|
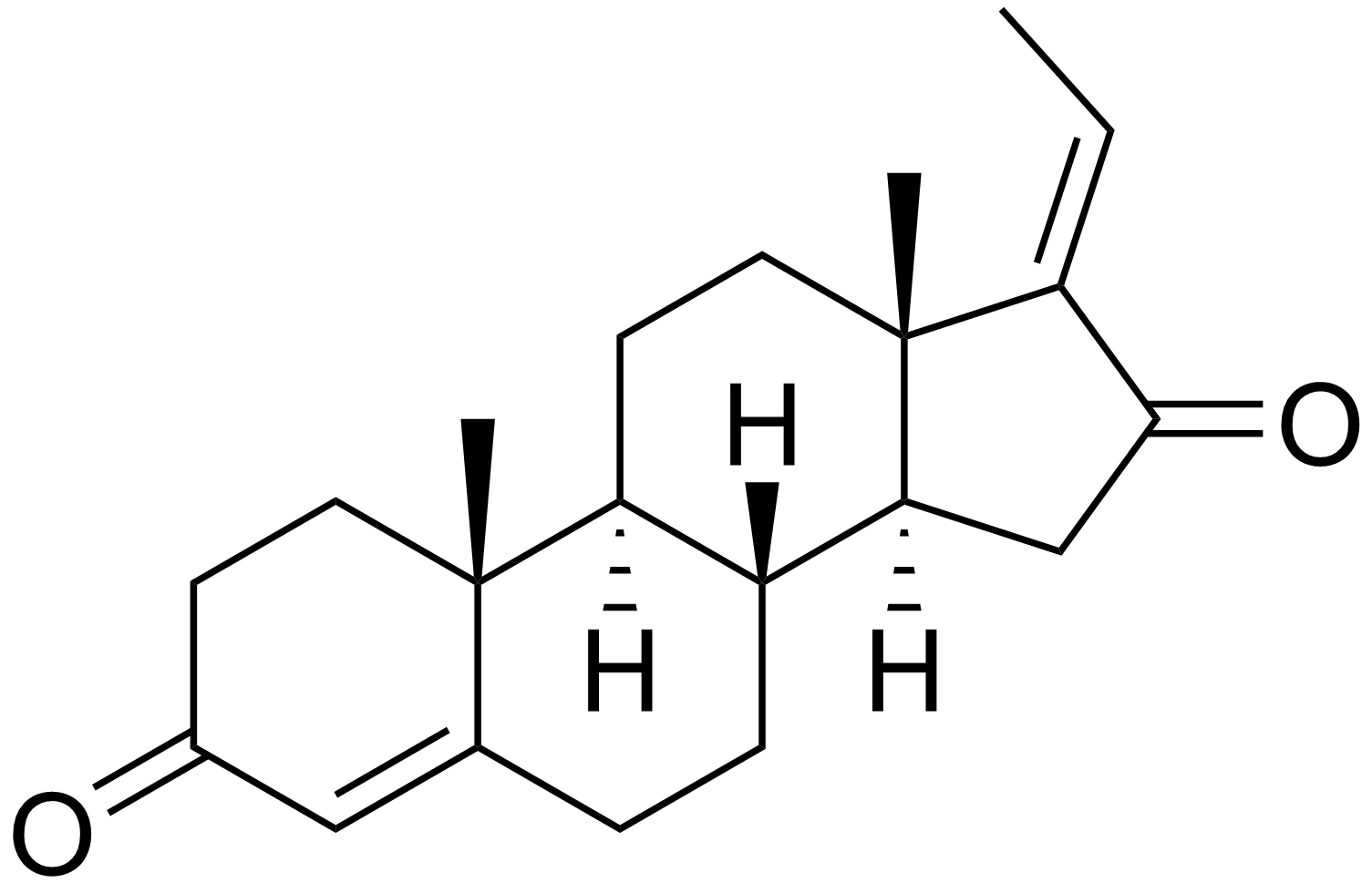
Guggulsterone
Guggulsterone is a phytosteroid found in the resin of the guggul plant, ''Commiphora mukul''. Guggulsterone can exist as either of two stereoisomers, ''E''-guggulsterone and ''Z''-guggulsterone. In humans, it acts as an antagonist of the farnesoid X receptor, which was once believed to result in decreased cholesterol synthesis in the liver. Several studies have been published that indicate no overall reduction in total cholesterol occurs using various dosages of guggulsterone, and levels of low-density lipoprotein ("bad cholesterol") increased in many people. Nevertheless, guggulsterone is an ingredient in many nutritional supplements. Guggulsterone was also found to have interactions with the viral ADP ribose phosphatase enzyme of SARS-CoV-2 and has been proposed as a potential candidate for the development of therapeutics for the treatment of COVID-19. Guggulsterone is a broad-spectrum ligand of steroid hormone receptors, and is known to possess the following activities: * Min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commiphora Wightii
''Commiphora wightii'', with common names Indian bdellium-tree, gugal, guggal, guggul, gugul, or mukul myrrh tree, is a flowering plant in the family Burseraceae, which produces a fragrant resin called gugal, guggul or gugul, that is used in incense and vedic medicine (or ayurveda). The species is native to western India, from where it was introduced westward to southern Pakistan and the middle-east. It prefers arid and semi-arid climates and is tolerant of poor soil. Description ''Commiphora wightii'' grows as a shrub or small tree, reaching a maximum height of , with thin papery bark. The branches are thorny. The leaves are simple or trifoliate, the leaflets ovate, long, broad, and irregularly toothed. It is gynodioecious, with some plants bearing bisexual and male flowers, and others with female flowers. The individual flowers are red to pink, with four small petals. The small round fruit are red when ripe. Cultivation and uses ''Commiphora wightii'' is sought for its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytosteroid
Phytosteroids, also known as plant steroids, are natural product, naturally occurring steroids that are found in plants. Examples include digoxin, digitoxin, diosgenin, and guggulsterone, as well as phytosterols like β-sitosterol. Industrial use Steroid pharmaceuticals that are identical or similar to human steroid hormones are very widely used in medicine. However, the four-ring structure of a steroid is quite expensive to replicate using direct synthetic methods. In 1938–1940, American chemist Russell Earl Marker developed the process known as Marker degradation, which converts diosgenin from Mexican ''Dioscorea'' yams into 16-dehydropregnenolone acetate, which has a four-ring structure and can be used to synthesize commonly used steroid hormones. Marker's process reduced the price of progesterone from $80/gram in early 1944 to $2/gram in 1951. Also in 1940, American chemist Percy Lavon Julian discovered a process to convert a much more abundant phytosteroid -- stigmast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Androgen Receptor
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 4), is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone, in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the Cell nucleus, nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor. The main function of the androgen receptor is as a DNA-binding protein, DNA-binding transcription factor that Gene expression regulation, regulates gene expression; however, the androgen receptor has other functions as well. Androgen-regulated genes are critical for the development and maintenance of the male sexual phenotype. Function Effect on development In some cell types, testosterone interacts directly with androgen receptors, whereas, in others, testosterone is converted by 5-alpha reductase, 5-alpha-reductase to dihydrot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemistry, biochemical and physiology, physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms (for example, infection). Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics are the main branches of pharmacology, being itself a topic of biology interested in the study of the interactions of both endogenous and exogenous chemical substances with living organisms. In particular, pharmacodynamics is the study of how a drug affects an organism, whereas pharmacokinetics is the study of how the organism affects the drug. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects. Pharmacodynamics is sometimes abbreviated as PD and pharmacokinetics as PK, especially in combined reference (for example, when speaking of PK/PD models). Pharmacodynamics places particular emphasis on dose–response relationships, that is, the relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacokinetic
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to describing how the body affects a specific substance after administration. The substances of interest include any chemical xenobiotic such as pharmaceutical drugs, pesticides, food additives, cosmetics, etc. It attempts to analyze chemical metabolism and to discover the fate of a chemical from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body. Pharmacokinetics is based on mathematical modeling that places great emphasis on the relationship between drug plasma concentration and the time elapsed since the drug's administration. Pharmacokinetics is the study of how an organism affects the drug, whereas pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of how the drug affects the organism. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Half-life
Biological half-life (elimination half-life, pharmacological half-life) is the time taken for concentration of a drug, biological substance (such as a medication) to decrease from its maximum concentration (chemistry), concentration (Cmax (pharmacology), Cmax) to half of Cmax in the blood plasma. It is denoted by the abbreviation t_. This is used to measure the removal of things such as metabolites, drugs, and signalling molecules from the body. Typically, the biological half-life refers to the body's natural detoxification (cleansing) through liver metabolism and through the excretion of the measured substance through the kidneys and intestines. This concept is used when the rate of removal is roughly Exponential function, exponential. In a medical context, half-life explicitly describes the time it takes for the blood plasma concentration of a substance to halve (''plasma half-life'') its steady-state when circulating in the full blood of an organism. This measurement is usefu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as Injection (medicine), injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth". The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally (but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation. By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. However, when a medication is administered via routes other than intravenous, its bioavailability is lower due to intestinal epithelium absorption and first-pass metabolism. Thereby, mathematically, bioavailability equals the ratio of comparing the area under the plasma drug concentration curve versus time (AUC) for the extravascular formulation to the AUC for the intravascular formulation. AUC is used because AUC is proportional to the dose that has entered the systemic circulation. Bioavailability of a drug is an average value; to take population variability into account, deviation range is shown as ±. To ensure that the drug taker who has poor absorption is dosed appropriately, the bottom value of the deviation range is employed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Research
Animal testing, also known as animal experimentation, animal research, and ''in vivo'' testing, is the use of animals, as model organisms, in experiments that seek answers to scientific and medical questions. This approach can be contrasted with field studies in which animals are observed in their natural environments or habitats. Experimental research with animals is usually conducted in universities, medical schools, pharmaceutical companies, defense establishments, and commercial facilities that provide animal-testing services to the industry. The focus of animal testing varies on a continuum from Basic research, pure research, focusing on developing fundamental knowledge of an organism, to applied research, which may focus on answering some questions of great practical importance, such as finding a cure for a disease. Examples of applied research include testing disease treatments, breeding, defense research, and Toxicology testing, toxicology, including Testing cosmetics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnane X Receptor
In the field of molecular biology, the pregnane X receptor (PXR), also known as the steroid and xenobiotic sensing nuclear receptor (SXR) or nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 2 (NR1I2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NR1I2'' (nuclear Receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 2) gene. Function PXR is a nuclear receptor whose primary function is to sense the presence of foreign toxic substances and in response up regulate the expression of proteins involved in the detoxification and clearance of these substances from the body. PXR belongs to the nuclear receptor superfamily, members of which are transcription factors characterized by a ligand-binding domain and a DNA-binding domain. PXR is a transcriptional regulator of the cytochrome P450 gene CYP3A4, binding to the response element of the CYP3A4 promoter as a heterodimer with the 9-cis retinoic acid receptor RXR. It is activated by a range of compounds that induce CYP3A4, including dexamethasone and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IC50
Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is a measure of the potency of a substance in inhibiting a specific biological or biochemical function. IC50 is a quantitative measure that indicates how much of a particular inhibitory substance (e.g. drug) is needed to inhibit, ''in vitro'', a given biological process or biological component by 50%. The biological component could be an enzyme, cell, cell receptor or microbe. IC50 values are typically expressed as molar concentration. IC50 is commonly used as a measure of antagonist drug potency in pharmacological research. IC50 is comparable to other measures of potency, such as EC50 for excitatory drugs. EC50 represents the dose or plasma concentration required for obtaining 50% of a maximum effect ''in vivo''. IC50 can be determined with functional assays or with competition binding assays. Sometimes, IC50 values are converted to the pIC50 scale. :\ce = -\log_ \ce Due to the minus sign, higher values of pIC50 indicate ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |