|
Episodic Memory
Episodic memory is the memory of everyday events (such as times, location geography, associated emotions, and other contextual information) that can be explicitly stated or conjured. It is the collection of past personal experiences that occurred at particular times and places; for example, the party on one's 7th birthday. Along with semantic memory, it comprises the category of explicit memory, one of the two major divisions of long-term memory (the other being implicit memory). The term "episodic memory" was coined by Endel Tulving in 1972, referring to the distinction between knowing and remembering: ''knowing'' is factual recollection (semantic) whereas ''remembering'' is a feeling that is located in the past (episodic). One of the main components of episodic memory is the process of recollection, which elicits the retrieval of contextual information pertaining to a specific event or experience that has occurred. Tulving seminally defined three key properties of episodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, it would be impossible for language, relationships, or personal identity to develop. Memory loss is usually described as forgetfulness or amnesia. Memory is often understood as an informational processing system with explicit and implicit functioning that is made up of a sensory processor, short-term (or working) memory, and long-term memory. This can be related to the neuron. The sensory processor allows information from the outside world to be sensed in the form of chemical and physical stimuli and attended to various levels of focus and intent. Working memory serves as an encoding and retrieval processor. Information in the form of stimuli is encoded in accordance with explicit or implicit functions by the working memory p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procedural Memory
Procedural memory is a type of implicit memory ( unconscious, long-term memory) which aids the performance of particular types of tasks without conscious awareness of these previous experiences. Procedural memory guides the processes we perform, and most frequently resides below the level of conscious awareness. When needed, procedural memories are automatically retrieved and utilized for execution of the integrated procedures involved in both cognitive and motor skills, from tying shoes, to reading, to flying an airplane. Procedural memories are accessed and used without the need for conscious control or attention. Procedural memory is created through ''procedural learning'', or repeating a complex activity over and over again until all of the relevant neural systems work together to automatically produce the activity. Implicit procedural learning is essential for the development of any motor skill or cognitive activity. History The difference between procedural and declarat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterograde Amnesia
In neurology, anterograde amnesia is the inability to create new memories after an event that caused amnesia, leading to a partial or complete inability to recall the recent past, while long-term memories from before the event remain intact. This is in contrast to retrograde amnesia, where memories created prior to the event are lost while new memories can still be created. Both can occur together in the same patient. To a large degree, anterograde amnesia remains a mysterious ailment because the precise mechanism of storing memories is not yet well understood, although it is known that the regions of the brain involved are certain sites in the temporal cortex, especially in the hippocampus and nearby subcortical regions. Signs and symptoms People with anterograde amnesic syndromes may present widely varying degrees of forgetfulness. Some with severe cases have a combined form of anterograde and retrograde amnesia, sometimes called global amnesia. In the case of drug-induce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Memory
Semantic memory refers to general world knowledge that humans have accumulated throughout their lives. This general knowledge (Semantics, word meanings, concepts, facts, and ideas) is intertwined in experience and dependent on culture. New concepts are learned by applying knowledge learned from things in the past. Semantic memory is distinct from episodic memory—the memory of experiences and specific events that occur in one's life that can be recreated at any given point. For instance, semantic memory might contain information about what a cat is, whereas episodic memory might contain a specific memory of stroking a particular cat. Semantic memory and episodic memory are both types of explicit memory, explicit memory (or declarative memory), or memory of facts or events that can be consciously recalled and "declared". The counterpart to declarative or explicit memory is implicit memory (also known as nondeclarative memory). History The idea of semantic memory was first intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). This occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells (NECs), radial glial cells (RGCs), basal progenitors (BPs), intermediate neuronal precursors (INPs), subventricular zone astrocytes, and subgranular zone radial astrocytes, among others. Neurogenesis is most active during embryonic development and is responsible for producing all the various types of neurons of the organism, but it continues throughout adult life in a variety of organisms. Once born, neurons do not divide (see mitosis), and many will live the lifespan of the animal, except under extraordinary and usually pathogenic circumstances. In mammals Developmental neurogenesis During embryonic development, the mammalian central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) is derived from the neural tube, which contains NSCs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
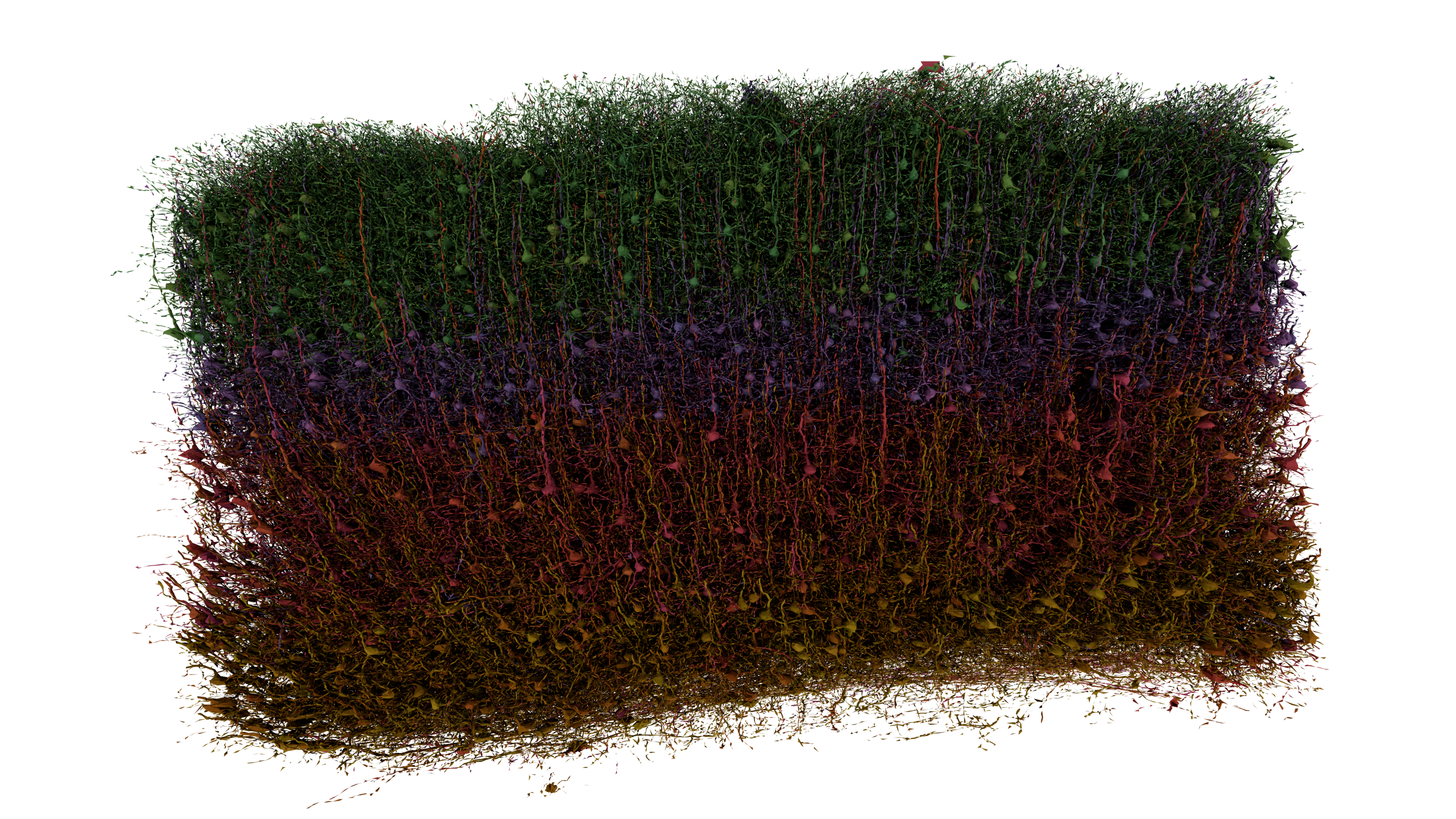
Neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning, and language. The neocortex is further subdivided into the true isocortex and the proisocortex. In the human brain, the cerebral cortex consists of the larger neocortex and the smaller allocortex, respectively taking up 90% and 10%. The neocortex is made up of six layers, labelled from the outermost inwards, I to VI. Etymology The term is from ''cortex'', Latin, " bark" or "rind", combined with ''neo-'', Greek, "new". ''Neopallium'' is a similar hybrid, from Latin ''pallium'', "cloak". ''Isocortex'' and ''allocortex'' are hybrids with Greek ''isos'', "same", and ''allos'', "other". Anatomy The neocortex is the most developed in its organisation and number of layers, of the cerebral tissues. The neocortex cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Consolidation
Memory consolidation is a category of processes that stabilize a memory trace after its initial acquisition. A memory trace is a change in the nervous system caused by memorizing something. Consolidation is distinguished into two specific processes. The first, synaptic consolidation, which is thought to correspond to long-term potentiation#Late phase, late-phase long-term potentiation, occurs on a small scale in the synaptic connections and neural circuits within the first few hours after learning. The second process is systems consolidation, occurring on a much larger scale in the brain, rendering Declarative memory, hippocampus-dependent memories independent of the hippocampus over a period of weeks to years. Recently, a third process has become the focus of research, reconsolidation, in which previously consolidated memories can be made Lability, labile again through reactivation of the memory trace. History Memory consolidation was first referred to in the writings of the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parietal Lobe
The parietal lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus. The parietal lobe integrates sensory information among various sensory modality, modalities, including spatial sense and navigation (proprioception), the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch in the somatosensory cortex which is just posterior to the central sulcus in the postcentral gyrus, and the two-streams hypothesis#Dorsal stream, dorsal stream of the visual system. The major sensory inputs from the skin (mechanoreceptor, touch, thermoreceptor, temperature, and nociceptor, pain receptors), relay through the thalamus to the parietal lobe. Several areas of the parietal lobe are important in language processing in the brain, language processing. The somatosensory cortex can be illustrated as a distorted figure – the cortical homunculus (Latin: "li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working Memory
Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that can Memory, hold information temporarily. It is important for reasoning and the guidance of decision-making and behavior. Working memory is often used synonymously with short-term memory, but some theorists consider the two forms of memory distinct, assuming that working memory allows for the manipulation of stored information, whereas short-term memory only refers to the short-term storage of information. Working memory is a theoretical concept central to cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and neuroscience. History The term "working memory" was coined by George Armitage Miller, Miller, Eugene Galanter, Galanter, and Karl H. Pribram, Pribram, and was used in the 1960s in the context of Computational theory of mind, theories that likened the mind to a computer. In 1968, Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model, Atkinson and Shiffrin used the term to describe their "short-term store". The term short-term store was the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic
Semantics is the study of linguistic Meaning (philosophy), meaning. It examines what meaning is, how words get their meaning, and how the meaning of a complex expression depends on its parts. Part of this process involves the distinction between sense and reference. Sense is given by the ideas and concepts associated with an expression while reference is the object to which an expression points. Semantics contrasts with syntax, which studies the rules that dictate how to create grammatically correct sentences, and pragmatics, which investigates how people use language in communication. Lexical semantics is the branch of semantics that studies word meaning. It examines whether words have one or several meanings and in what lexical relations they stand to one another. Phrasal semantics studies the meaning of sentences by exploring the phenomenon of compositionality or how new meanings can be created by arranging words. Formal semantics (natural language), Formal semantics relies o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executive Function
In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions (collectively referred to as executive function and cognitive control) are a set of cognitive processes that support goal-directed behavior, by regulating thoughts and actions through cognitive control, selecting and successfully monitoring actions that facilitate the attainment of chosen objectives. Executive functions include basic cognitive processes such as attentional control, cognitive inhibition, inhibitory control, working memory, and cognitive flexibility. Higher-order executive functions require the simultaneous use of multiple basic executive functions and include planning and fluid intelligence (e.g., reasoning and problem-solving). Executive functions gradually develop and change across the lifespan of an individual and can be improved at any time over the course of a person's life. Similarly, these cognitive processes can be adversely affected by a variety of events which affect an individual. Both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Source Amnesia
Source amnesia is the inability to remember where, when or how previously learned information has been acquired, while retaining the factual knowledge. This branch of amnesia is associated with the malfunctioning of one's explicit memory. It is likely that the disconnect between having the knowledge and remembering the context in which the knowledge was acquired is due to a dissociation between semantic and episodic memoryTulving, E. (1972)Episodic and semantic memory In E. Tulving and W. Donaldson (Eds.), ''Organization of Memory'' (pp. 381–403). New York: Academic Press. – an individual retains the semantic knowledge (the fact), but lacks the episodic knowledge to indicate the context in which the knowledge was gained. Memory representations reflect the encoding processes during acquisition. Different types of acquisition processes (e.g.: reading, thinking, listening) and different types of events (e.g.: newspaper, thoughts, conversation) will produce mental depictions that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |