|
Holographic Grating
In optics, a holographic grating is a type of diffraction grating formed by an interference-fringe field of two laser beams whose standing-wave pattern is exposed to a set of photosensitive materials. The exposure triggers chemical processes within the sample and results in the formation of a periodic structure that has the same periodicity of the recorded pattern. One of the most interesting features of these structures is their versatility and tunability as the optical response strongly depends on the blend of used materials, and their interactions with light during, and after, the recording procedure. With the expertise earned over the years, nowadays holographic gratings are very efficient with no notable difference when compared to mechanically ruled gratings. Nevertheless, the lower limit over the grating spacing is one order of magnitude smaller than the latter. Their availability, low cost, and versatility opened the path for their use in a various range of applications s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible light, visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation, and other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the Classical electromagnetism, classical electromagnetic description of light, however complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of Ray (optics), rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction Grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical grating with a periodic structure that diffraction, diffracts light, or another type of electromagnetic radiation, into several beams traveling in different directions (i.e., different diffraction angles). The emerging coloration is a form of structural coloration. The directions or diffraction angles of these beams depend on the wave (light) Angle of incidence (optics), incident angle to the diffraction grating, the spacing or periodic distance between adjacent diffracting elements (e.g., parallel slits for a transmission grating) on the grating, and the wavelength of the incident light. The grating acts as a dispersion (optics), dispersive element. Because of this, diffraction gratings are commonly used in monochromators and spectrometers, but other applications are also possible such as optical encoders for high-precision motion control and wavefront measurement. For typical applications, a reflection (optics), reflective grati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
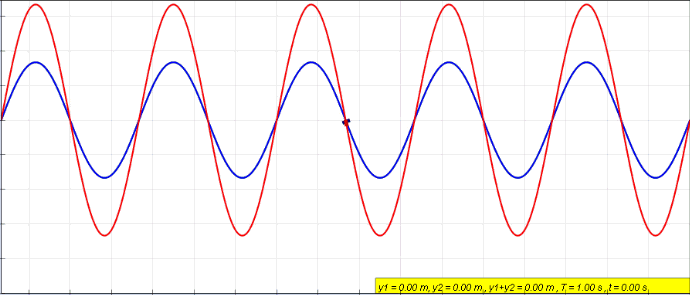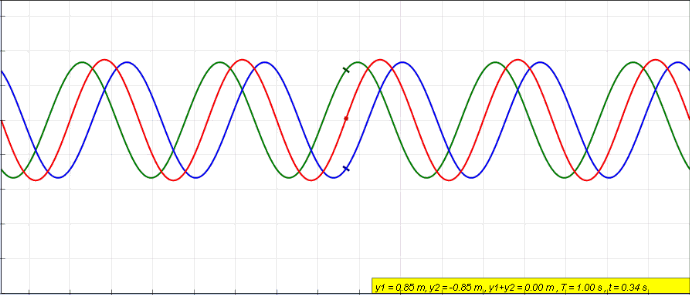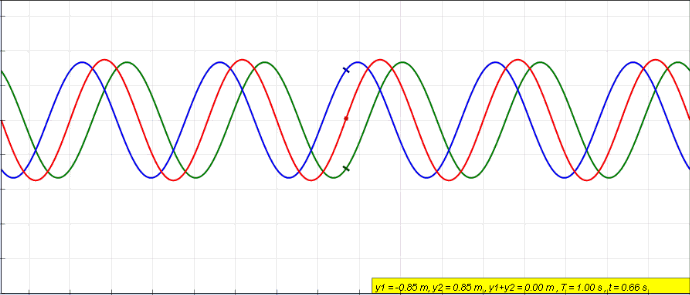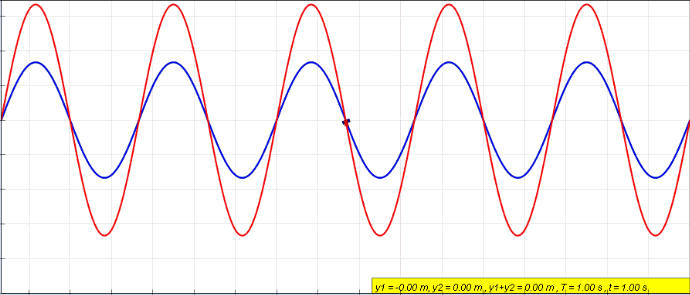
Wave Interference
In physics, interference is a phenomenon in which two coherent waves are combined by adding their intensities or displacements with due consideration for their phase difference. The resultant wave may have greater amplitude (constructive interference) or lower amplitude (destructive interference) if the two waves are in phase or out of phase, respectively. Interference effects can be observed with all types of waves, for example, light, radio, acoustic, surface water waves, gravity waves, or matter waves as well as in loudspeakers as electrical waves. Etymology The word ''interference'' is derived from the Latin words ''inter'' which means "between" and ''fere'' which means "hit or strike", and was used in the context of wave superposition by Thomas Young in 1801. Mechanisms The principle of superposition of waves states that when two or more propagating waves of the same type are incident on the same point, the resultant amplitude at that point is equal to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles H. Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow and the optical amplifier patented by Gordon Gould. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light that is coherence (physics), ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling uses such as optical communication, laser cutting, and Photolithography#Light sources, lithography. It also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimated light, collimation), used in laser pointers, lidar, and free-space optical communication. Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which permits them to emit light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing-wave
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect to time, and the oscillations at different points throughout the wave are in phase. The locations at which the absolute value of the amplitude is minimum are called nodes, and the locations where the absolute value of the amplitude is maximum are called antinodes. Standing waves were first described scientifically by Michael Faraday in 1831. Faraday observed standing waves on the surface of a liquid in a vibrating container. Franz Melde coined the term "standing wave" (German: ''stehende Welle'' or ''Stehwelle'') around 1860 and demonstrated the phenomenon in his classic experiment with vibrating strings. This phenomenon can occur because the medium is moving in the direction opposite to the movement of the wave, or it can arise in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosensitive
Photosensitivity is the amount to which an object reacts upon receiving photons, especially visible light. In medicine, the term is principally used for abnormal reactions of the skin, and two types are distinguished, photoallergy and phototoxicity. The photosensitive ganglion cells in the mammalian eye are a separate class of light-detecting cells from the photoreceptor cells that function in vision. Skin reactions Human medicine Sensitivity of the skin to a light source can take various forms. People with particular skin types are more sensitive to sunburn. Particular medications make the skin more sensitive to sunlight; these include most of the tetracycline antibiotics, heart drugs amiodarone, and Sulfonamide (medicine), sulfonamides. Some dietary supplements, such as St. John's Wort, include photosensitivity as a possible side effect. Particular conditions lead to increased light sensitivity. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus experience skin symptoms after sunligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Storage
Optical storage refers to a class of data storage systems that use light to read or write data to an underlying optical media. Although a number of optical formats have been used over time, the most common examples are optical disks like the compact disc (CD) and digital versatile disc (DVD). Reading and writing methods have also varied over time, but most modern systems use lasers as the light source and use it both for reading and writing to the discs. '' Britannica'' notes that it "uses low-power laser beams to record and retrieve digital (binary) data." Overview Optical storage is the storage of data on an optically readable medium. Data is recorded by making marks in a pattern that can be read back with the aid of light, usually a beam of laser light precisely focused on a spinning optical disc. An older example of optical storage that does not require the use of computers, is microform. There are other means of optically storing data and new methods are in developmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holographic Display
A holographic display is a type of 3D display that utilizes light diffraction to display a three-dimensional image to the viewer. Holographic displays are distinguished from other forms of 3D displays in that they do not require the viewer to wear any special glasses or use external equipment to be able to see the image, and do not cause a vergence-accommodation conflict. Some commercially available 3D displays are advertised as being holographic, but are actually multiscopic. Timeline 1947 – Hungarian scientist Dennis Gabor first came up with the concept of a hologram while trying to improve the resolution of electron microscopes. He derived the name for holography, with "holos" being the Greek word for "whole," and "gramma" which is the term for "message." 1960 – The world's first laser was developed by soviet scientists Nikolay Basov and Alexander Prokhorov, and American scientist Charles H. Townes. This was a major milestone for holography because laser technology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction Gratings
Diffraction is the deviation of waves from straight-line propagation without any change in their energy due to an obstacle or through an aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the propagating wave. Diffraction is the same physical effect as interference, but interference is typically applied to superposition of a few waves and the term diffraction is used when many waves are superposed. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word ''diffraction'' and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1660. In classical physics, the diffraction phenomenon is described by the Huygens–Fresnel principle that treats each point in a propagating wavefront as a collection of individual spherical wavelets. The characteristic pattern is most pronounced when a wave from a coherent source (such as a laser) encounters a slit/aperture that is comparable in size to its wavelength, as shown in the inserted image. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |