|
Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein A2
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins A2/B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HNRNPA2B1'' gene. Structure ''HNRNPA2B1'' gene contains 12 exons, including a B1 protein specific 36-nucleotide mini-exon. The entire length of intron/exon organization of ''HNRNPA2B1'' is identical to that of the ''HNRNPA1'' gene which indicates a common origin by gene duplication. Function This gene belongs to the A/B subfamily of ubiquitously expressed heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs). The hnRNPs are RNA binding proteins and they complex with heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA). These proteins are associated with pre-mRNAs in the nucleus and appear to influence pre-mRNA processing and other aspects of mRNA metabolism and transport. While all of the hnRNPs are present in the nucleus, some seem to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The hnRNP proteins have distinct nucleic acid binding properties. The protein encoded by this gene has two repeats of quasi-R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HNRNPA1
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HNRNPA1'' gene. Mutations in hnRNP A1 are causative of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and the syndrome multisystem proteinopathy. Function This gene belongs to the A/B subfamily of ubiquitously expressed heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs). The hnRNPs are RNA binding proteins and they complex with heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA). These proteins are associated with pre-mRNAs in the nucleus and appear to influence pre-mRNA processing and other aspects of mRNA metabolism and transport. While all of the hnRNPs are present in the nucleus, some seem to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The hnRNP proteins have distinct nucleic acid binding properties. The protein encoded by this gene has two repeats of quasi- RRM domains that bind to RNAs in the N-terminal domain which are pivotal for RNA specificity and binding. The protein also has a glycine rich arginine-glycin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves, and blood. This may result in a anemia, low red blood cell count, pleurisy, inflammation around the lungs, and pericarditis, inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves the body's immune system attacking the joints. This results in inflammation and thickening of the synovium, joint capsule. It also affects the und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus, formally called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, feeling tired, and a red rash which is most commonly on the face. Often there are periods of illness, called flares, and periods of remission during which there are few symptoms. Children up to 18 years old develop a more severe form of SLE termed childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. The cause of SLE is not clear. It is thought to involve a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Among identical twins, if one is affected there is a 24% chance the other one will also develop the disease. Female sex hormones, sunlight, smoking, vitamin D deficiency, and certain infections are also believed to increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease
Mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) is a systemic autoimmune disease that shares characteristics with at least two other systemic autoimmune diseases, including Systemic scleroderma, systemic sclerosis (Ssc), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), polymyositis/dermatomyositis (PM/DM), and rheumatoid arthritis. The idea behind the "mixed" disease is that this specific autoantibody is also present in other autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, polymyositis, scleroderma, etc. MCTD was characterized as an individual disease in 1972 by Sharp et al., and the term was introduced by Leroy in 1980. Some experts consider MCTD to be the same as undifferentiated connective tissue disease, but other experts specifically reject this idea because undifferentiated connective tissue disease is not necessarily associated with serum antibodies directed against the U1-RNP. Furthermore, MCTD is associated with a more clearly defined set of signs and symptoms. Signs and symptoms T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoantigen
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". Prominent examples include celiac disease, diabetes mellitus type 1, Henoch–Schönlein purpura, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Graves' disease, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, Addison's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, and multiple sclerosis. Autoimmune diseases are very often treated with steroids. Autoimmunity means presence of antibodies or T cells that react with self-protein and is present in all individuals, even in normal health state. It causes autoimmune diseases if self-reactivity can lead to tissue damage. History In the later 19th century, it was believed that the immune sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RA33
RA33, also known as heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1, is an autoantigen in human systemic autoimmune diseases. In 1989, a novel class of autoantibodies was detected in sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), which were directed against a protein with an estimated molecular mass of 33 kDa in nuclear extracts from HeLa cells. The antigen was therefore named RA33. Protein sequencing of highly purified RA33 revealed that it was identical to hetergoneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 (hnRPA2B1). Nowadays, the name anti-RA33 defines autoantibodies that are directed against hnRNP A2 and its splice variant hnRNP B1. Anti-RA33 occur in approximately 15-35% of patients with RA, in 20-25% of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and in 35-40% of patients with mixed connective tissue disease, being rare or absent in other forms of arthritis. Anti-RA33 antibodies can be easily detected by immunoblotting employing crude nuclear extracts or the recombinant antigen. ELI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casein Kinase 2, Alpha 1
Casein kinase II subunit alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CSNK2A1'' gene. Casein kinase II is a serine/threonine protein kinase that phosphorylates acidic proteins such as casein. The kinase exists as a tetramer and is composed of an alpha, an alpha-prime, and two beta subunits. The alpha subunits contain the catalytic activity while the beta subunits undergo autophosphorylation. The protein encoded by this gene represents the alpha subunit. While this gene is found on chromosome 20, a related transcribed pseudogene is found on chromosome 11. Three transcript variants encoding two different proteins have been found for this gene. Interactions Casein kinase 2, alpha 1 has been shown to interact with: * APC, * ATF1, * ATF2, * C-Fos, * C-jun, * CDC25B, * CHEK1, * CREBBP, * CSNK2B, * DDIT3, * FGF1, * FGF2, * HNRPA2B1 * MAPK14, * PIN1, * PLEKHO1, * PTEN, * RELA, * TAF1 Transcription initiation factor TFIID subunit 1, also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paget's Disease Of Bone
Paget's disease of bone (commonly known as Paget's disease or, historically, osteitis deformans) is a condition involving Bone remodeling, cellular remodeling and deformity of one or more bones. The affected bones show signs of dysregulated bone remodeling at the microscopic level, specifically excessive Osteoclast, bone breakdown and subsequent disorganized new bone formation. These structural changes cause the bone to weaken, which may result in deformity, pain, bone fractures, fracture or arthritis of associated joints. The exact cause is unknown, although leading theories indicate both genetic and acquired factors (see #Causes, Causes). Paget's disease may affect any one or several bones of the body (most commonly pelvis, tibia, femur, lumbar vertebrae, and skull), but never the entire skeleton, and does not spread from bone to bone. Rarely, a bone affected by Paget's disease can transform into a Osteosarcoma, malignant bone cancer. As the disease often affects people diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
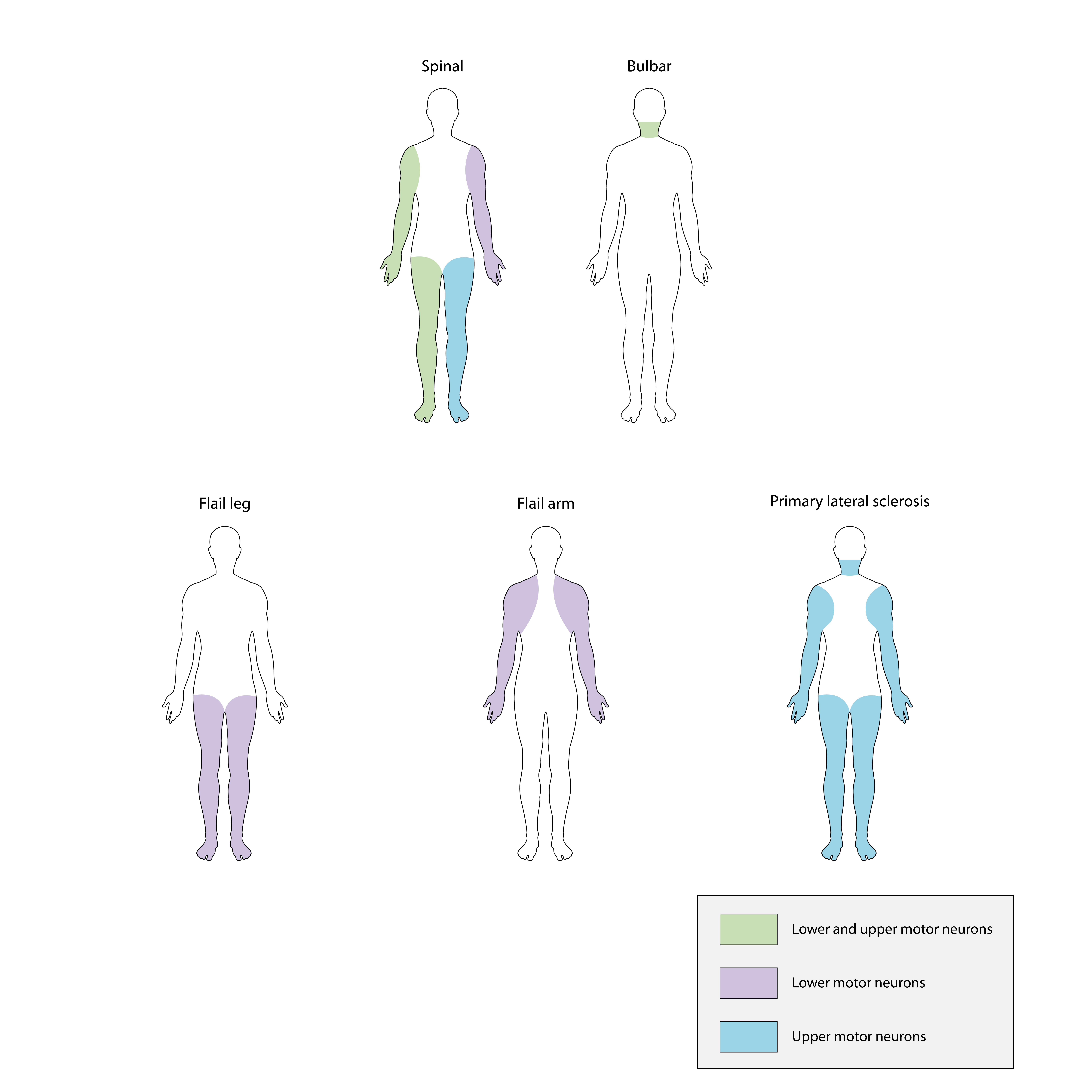
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control Skeletal muscle, voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle Spasticity, stiffness, Fasciculation, twitches, Muscle weakness, weakness, and Muscle atrophy, wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with cognitive disorder, thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as ''limb-onset'' (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |