|
Hybridoma Technology
Hybridoma technology is a method for producing large quantities of monoclonal antibodies by fusing antibody producing B cells with myeloma cells (cancerous B cells). This creates hybrid cells, ''hybridomas,'' that produce the antibody from their parent B cell whilst maintaining the properties of the parental myeloma cell line being immortal (endlessly reproducing) and having desirable properties for cell culture. The B cells to be used are generally gathered from animals who have been immunized with an antigen against which an antibody targeting it is desired. After forming hybridomas any non-hybrid cells are killed before screening and monoclonalization to create hybridoma lines that are derived from one parental cell and thus producing the same antibody against the desired target. The production of monoclonal antibodies was invented by César Milstein and Georges J. F. Köhler in 1975. They shared the Nobel Prize of 1984 for Medicine and Physiology with Niels Kaj Jerne, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonals
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a Lineage (evolution), cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies are identical and can thus have Valence (chemistry), monovalent affinity, binding only to a particular epitope (the part of an antigen that is recognized by the antibody). In contrast, polyclonal antibodies are mixtures of antibodies derived from multiple plasma cell lineages which each bind to their particular target epitope. Artificial antibodies known as bispecific monoclonal antibodies can also be engineered which include two different antigen binding sites (Fragment antigen-binding region, FABs) on the same antibody. It is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to almost any suitable substance; they can then serve to detect or purify it. This capability has become an investigative tool in b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
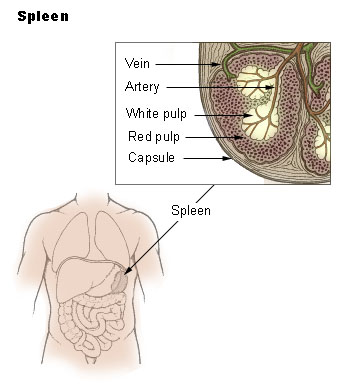
Splenocyte
Splenocytes are white blood cells that reside in the spleen and are involved in functions of the spleen, such as filtering blood and the immune response. Splenocytes consist of a variety of cell populations such as T and B lymphocytes, dendritic cells and macrophages, which have different immune functions. Overview Splenocytes are spleen cells and consist of White blood cell, leukocytes like B cell, B and T cell, T cells, Dendritic cell, dendritic cells, and Macrophage, macrophages. The spleen is split into Red pulp, red and White pulp, white pulp regions with the marginal zone separating the two areas. The red pulp is involved with filtering blood and recycling iron, while the white pulp is involved in the immune response. The red pulp contains macrophages that phagocytosis, phagocytose old or damaged red blood cells. The white pulp contains separate compartments for B and T cells called the B cell zone (BCZ) and the T cell zone (TCZ). B cells make antibodies to fight off bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
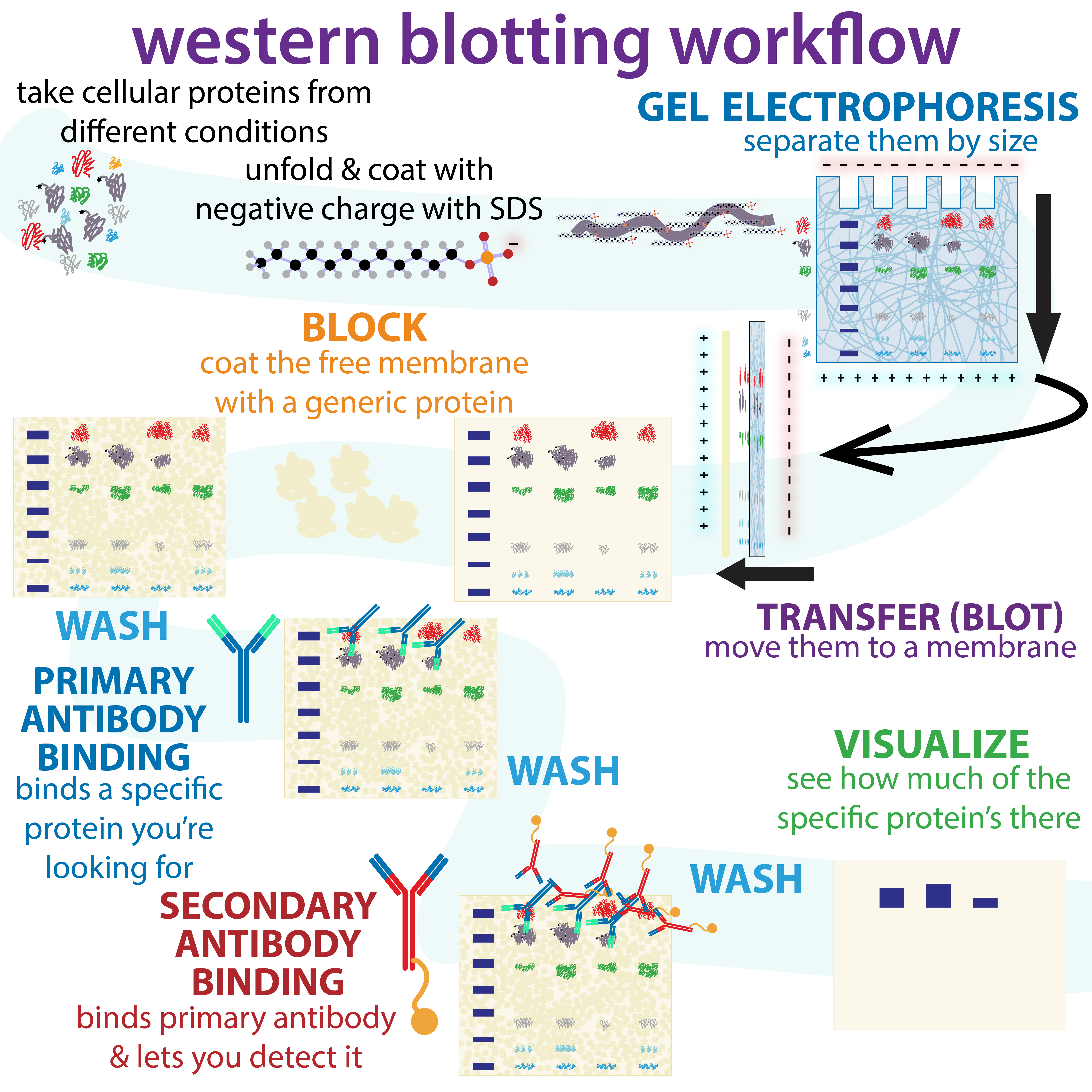
Western Blot
The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot), or western blotting, is a widely used analytical technique in molecular biology and immunogenetics to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. Besides detecting the proteins, this technique is also utilized to visualize, distinguish, and quantify the different proteins in a complicated protein combination. Western blot technique uses three elements to achieve its task of separating a specific protein from a complex: separation by size, transfer of protein to a solid support, and marking target protein using a primary and secondary antibody to visualize. A synthetic or animal-derived antibody (known as the primary antibody) is created that recognizes and binds to a specific target protein. The electrophoresis membrane is washed in a solution containing the primary antibody, before excess antibody is washed off. A secondary antibody is added which recognizes and binds to the primary antibod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay is a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand (commonly an amino acid) in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the ligand to be measured. ELISA has been used as a medical diagnosis, diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries. In the most simple form of an ELISA, antigens from the sample to be tested are attached to a surface. Then, a matching antibody is applied over the surface so it can bind the antigen. This antibody is linked to an enzyme, and then any unbound antibodies are removed. In the final step, a substance containing the enzyme's Enzyme substrate, substrate is added. If there was binding, the subsequent reaction produces a detectable signal, most commonly a color change. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salvage Pathway
A salvage pathway is a pathway in which a biological product is produced from intermediates in the degradative pathway of its own or a similar substance. The term often refers to nucleotide salvage in particular, in which nucleotides (purine and pyrimidine) are synthesized from intermediates in their degradative pathway. Nucleotide salvage pathways are used to recover bases and nucleosides that are formed during degradation of RNA and DNA. This is important in some organs because some tissues cannot undergo de novo synthesis. The salvaged products can then be converted back into nucleotides. Salvage pathways are targets for drug development, one family being called antifolates. A number of other biologically-important substances, like methionine and nicotinate, have their own salvage pathways to recycle parts of the molecule. Substrates The nucleotide salvage pathway requires distinct substrates: Pyrimidines Uridine phosphorylase or pyrimidine-nucleoside phosphorylase subst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Novo Synthesis
In chemistry, ''de novo'' synthesis () is the synthesis of complex molecules from simple molecules such as sugars or amino acids, as opposed to recycling after partial degradation. For example, nucleotides are not needed in the diet as they can be constructed from small precursor molecules such as formate and aspartate. Methionine, on the other hand, is needed in the diet because while it can be degraded to and then regenerated from homocysteine, it cannot be synthesized ''de novo''. Nucleotide ''De novo'' pathways of nucleotides do not use free bases: adenine (abbreviated as A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), thymine (T), or uracil (U). The purine ring is built up one atom or a few atoms at a time and attached to ribose throughout the process. Pyrimidine ring is synthesized as orotate and attached to ribose phosphate and later converted to common pyrimidine nucleotides. Cholesterol Cholesterol is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. Cholesterol a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminopterin
Aminopterin (or 4-aminopteroic acid), the 4–amino derivative of folic acid, is an antineoplastic drug with immunosuppressive properties often used in chemotherapy. Aminopterin is a synthetic derivative of pterin. Aminopterin works as an enzyme inhibitor by competing for the folate binding site of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase. Its binding affinity for dihydrofolate reductase effectively blocks tetrahydrofolate synthesis. This results in the depletion of nucleotide precursors and inhibition of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities. Uses Discovered by Yellapragada Subbarow, the drug was first used by Sidney Farber in 1947 to induce remissions among children with leukemia. Amino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymidine
Thymidine (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol dT or dThd), also known as deoxythymidine, deoxyribosylthymine, or thymine deoxyriboside, is a pyrimidine nucleoside, deoxynucleoside. Deoxythymidine is the DNA nucleoside T, which pairs with deoxyadenosine (A) in double-stranded DNA. In cell biology it is used to cell synchronization, synchronize the cells in G1/early S phase. The prefix deoxy- is often left out since there are no precursors of thymine nucleotides involved in RNA synthesis. Before the boom in thymidine use caused by the need for thymidine in the production of the antiretroviral drug Zidovudine, azidothymidine (AZT), much of the world's thymidine production came from herring sperm. Thymidine occurs almost exclusively in DNA but it also occurs in the T arm, T-loop of tRNA. Structure and properties In its composition, deoxythymidine is a nucleoside composed of deoxyribose (a pentose sugar) joined to the pyrimidine base thymine. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminopterin
Aminopterin (or 4-aminopteroic acid), the 4–amino derivative of folic acid, is an antineoplastic drug with immunosuppressive properties often used in chemotherapy. Aminopterin is a synthetic derivative of pterin. Aminopterin works as an enzyme inhibitor by competing for the folate binding site of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase. Its binding affinity for dihydrofolate reductase effectively blocks tetrahydrofolate synthesis. This results in the depletion of nucleotide precursors and inhibition of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities. Uses Discovered by Yellapragada Subbarow, the drug was first used by Sidney Farber in 1947 to induce remissions among children with leukemia. Amino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxanthine
Hypoxanthine is a naturally occurring purine derivative. It is occasionally found as a constituent of nucleic acids, where it is present in the anticodon of tRNA in the form of its nucleoside inosine. It has a tautomer known as 6-hydroxypurine. Hypoxanthine is a necessary additive in certain cells, bacteria, and parasite cultures as a substrate and nitrogen source. For example, it is commonly a required reagent in malaria culture, malaria parasite cultures, since ''Plasmodium falciparum'' requires a source of hypoxanthine for nucleic acid synthesis and energy metabolism. In August 2011, a report, based on NASA studies with meteorites found on Earth, was published suggesting hypoxanthine and related organic molecules, including the DNA and RNA components adenine and guanine, may have been formed extraterrestrially in outer space. The ''Pheretima, Pheretima aspergillum'' worm, used in Chinese medicine preparations, contains hypoxanthine. Reactions It is one of the products of the ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HAT Medium
HAT Medium (hypoxanthine-aminopterin-thymidine medium) is a selection medium for mammalian cell culture, which relies on the combination of aminopterin, a drug that acts as a powerful folate metabolism inhibitor by inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase, with hypoxanthine (a purine derivative) and thymidine (a deoxynucleoside) which are intermediates in DNA synthesis. The trick is that aminopterin blocks DNA ''de novo'' synthesis, which is absolutely required for cell division to proceed, but hypoxanthine and thymidine provide cells with the raw material to evade the blockage (the "salvage pathway"), provided that they have the right enzymes, which means having functioning copies of the genes that encode them. The enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, which produces tetrahydrofolate (THF) by the reduction of dihydrofolate, is specifically blocked by aminopterin. THF, acting in association with specific proteins, can receive single carbon units that are then transferred to specific target ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |