|
Haplogroup G (mtDNA)
In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup G is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. Origin Haplogroup G is a descendant of haplogroup M. Haplogroup G is divided into subclades G1, G2, G3, and G4. Distribution It is an East Asian haplogroup. Today, haplogroup G is found at its highest frequency in indigenous populations of the lands surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk.mtDNA Haplogroup Testing Haplogroup G is one of the most common mtDNA haplogroups among modern Ainu, Siberian, Mongol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Mitochondrial DNA Haplogroup
In human genetics, a human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by differences in human mitochondrial DNA. Haplogroups are used to represent the major branch points on the mitochondrial phylogenetic tree. Understanding the evolutionary path of the female lineage has helped population geneticists trace the matrilineal inheritance of modern humans back to human origins in Africa and the subsequent spread around the globe. The letter names of the haplogroups (not just mitochondrial DNA haplogroups) run from A to Z. As haplogroups were named in the order of their discovery, the alphabetical ordering does not have any meaning in terms of actual genetic relationships. The hypothetical woman at the root of all these groups (meaning just the mitochondrial DNA haplogroups) is the matrilineal most recent common ancestor (MRCA) for all currently living humans. She is commonly called Mitochondrial Eve. The rate at which mitochondrial DNA mutates is known as the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Japan, Japan, Economy of South Korea, South Korea, and Economy of Taiwan, Taiwan are among the world's largest and most prosperous. East Asia borders North Asia to the north, Southeast Asia to the south, South Asia to the southwest, and Central Asia to the west. To its east is the Pacific Ocean. East Asia, especially History of China, Chinese civilization, is regarded as one of the earliest Cradle of civilization#China, cradles of civilization. Other ancient civilizations in East Asia that still exist as independent countries in the present day include the History of Japan, Japanese, History of Korea, Korean, and History of Mongolia, Mongolian civilizations. Various other civilizations existed as independent polities in East Asia in the past ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
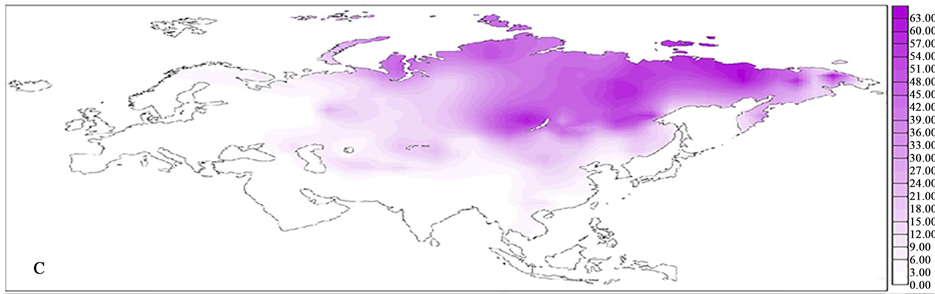
Haplogroup C (mtDNA)
In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup C is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. Origin Haplogroup C is believed to have arisen in East Asia some 24,000 years before present. It is a descendant of the haplogroup M. Haplogroup C shares six mutations downstream of the MRCA of haplogroup M with haplogroup Z and five mutations downstream of the MRCA of haplogroup M with other members of haplogroup M8. This macro-haplogroup is known as haplogroup M8'CZ or simply as haplogroup M8. Distribution Haplogroup C is found in Northeast Asia (including Siberia) and the Americas. In Eurasia, Haplogroup C is especially frequent among populations of arctic Siberia, such as Nganasans, Dolgans, Yakuts, Evenks, Evens, Yukaghirs, and Koryaks. Haplogroup C is one of five mtDNA haplogroups found in the indigenous peoples of the Americas, the others being A, B, D, and X. The subclades C1b, C1c, C1d, and C4c are found in the first people of the Americas. C1a is found only in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR), often shortened to Tibet in English or Xizang in Pinyin, Hanyu Pinyin, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China. It was established in 1965 to replace the Tibet Area (administrative division), Tibet Area, a former administrative division of the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. The current borders of the Tibet Autonomous Region were generally established in the 18th century and include about half of Tibet, cultural Tibet, which was at times independent and at times under Mongol or Chinese rule. The TAR spans more than and is the second-largest Administrative divisions of China, province-level division of China by area. Due to its harsh and rugged terrain, it has a total population of only 3.6 million people or approximately . Names and etymologies Tibet Autonomous Region is often shortened to Tibet in English or Xizang in Hanyu Pinyin. The earliest official record of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lhasa Prefecture
Lhasa is a prefecture-level city, one of the main administrative divisions of the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It covers an area of of rugged and sparsely populated terrain. Its urban center is Lhasa, with around 300,000 residents, which mostly corresponds with the administrative Chengguan District, while its suburbs extend into Doilungdêqên District and Dagzê District. The consolidated prefecture-level city contains an additional five, mostly rural, counties. The city boundaries roughly correspond to the basin of the Lhasa River, a major tributary of the Yarlung Tsangpo, Yarlung Tsangpo River. It lies on the Lhasa terrane, the last unit of crust to accrete to the Eurasian plate before the continent of India collided with Asia about 50 million years ago and pushed up the Himalayas. The terrain is high, contains a complex pattern of faults and is tectonically active. The temperature is generally warm in summer and rises above freezing on sunny days in winter. Most of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakhs
The Kazakhs (Kazakh language, Kazakh: , , , ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia and Eastern Europe. They share a common Culture of Kazakhstan, culture, Kazakh language, language and History of Kazakhstan, history that is closely related to those of other Turkic peoples of Western and Central Asia. The majority of ethnic Kazakhs live in their transcontinental nation state of Kazakhstan. Ethnic Kazakh communities are present in Kazakhstan's border regions in Russia, northern Uzbekistan, northwestern China (Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture), western Mongolia (Bayan-Ölgii Province) and Iran (Golestan province). The Kazakhs arose from the merging of various medieval tribes of Turkic and Mongolic origin in the 15th century. Kazakh identity was shaped following the foundation of the Kazakh Khanate between 1456 and 1465, when following the disintegration of the Turkification, Turkified state of Golden Horde, several tribes under the rule of the sultans J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitwan District
Chitwan District (, , ) is one of seventy-seven districts of Nepal, and takes up the southwestern corner of Bagmati Province. Bharatpur, largest city of Nepal after Kathmandu, is its administrative centre. It covers , and in 2011 had a population of 579,984 (279,087 male and 300,897 female) people. Bharatpur is the commercial and service centre of South Central Nepal and a major destination for higher education, health care and transportation in the region. Chitwan lies in the Terai region of Nepal. It is in the drainage basin of the Gandaki River and is roughly triangular, taking that river as its meandering northwestern border, and a modest watershed border, with India, as the basis of its southern limit. Local government: Bharatpur Metropolitan, Rapti Municipality, Ratnanagar Municipality, Kalika Municipality, Khairahani Municipality, Madi Municipality, Ikshyakamana Gaupalika History The district takes its name from the Chitwan Valley, one of Nepal's Inner Terai valleys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tharu People
The Tharu people are an ethnic group living in the Terai in southern Nepal and northern India. They speak Tharu languages. They are recognized as an official ethnicity by the Government of Nepal. In the Indian Terai, they live foremost in Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. The Government of India recognizes the Tharu people as a Scheduled Tribes in India, scheduled Indian tribe. Etymology The word (''thāru'') is thought to be derived from ''Sthavira nikāya, sthavir'' meaning follower of Theravada Buddhism. The Tharu people in the central Nepali Terai see themselves as the original people of the land and descendants of Gautama Buddha. Rana Tharu people of western Nepal connect the name to the Thar Desert and understand themselves as descendants of Rajputs who migrated to the forests in the 16th century. Possible is also that the name is derived from the classical Tibetan words ''mtha'-ru'i brgyud'', meaning the 'country at the border', which the Tibetan scholar Taranatha u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negidals
Negidals (, "local people"; , ''negidaltsy'') are an Indigenous ethnic group in the Khabarovsk Krai in Russia, who live along the Amgun River and Amur River. The ethnonym "Negidal" is a Russian rendering of the Ewenki term ''ngegida'', which means "coastal people". Distribution Negidals are an indigenous ethnic group inhabiting the lower reaches of Amgun River (formerly also living in the Amur River region) in Priamurye, Russian Far East. Nowadays, the majority of Negidals live in Ulchskiy District and, to a lesser extent, in Imeni Poliny Osipenko District (mostly in Vladimirovka village) in Khabarovsk Krai; a number of Negidal families also live in Nikolayevsky, Nanaisky and other districts.Negidals have been a small indigenous community in the Russian Far East since the first population censuses, as demonstrated by the Negidal Population Table. A major drawback of most censuses is the insufficient coverage of the Negidal population, in particular, the Soviet censuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chukotka Autonomous Okrug
Chukotka ( ; ), officially the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, is the easternmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia. It is an Autonomous okrugs of Russia, autonomous okrug situated in the Russian Far East, and shares a border with the Sakha Republic to the west, Magadan Oblast to the south-west, and Kamchatka Krai to the south, as well as a Maritime boundary, maritime border on the Bering Strait with the U.S. state of Alaska to the east. Anadyr (town), Anadyr is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, town and the administrative center, capital, and the easternmost settlement to have town status in Russia. It is the closest point from Russia to the United States, measuring at 88.51 kilometres or 55 miles. Chukotka is primarily populated by ethnic Russians, Chukchi people, Chukchi, and other Indigenous peoples of Siberia, indigenous peoples. It is the only autonomous okrug in Russia that is not included in, or subordinate to, another federal subject, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markovo, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug
Markovo (; Chukchi language, Chukchi: , ''Ujvyn'' / ''Gujgun'', lit. ''wooden hut'';Leontyev and Novikova, p. 329 Koryak language, Koryak: , ''Vujvәn'', lit. ''big village'') is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, rural locality (a ''village#Russia, selo'') in Anadyrsky District of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, located near the head of small-boat navigation of the Anadyr River. As of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census, its population was 809.The results of the 2010 Census and the 2018 estimate are given for Markovo Rural Settlement, a municipal formation of Anadyrsky Municipal District. According to Law #148-OZ, Markovo is the only inhabited locality on the territory of Markovo Rural Settlement. A small locality now—albeit still quite large by Chukotkan standards—Markovo had historically been an important trade hub during the early period of Cossacks, Cossack exploration. Geography Markovo is situated in the middle reaches of the Anadyr River, the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chuvans
Chuvans () are one of the forty or so "Indigenous small-numbered peoples of the North, Siberia and the Far East" recognized by the Russian government. Most Chuvans today live within Chukotka Autonomous Okrug in the far northeast of Russia. Based on first-hand field research by several ethnographers in the 1990s, people who self-identify as Chuvans seem to do so by living in small villages and in the tundra in areas that are primarily associated with reindeer herding. History Historical accounts describe the Chuvans as a Yukaghir people, Yukaghir group. They roamed along the upper tributaries of the Anadyr River and Anyuy River (Chukotka), Anyuy River in the 17th century. The Chuvans were engaged in hunting, fishing and reindeer-breeding. In the 18th century, some Chuvans retreated to the Kolyma River following attacks by the Chukchi people, Chukchi. There, they gradually Russification, russified. The other part was assimilated by the Koryaks and Chukchis. According to the 2002 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |