|
Hemorheology
Hemorheology, also spelled haemorheology (''haemo'' from Greek ‘αἷμα, ''haima'' 'blood'; and ''rheology'', from Greek ῥέω ''rhéō'', ' flow' and -λoγία, ''-logia'' 'study of'), or blood rheology, is the study of flow properties of blood and its elements of plasma and cells. Proper tissue perfusion can occur only when blood's rheological properties are within certain levels. Alterations of these properties play significant roles in disease processes. Blood viscosity is determined by plasma viscosity, hematocrit (volume fraction of red blood cell, which constitute 99.9% of the cellular elements) and mechanical properties of red blood cells. Red blood cells have unique mechanical behavior, which can be discussed under the terms erythrocyte deformability and erythrocyte aggregation. Because of that, blood behaves as a non-Newtonian fluid. As such, the viscosity of blood varies with shear rate. Blood becomes less viscous at high shear rates like those experienced w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
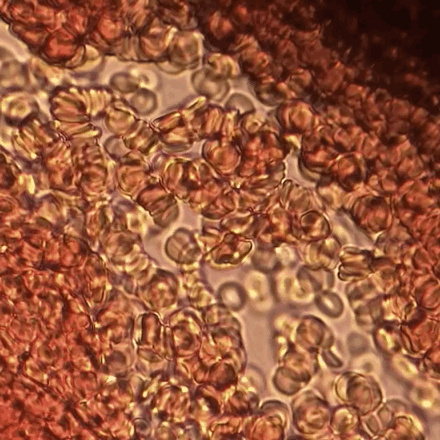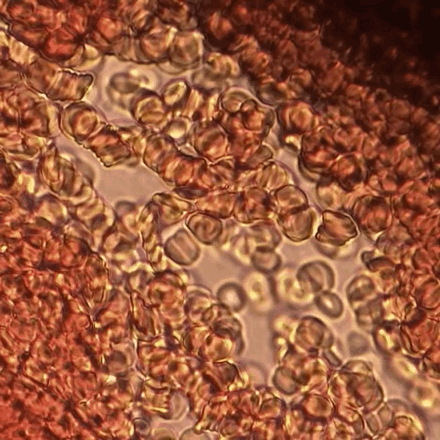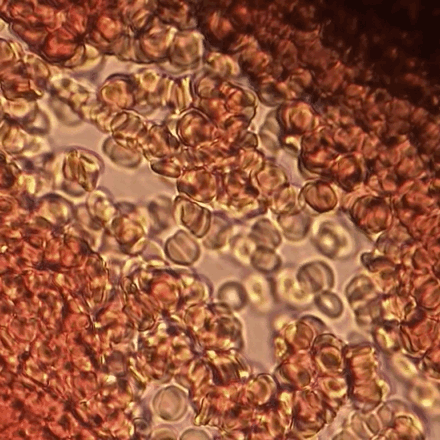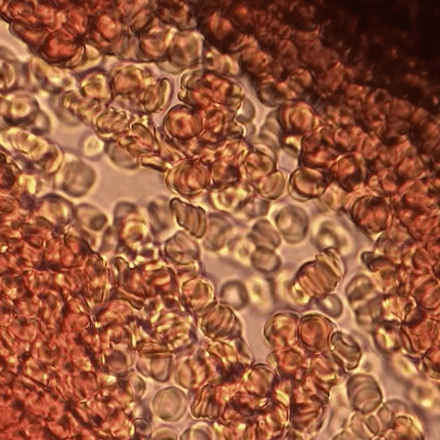
Erythrocyte Aggregation
Erythrocyte aggregation is the reversible clumping of red blood cells (RBCs) under low shear forces or at stasis. Erythrocytes aggregate in a special way, forming rouleaux. Rouleaux are stacks of erythrocytes which form because of the unique discoid shape of the cells in vertebrate body. The flat surface of the discoid RBCs give them a large surface area to make contact and stick to each other; thus, forming a rouleau. Rouleaux formation takes place only in suspensions of RBC containing high-molecular, fibrilar proteins or polymers in the suspending medium (often Dextran-2000 in-vitro). The most important protein causing rouleaux formation in plasma is fibrinogen. RBC suspended in simple salt solutions do not form rouleaux. Mechanism Erythrocyte aggregation is a physiological phenomenon that takes places in normal blood under low-flow conditions or at stasis. The presence or increased concentrations of acute phase proteins, particularly fibrinogen, results in enhanced erythrocyte a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythrocyte Deformability
In hematology, erythrocyte deformability refers to the ability of erythrocytes (red blood cells, RBCs) to change shape under a given level of applied stress without hemolysing (rupturing). This is an important property because erythrocytes must change their shape extensively under the influence of mechanical forces in fluid flow or while passing through microcirculation (see hemodynamics). The extent and geometry of this shape change can be affected by the mechanical properties of the erythrocytes, the magnitude of the applied forces, and the orientation of erythrocytes with the applied forces. Deformability is an intrinsic cellular property of erythrocytes determined by geometric and material properties of the cell membrane, although as with many measurable properties the ambient conditions may also be relevant factors in any given measurement. No other cells of mammalian organisms have deformability comparable with erythrocytes; furthermore, non-mammalian erythrocytes are not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma. Plasma, which constitutes 55% of blood fluid, is mostly water (92% by volume), and contains proteins, glucose, mineral ions, and hormones. The blood cells are mainly red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and (in mammals) platelets (thrombocytes). The most abundant cells are red blood cells. These contain hemoglobin, which facilitates oxygen transport by reversibly binding to it, increasing its solubility. Jawed vertebrates have an adaptive immune system, based largely on white blood cells. White blood cells help to resist infections and parasites. Platelets are important in the clotting of blood. Blood is circulated around the body through blood vessels by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheology
Rheology (; ) is the study of the flow of matter, primarily in a fluid (liquid or gas) state but also as "soft solids" or solids under conditions in which they respond with plastic flow rather than deforming elastically in response to an applied forcRheology is the branch of physics that deals with the deformation and flow of materials, both solids and liquids.W. R. Schowalter (1978) Mechanics of Non-Newtonian Fluids Pergamon The term '' rheology'' was coined by Eugene C. Bingham, a professor at Lafayette College, in 1920 from a suggestion by a colleague, Markus Reiner.The Deborah Number The term was inspired by the aphorism of Heraclitus (often mistakenly attributed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythrocyte Deformability
In hematology, erythrocyte deformability refers to the ability of erythrocytes (red blood cells, RBCs) to change shape under a given level of applied stress without hemolysing (rupturing). This is an important property because erythrocytes must change their shape extensively under the influence of mechanical forces in fluid flow or while passing through microcirculation (see hemodynamics). The extent and geometry of this shape change can be affected by the mechanical properties of the erythrocytes, the magnitude of the applied forces, and the orientation of erythrocytes with the applied forces. Deformability is an intrinsic cellular property of erythrocytes determined by geometric and material properties of the cell membrane, although as with many measurable properties the ambient conditions may also be relevant factors in any given measurement. No other cells of mammalian organisms have deformability comparable with erythrocytes; furthermore, non-mammalian erythrocytes are not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheological
Rheology (; ) is the study of the flow of matter, primarily in a fluid (liquid or gas) state but also as "soft solids" or solids under conditions in which they respond with plastic flow rather than deforming elastically in response to an applied forcRheology is the branch of physics that deals with the deformation and flow of materials, both solids and liquids.W. R. Schowalter (1978) Mechanics of Non-Newtonian Fluids Pergamon The term ''rheology'' was coined by Eugene C. Bingham, a professor at Lafayette College, in 1920 from a suggestion by a colleague, Markus Reiner.The Deborah Number The term was inspired by the of |
American And British English Spelling Differences
Despite the various list of dialects of English, English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable variations being British and American spelling. Many of Comparison of American and British English, the differences between American English, American and British English, British or English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English date back to a time before spelling standards were developed. For instance, some spellings seen as "American" today were once commonly used in Britain, and some spellings seen as "British" were once commonly used in the United States. A "British standard" began to emerge following the 1755 publication of Samuel Johnson's ''A Dictionary of the English Language'', and an "American standard" started following the work of Noah Webster and, in particular, his ''Webster's Dictionary, An American Dictionary of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venous Return Curve
Venous return is the rate of blood flow back to the heart. It normally limits cardiac output. Superposition of the cardiac function curve and venous return curve is used in one hemodynamic model. __TOC__ Physiology Venous return (VR) is the flow of blood back to the heart. Under steady-state conditions, venous return must equal cardiac output (Q), when averaged over time because the cardiovascular system is essentially a closed loop. Otherwise, blood would accumulate in either the systemic or pulmonary circulations. Although cardiac output and venous return are interdependent, each can be independently regulated. The circulatory system is made up of two circulations (pulmonary and systemic) situated in series between the right ventricle (RV) and left ventricle (LV). Balance is achieved, in large part, by the Frank–Starling mechanism. For example, if systemic venous return is suddenly increased (e.g., changing from upright to supine position), right ventricular preload increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the thorax, chest, called the mediastinum. In humans, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right Atrium (heart), atria and lower left and right Ventricle (heart), ventricles. Commonly, the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. In a healthy heart, blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent cardiac regurgitation, backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preload (cardiology)
In cardiac physiology, preload is the amount of sarcomere stretch experienced by cardiac muscle cells, called cardiomyocytes, at the end of ventricular filling during diastole. Preload is directly related to ventricular filling. As the relaxed ventricle fills during diastole, the walls are stretched and the length of sarcomeres increases. Sarcomere length can be approximated by the volume of the ventricle because each shape has a conserved surface-area-to-volume ratio. This is useful clinically because measuring the sarcomere length is destructive to heart tissue. It requires cutting out a piece of cardiac muscle to look at the sarcomeres under a microscope. It is currently not possible to directly measure preload in the beating heart of a living animal. Preload is estimated from end-diastolic ventricular pressure and is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Estimating preload Though not exactly equivalent to the strict definition of ''preload,'' end-diastolic volume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |