Splenocyte on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Splenocytes are white blood cells that reside in the spleen and are involved in functions of the spleen, such as filtering blood and the immune response.
Splenocytes consist of a variety of cell populations such as T and B lymphocytes, dendritic cells and macrophages, which have different immune functions.
 Splenocytes are spleen cells and consist of
Splenocytes are spleen cells and consist of
Overview
 Splenocytes are spleen cells and consist of
Splenocytes are spleen cells and consist of leukocytes
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are genera ...
like B and T cells
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their ce ...
, dendritic cells
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system ...
, and macrophages
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
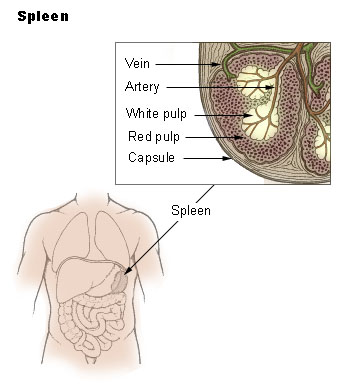
. The spleen is split into red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–750 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a seconda ...
and white pulp regions with the marginal zone
The marginal zone is the region at the interface between the non-lymphoid red pulp and the lymphoid white-pulp of the spleen. (Some sources consider it to be the part of red pulp which borders on the white pulp, while other sources consider it ...
separating the two areas. The red pulp is involved with filtering blood and recycling iron, while the white pulp is involved in the immune response.
The red pulp contains macrophages that phagocytose
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is c ...
old or damaged red blood cells.
The white pulp contains separate compartments for B and T cells called the B cell zone (BCZ) and the T cell zone (TCZ). B cells make antibodies to fight off bacterial, viral, and fungal infections, and T cells are activated in response to antigens.
The marginal zone (MZ) separates the red and white pulp regions and contains macrophages, B cells, and dendritic cells. MZ macrophages remove some types of blood-borne bacteria and viruses. MZ B and dendritic cells are involved in antigen processing and presentation to lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and ...
in the white pulp.
References
Spleen (anatomy) Mononuclear phagocytes Leukocytes Cell biology {{cell-biology-stub