|
Hyperthymesia
Hyperthymesia, also known as hyperthymestic syndrome or highly superior autobiographical memory (HSAM), is a condition that leads people to be able to remember an abnormally large number of their life experiences in vivid detail. It is extraordinarily rare, with fewer than 100 people in the world having been diagnosed with the condition . A person who has hyperthymesia is called a hyperthymesiac. American neurobiologists Elizabeth Parker, Larry Cahill and James McGaugh (2006) identified two defining characteristics of hyperthymesia: spending an excessive amount of time thinking about one's past, and displaying an extraordinary ability to recall specific events from one's past. The authors wrote that they derived the word from Ancient Greek: ''hyper-'' 'excessive' and allegedly ''thymesis'' 'remembering', although such a word is not attested in Ancient Greek, but they may have been thinking of Modern Greek '' thymisi'' 'memory' or Ancient Greek ''enthymesis'' 'consideration', which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Exceptional Memory
Exceptional memory is the ability to have accurate and detailed recall in a variety of ways, including hyperthymesia, eidetic memory, synesthesia, and emotional memory. Exceptional memory is also prevalent in those with savant syndrome and mnemonists. Hyperthymesia Hyperthymesia, or hyperthymesitic syndrome, is superior autobiographical memory, the type of memory that forms people's life stories. The term ''hyperthymesia'' is derived from the Modern Greek word ''thýmesē'' 'memory' and Ancient Greek ''hypér'' 'over'. The capabilities of the affected individuals are not limited to recalling specific events from their personal experience. Hyperthymesia has both enhanced autobiographical and episodic memory There is an important characteristic of hyperthymesia: People with the syndrome have an unusual form of eidetic memory to remember as well as recall any specific personal events or trivial details, including a date, the weather, what people wore on that day, from their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jill Price
Jill Price (née Rosenberg, born December 30, 1965) is an American author from Southern California, who has been diagnosed with hyperthymesia. She was the first person to receive such a diagnosis, and it was her case that inspired research into hyperthymesia. She has co-authored a book on the subject. Abilities Price is able to recite details of every day of her life from the time when she was fourteen years old.Gray, Keturah; Escherich, Katie'It Makes Me Crazy: Woman Can't Forget, ABC News May 9, 2008 She can recall various obscure moments of her life in great detail. Her condition, termed hyperthymesia, or "hyperthymestic syndrome", is characterized by a highly superior autobiographical memory. Her case was originally researched by a team at the University of California, Irvine: Elizabeth Parker; Larry Cahill; and James McGaugh. Originally anonymised as "AJ", Price was described as being able to recall every day of her life from when she was 14 years old: "Starting on February ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Savant Syndrome
Savant syndrome ( , ) is a phenomenon where someone demonstrates exceptional aptitude in one domain, such as art or mathematics, despite significant social or intellectual impairment. Those with the condition generally have a neurodevelopmental condition, such as autism, or have experienced a brain injury. About half of cases are associated with autism, and these individuals may be known as autistic savants. The other half often have some form of central nervous system injury or disease. While the condition usually becomes apparent in childhood, some cases develop later in life. It is not recognized as a mental disorder within the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), as it relates to parts of the brain healing or restructuring. Savant syndrome is estimated to affect around one in a million people. The condition affects more males than females, at a ratio of 6:1. The first medical account of the condition was in 1783. It is estima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feelings, and motivation, motives. Psychology is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the Natural science, natural and social sciences. Biological psychologists seek an understanding of the Emergence, emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as Behavioural sciences, behavioral or Cognitive science, cognitive scientists. Some psychologists attempt to understand the role of mental functions in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Time (magazine)
''Time'' (stylized in all caps as ''TIME'') is an American news magazine based in New York City. It was published Weekly newspaper, weekly for nearly a century. Starting in March 2020, it transitioned to every other week. It was first published in New York City on March 3, 1923, and for many years it was run by its influential co-founder, Henry Luce. A European edition (''Time Europe'', formerly known as ''Time Atlantic'') is published in London and also covers the Middle East, Africa, and, since 2003, Latin America. An Asian edition (''Time Asia'') is based in Hong Kong. The South Pacific edition, which covers Australia, New Zealand, and the Pacific Islands, is based in Sydney. Since 2018, ''Time'' has been owned by Salesforce founder Marc Benioff, who acquired it from Meredith Corporation. Benioff currently publishes the magazine through the company Time USA, LLC. History 20th century ''Time'' has been based in New York City since its first issue published on March 3, 1923 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Synesthesia
Synesthesia (American English) or synaesthesia (British English) is a perceptual phenomenon in which stimulation of one sensory or cognitive pathway leads to involuntary experiences in a second sensory or cognitive pathway. People with synesthesia may experience colors when listening to music, see shapes when smelling certain scents, or perceive tastes when looking at words. People who report a lifelong history of such experiences are known as synesthetes. Awareness of synesthetic perceptions varies from person to person with the perception of synesthesia differing based on an individual's unique life experiences and the specific type of synesthesia that they have. In one common form of synesthesia, known as grapheme–color synesthesia or color–graphemic synesthesia, letters or numbers are perceived as inherently colour, colored. In spatial-sequence, or number form synesthesia, numbers, months of the year, or days of the week elicit precise locations in space (''e.g.,'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Allocentrism
Allocentrism is a collectivistic personality attribute whereby people center their attention and actions on other people rather than themselves. It is a psychological dimension which corresponds to the general cultural dimension of collectivism. In fact, allocentrics "believe, feel, and act very much like collectivists do around the world." Allocentric people tend to be interdependent, define themselves in terms of the group that they are part of, and behave according to that group's cultural norms. They tend to have a sense of duty and share beliefs with other allocentrics among their in-group. Allocentric people appear to see themselves as an extension of their in-group and allow their own goals to be subsumed by the in-group's goals. Additionally, allocentrism has been defined as giving priority to the collective self over the private self, particularly if these two selves happen to come into conflict. History Allocentrism is closely related to collectivism; it is the psycholo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
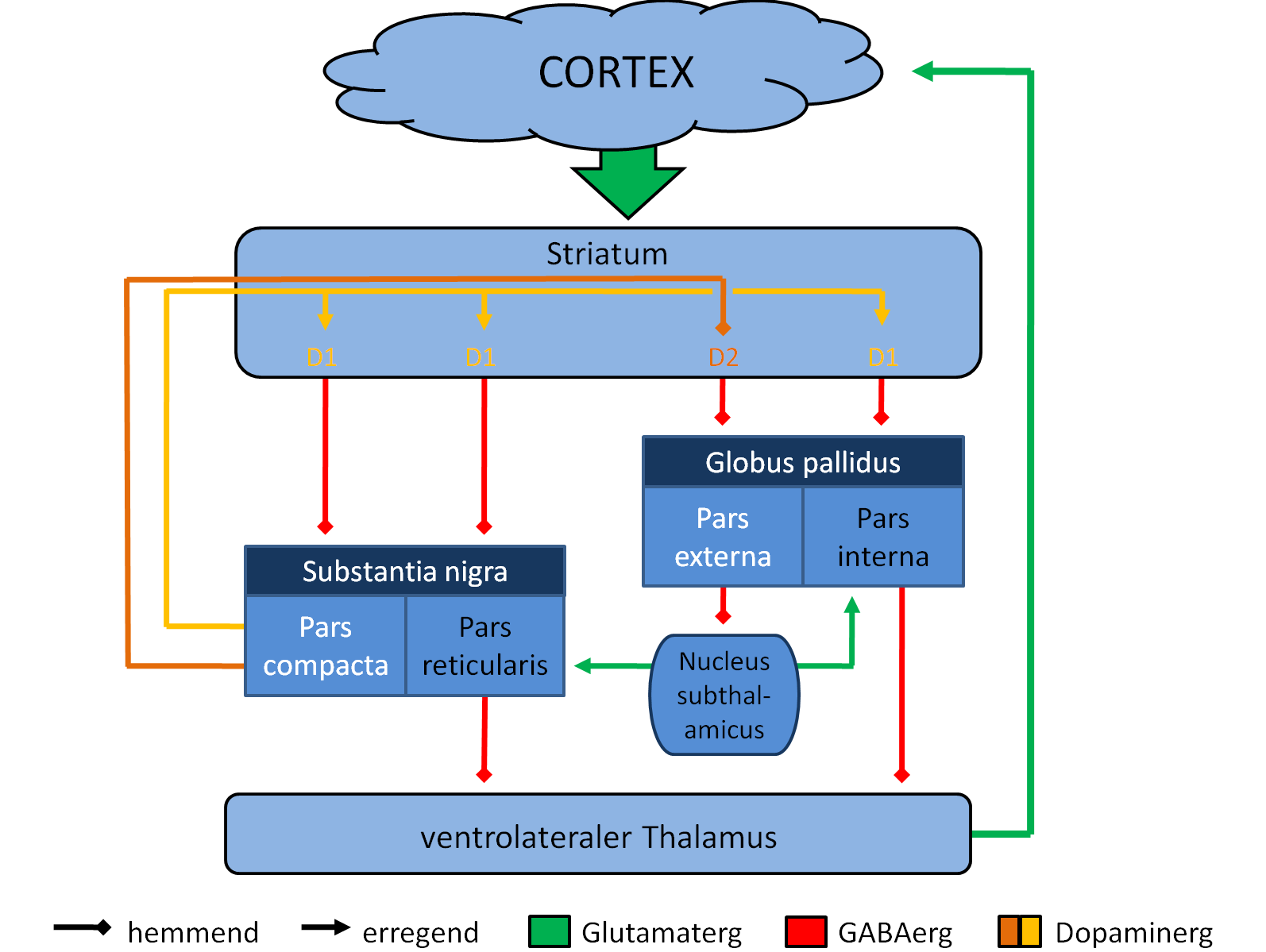
Frontostriatal Circuit
Frontostriatal circuits are neural pathways that connect frontal lobe regions with the striatum and mediate motor, cognitive, and behavioural functions within the brain. They receive inputs from dopaminergic, serotonergic, noradrenergic, and cholinergic cell groups that modulate information processing. Frontostriatal circuits are part of the executive functions. Executive functions include the following: selection and perception of important information, manipulation of information in working memory, planning and organization, behavioral control, adaptation to changes, and decision making. These circuits are involved in neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease as well as neuropsychiatric disorders including schizophrenia, depression, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), and in neurodevelopmental disorder such as attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Anatomy There are five defined frontostriatal circuits: motor and oculomoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spreading Activation
Spreading activation is a method for searching associative networks, biological and artificial neural networks, or semantic networks.Fähndrich, J. (2018). Semantic decomposition and marker passing in an artificial representation of meaning. Technische Universitaet Berlin (Germany)/ref> The search process is initiated by labeling a set of source nodes (e.g. concepts in a semantic network) with weights or "activation" and then iteratively propagating or "spreading" that activation out to other nodes linked to the source nodes. Most often these "weights" are real values that decay as activation propagates through the network. When the weights are discrete this process is often referred to as marker passing. Activation may originate from alternate paths, identified by distinct markers, and terminate when two alternate paths reach the same node. However brain studies show that several different brain areas play an important role in semantic processing.Karalyn Patterson, Peter J. Nesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alexander Luria
Alexander Romanovich Luria (; , ; 16 July 1902 – 14 August 1977) was a Soviet neuropsychology, neuropsychologist, often credited as a father of modern neuropsychology. He developed an extensive and original battery of neuropsychological assessment, neuropsychological tests during his clinical work with brain-injured victims of World War II, which are still used in various forms. He made an in-depth analysis of the functioning of various brain regions and integrative processes of the brain in general. Luria's magnum opus, ''Higher Cortical Functions in Man'' (1962), is a much-used psychological textbook which has been translated into many languages and which he supplemented with ''The Working Brain'' in 1973. It is less known that Luria's main interests, before the war, were in the field of cultural and developmental research in psychology. He became famous for his studies of low-educated populations of nomadic Uzbeks in the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic, Uzbek SSR argui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Semantic Memory
Semantic memory refers to general world knowledge that humans have accumulated throughout their lives. This general knowledge (Semantics, word meanings, concepts, facts, and ideas) is intertwined in experience and dependent on culture. New concepts are learned by applying knowledge learned from things in the past. Semantic memory is distinct from episodic memory—the memory of experiences and specific events that occur in one's life that can be recreated at any given point. For instance, semantic memory might contain information about what a cat is, whereas episodic memory might contain a specific memory of stroking a particular cat. Semantic memory and episodic memory are both types of explicit memory, explicit memory (or declarative memory), or memory of facts or events that can be consciously recalled and "declared". The counterpart to declarative or explicit memory is implicit memory (also known as nondeclarative memory). History The idea of semantic memory was first intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Episodic Memory
Episodic memory is the memory of everyday events (such as times, location geography, associated emotions, and other contextual information) that can be explicitly stated or conjured. It is the collection of past personal experiences that occurred at particular times and places; for example, the party on one's 7th birthday. Along with semantic memory, it comprises the category of explicit memory, one of the two major divisions of long-term memory (the other being implicit memory). The term "episodic memory" was coined by Endel Tulving in 1972, referring to the distinction between knowing and remembering: ''knowing'' is factual recollection (semantic) whereas ''remembering'' is a feeling that is located in the past (episodic). One of the main components of episodic memory is the process of recollection, which elicits the retrieval of contextual information pertaining to a specific event or experience that has occurred. Tulving seminally defined three key properties of episodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |