchpad or touchscreen) to recognize the presence of more than one somatosensory system, point of contact with the surface at the same time. The origins of multitouch began at CERN, MIT, University of Toronto, Carnegie Mellon University and Bell Labs in the 1970s. CERN started using multi-touch screens as early as 1976 for the controls of the Super Proton Synchrotron. Capacitive multi-touch displays were popularized by Apple Inc., Apple's iPhone in 2007. Multi-touch may be used to implement additional functionality, such as pinch to zoom or to activate certain subroutines attached to predefined gestures using gesture recognition. Several uses of the term multi-touch resulted from the quick developments in this field, and many companies using the term to market older technology which is called ''gesture-enhanced single-touch'' or several other terms by other companies and researchers. Several other similar or relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel Consumer Electronics
Places where PowerVR technology and its various iterations have been used: Series1 (NEC) Series2 (NEC) Series3 (STMicro) VGX PowerVR VGX150 Series4 (MBX and MBX Lite) Freescale i.MX31 — ''MBX Lite + FPU (VFP11) + ARM1136'' * DAVE Embedded Systems Qong (SOM) * ELSA PAL Mini Book e-A533-L * Garz & Fricke Adelaide * TQ Components TQMa31 * iCEphone * LORE Embedded TS1 Freescale i.MX31C — ''MBX Lite + FPU (VFP11) + ARM1136'' * Cogent CSB733 (SOM) * DAVE Embedded Systems Qong (SOM) Freescale MPC5121e — ''MBX Lite + VGP Lite + PowerPC e300'' * CherryPal C114 * DAVE Embedded Systems Aria (SOM) * LimePC range (UMPC, HandheldPC, PalmPC, LimePC HDTV set) * PhaedruS SystemS CSB781 * GDA Technologies Bali Reference Board Intel CE 2110 (Olo River) — ''MBX Lite + XScale CPU'' * ASUS set-top boxes * Chunghwa Telecom Multimedia on Demand set-top boxes * Digeo Moxi Multi-Room HD Digital Media Recorder * Digeo Moxi Mate * Digital Video Networks set-top boxes * OKI Next Generatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerVR
PowerVR is a division of Imagination Technologies (formerly VideoLogic) that develops hardware and software for 2D and 3D rendering, and for video encoding, video decoding, decoding, associated image processing and DirectX, OpenGL ES, OpenVG, and OpenCL acceleration. PowerVR also develops AI accelerators called Neural Network Accelerator (NNA). The PowerVR product line was originally introduced to compete in the desktop PC market for Graphics card, 3D hardware accelerators with a product with a better price–performance ratio than existing products like those from 3dfx Interactive. Rapid changes in that market, notably with the introduction of OpenGL and Direct3D, led to rapid consolidation. PowerVR introduced new versions with low-power electronics that were aimed at the laptop computer market. Over time, this developed into a series of designs that could be incorporated into system-on-a-chip architectures suitable for handheld device use. PowerVR accelerators are not manufactur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspect Ratio (image)
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of its width to its height. It is expressed as two numbers separated by a colon, in the format width:height. Common aspect ratios are 1.85:1 and 2.39:1 in cinematography, 4:3 and 16:9 in television, and 3:2 in still photography and 1:1: Used for square images, often seen on social media platforms like Instagram, 21:9: An ultrawide aspect ratio popular for gaming and desktop monitors. Some common examples The common film aspect ratios used in cinemas are 1.85:1 and 2.39:1.The 2.39:1 ratio is commonly labeled 2.40:1, e.g., in the American Society of Cinematographers' ''American Cinematographer Manual'' (Many widescreen films before the 1970 Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers, SMPTE revision used 2.35:1). Two common videography, videographic aspect ratios are 4:3 (1.:1), the universal video format of the 20th century, and 16:9 (1.:1), universal for high-definition television and European digital television. Other cinematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |