|
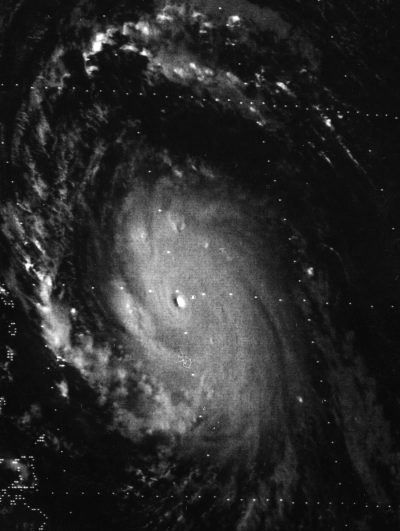
Hurricane Luis
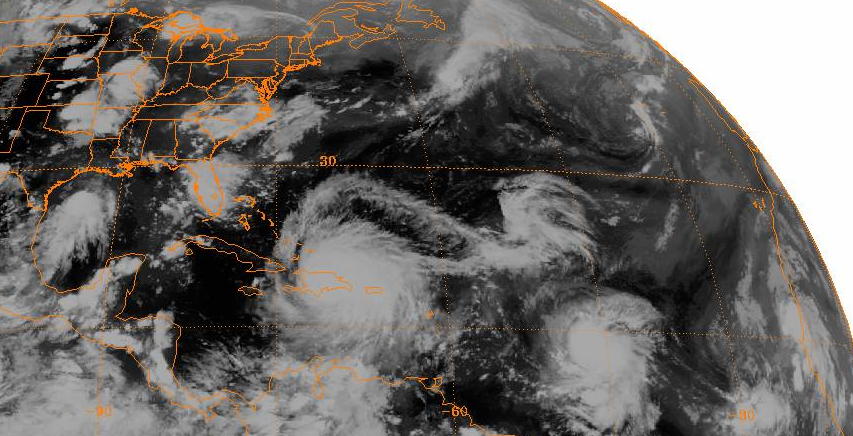
Hurricane Luis was a long lived and powerful Category 4 hurricane. It was the strongest hurricane to make landfall and the third-most intense hurricane recorded during the 1995 Atlantic hurricane season. The storm, along with Humberto, Iris, and Karen, was one of four simultaneous tropical systems in the Atlantic basin. Luis caused very extensive damage to Antigua, St. Barthelemy, the island of St. Martin and Anguilla as it affected Bermuda. The storm accounted for 19 confirmed deaths, left nearly 20,000 homeless (mostly in Anguilla, Barbuda, and St. Martin), and affected more than 70,000 people. Total damage was estimated at $3.3 billion (1995 USD) across the affected areas. Earlier Category 4 storms that impacted the Leeward Islands in the 20th century include Hurricane Dog in 1950, Hurricane Donna in 1960, Hurricane David in 1979, and Hurricane Hugo in 1989. Luis was the second of three tropical cyclones to affect Guadeloupe in a short period; Hurricane Iris had hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc between the Greater Antilles to the north-west and the continent of South America."West Indies." ''Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary'', 3rd ed. 2001. () Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., p. 1298. The islands of the Lesser Antilles form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea where it meets the Atlantic Ocean. Together, the Lesser Antilles and the Greater Antilles make up the Antilles. (Somewhat confusingly, the word Caribbean is sometimes used to refer only to the Antilles, and sometimes used to refer to a much larger region.) The Lesser and Greater Antilles, together with the Lucayan Archipelago, are collectively known as the West Indies. History after European arrival The Spanish were the first Europeans to arrive on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Humberto (1995)
The 1995 Atlantic hurricane season was an extremely active Atlantic hurricane season and is considered to be the start of an ongoing era of high-activity tropical cyclone formation. The season produced twenty-one tropical cyclones, nineteen named storms, as well as eleven hurricanes and five major hurricanes. The season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates which conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones develop in the Atlantic basin. The first tropical cyclone, Hurricane Allison, developed on June 2, while the season's final storm, Hurricane Tanya, transitioned into an extratropical cyclone on November 1. The very active Atlantic hurricane activity in 1995 was caused by La Niña conditions, which also influenced a very inactive Pacific hurricane season. There were four particularly destructive hurricanes during the season, including Luis, Marilyn, Opal and Roxanne. Hurricanes Luis and Marilyn both ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Marilyn
Hurricane Marilyn was the most powerful hurricane to strike the Virgin Islands since Hurricane Hugo of 1989, and the third such tropical cyclone in roughly a two-week time span to strike or impact the Leeward Islands, the others being Hurricane Iris and the much more powerful and destructive Hurricane Luis. The thirteenth named storm, seventh hurricane and third major hurricane of the extremely active 1995 Atlantic hurricane season, Marilyn formed on September 12 as a tropical depression from a tropical wave that moved off the coast of Africa on September 7. After formation, the storm quickly became a tropical storm, and steadily intensified into a hurricane by the time it struck the Lesser Antilles on September 14 at Category 1 strength. Entering the northeastern Caribbean Sea, rapid intensification ensued and it peaked on September 16 north of Puerto Rico as a Category 3 hurricane shortly after it had impacted the U.S. Virgin Islands. A Hurricane Hunter reconnais ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different names, including hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean, and a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean, South Pacific, or (rarely) South Atlantic, comparable storms are referred to simply as "tropical cyclones", and such storms in the Indian Ocean can also be called "severe cyclonic storms". "Tropical" refers to the geographical origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively over tropical seas. "Cyclone" refers to their winds moving in a circle, whirling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1989 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1989 Atlantic hurricane season was an average season with 11 named storms. The season officially began on June 1, and ended on November 30. The first storm, Tropical Depression One, developed on June 15, and dissipated two days later without effects on land. Later that month, Tropical Storm Allison caused severe flooding, especially in Texas and Louisiana. Tropical Storm Barry, Tropical Depressions Six, Nine, and Thirteen, and Hurricanes Erin and Felix caused negligible impact. Hurricane Gabrielle and Tropical Storm Iris caused light effects on land, with the former resulting in nine fatalities from rip currents offshore the East Coast of the United States and Atlantic Canada, while the latter produced minor flooding in the United States Virgin Islands. The most notable storm of the season was the costliest tropical cyclone in the Atlantic basin at the time, Hurricane Hugo, that caused $9.47 billion (1989 USD) in damage and 88 fatalitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Hugo
Hurricane Hugo was a powerful Cape Verde tropical cyclone that inflicted widespread damage across the northeastern Caribbean and the Southeastern United States in September 1989. Across its track, Hugo affected approximately 2 million people. Its direct effects killed 67 people and inflicted $11 billion (equivalent to $ billion in ) in damage. The damage wrought by the storm was more costly than any Atlantic hurricane preceding it. At its peak strength east of the Lesser Antilles, Hugo was classified as a Category 5 hurricane—the highest rating on the Saffir–Simpson scale. Over the course of five days, Hugo made landfalls on Guadeloupe, Saint Croix, Puerto Rico, and South Carolina, bringing major hurricane conditions to these and surrounding areas. Lesser effects were felt along the periphery of the hurricane's path in the Lesser Antilles and across the Eastern United States into Eastern Canada. The scale of Hugo's impacts led to the retirement of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1979 Atlantic hurricane season was the first season to include both male and female names, as well as the common six-year rotating lists of tropical cyclone names. The season officially began on June 1, and lasted until November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. It was slightly below average, with nine systems reaching tropical storm intensity. The first system, an unnumbered tropical depression, developed north of Puerto Rico on June 9. Two days later, Tropical Depression One formed and produced severe flooding in Jamaica, with 40 deaths and about $27 million (1979 USD) in damage. Tropical Storm Ana caused minimal impact in the Lesser Antilles. Hurricane Bob spawned tornadoes and produced minor wind damage along the Gulf Coast of the United States, primarily in Louisiana, while the remnants caused flooding, especially in Indiana. Tropical Storm Claudette cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane David
Hurricane David was an extremely deadly hurricane which caused massive loss of life in the Dominican Republic in August 1979, and was the most intense hurricane to make landfall in the country in recorded history. A Cape Verde hurricane that reached Category 5 hurricane status on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale, David was the fourth named tropical cyclone, second hurricane, and first major hurricane of the 1979 Atlantic hurricane season, traversing through the Leeward Islands, Greater Antilles, and East Coast of the United States during late August and early September. David was the first hurricane to affect the Lesser Antilles since Hurricane Inez in 1966. With winds of 175 mph (280 km/h), David was one of only 2 storms of Category 5 intensity to make landfall on the Dominican Republic in the 20th century, the other also being Inez, and the deadliest since the 1930 Dominican Republic hurricane, San Zenon, killing over 2,000 people in its pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1960 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1960 Atlantic hurricane season was the least active season since 1952. The season officially began on June 15, and lasted until November 15. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. The first system, an unnamed storm, developed in the Bay of Campeche on June 22. It brought severe local flooding to southeastern Texas and was considered the worst disaster in some towns since a Hurricane in 1945. The unnamed storm moved across the United States for almost a week before dissipating on June 29. In July, Hurricane Abby resulted in minor damage in the Leeward Islands, before impacting a few Central American counties — the remnants of the storm would go on to form Hurricane Celeste in the East Pacific. Later that month, Tropical Storm Brenda caused flooding across much of the East Coast of the United States. The next storm, Hurricane Cleo, caused no known impact, despite its close pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Donna
Hurricane Donna, known in Puerto Rico as Hurricane San Lorenzo, was the strongest hurricane of the 1960 Atlantic hurricane season, and caused severe damage to the Lesser Antilles, the Greater Antilles, and the East Coast of the United States, especially Florida, in August–September. The fifth tropical cyclone, third hurricane, and first major hurricane of the season, Donna developed south of Cape Verde on August 29, spawned by a tropical wave to which 63 deaths from a plane crash in Senegal were attributed. The depression strengthened into Tropical Storm Donna by the following day. Donna moved west-northwestward at roughly and by September 1, it reached hurricane status. Over the next three days, Donna deepened significantly and reached maximum sustained winds of 130 mph (210 km/h) on September 4. Thereafter, it maintained intensity as it struck the Lesser Antilles later that day. On Sint Maarten, the storm left a quarter of the island's populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1950 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1950 Atlantic hurricane season was the first year in the Atlantic hurricane database (HURDAT) that storms were given names in the Atlantic basin. Names were taken from the Joint Army/Navy Phonetic Alphabet, with the first named storm being designated "Able", the second "Baker", and so on. It was a very active season with sixteen tropical storms, with eleven of them developing into hurricanes. Six of these hurricanes were intense enough to be classified as major hurricanes—a denomination reserved for storms that attained sustained winds equivalent to a Category 3 or greater on the present-day Saffir–Simpson scale. One storm, the twelfth of the season, was unnamed and was originally excluded from the yearly summary, and three additional storms were discovered in re-analysis. The large quantity of strong storms during the year yielded, prior to modern reanalysis, what was the highest seasonal accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) of the 20th century in the Atlantic basin; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Dog (1950)
Hurricane Dog was the most intense hurricane in the 1950 Atlantic hurricane season. Prior to reanalysis by the Hurricane Research Division in 2014, it was considered one of the strongest Atlantic hurricanes on record, equivalent to Category 5 status on the modern Saffir-Simpson scale, with winds of . The fourth named storm of the season, Dog developed on August 30 to the east of Antigua; after passing through the northern Lesser Antilles, it turned to the north and intensified into a Category 4 hurricane. Dog reached its peak intensity with winds of over the open Atlantic, and after weakening it passed within of Cape Cod, Massachusetts. The storm became extratropical on September 12. Hurricane Dog caused extensive damage to the Leeward Islands, and was considered the most severe hurricane on record in Antigua. Many buildings were destroyed or severely damaged on the island, with thousands left homeless just weeks after Hurricane Baker caused serious damage t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)