|
Gnathochilarium
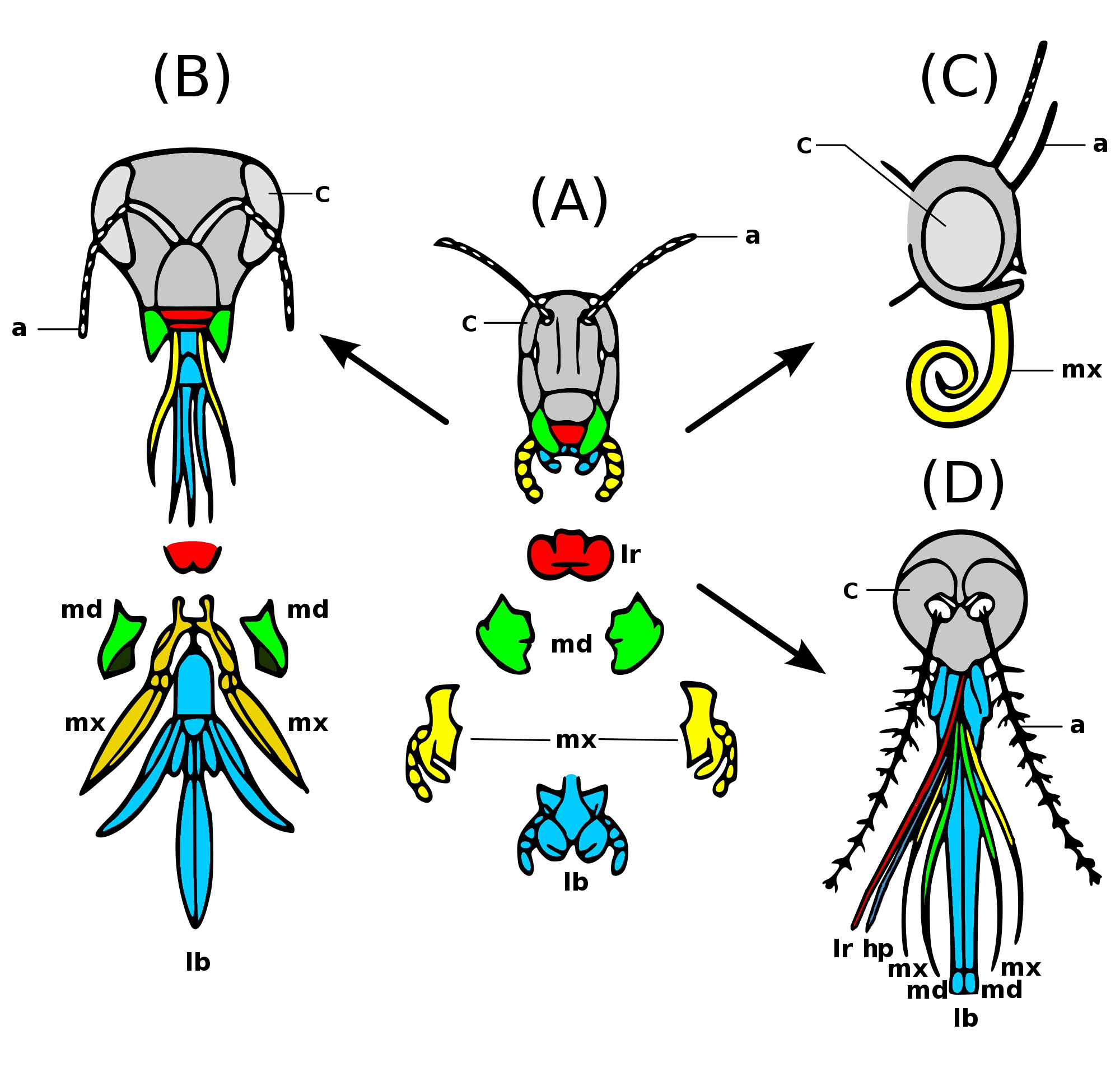
In arthropods, the maxillae (singular maxilla) are paired structures present on the head as mouthparts in members of the clade Mandibulata, used for tasting and manipulating food. Embryologically, the maxillae are derived from the 4th and 5th segment of the head and the maxillary palps; segmented appendages extending from the base of the maxilla represent the former leg of those respective segments. In most cases, two pairs of maxillae are present and in different arthropod groups the two pairs of maxillae have been variously modified. In crustaceans, the first pair are called maxillulae (singular maxillula). Modified coxae at the base of the pedipalps in spiders are also called "maxillae", although they are not homologous with mandibulate maxillae. Myriapoda Millipedes In millipedes, the second maxillae have been lost, reducing the mouthparts to only the first maxillae which have fused together to form a gnathochilarium, acting as a lower lip to the buccal cavity and the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millipede
Millipedes (originating from the Latin , "thousand", and , "foot") are a group of arthropods that are characterised by having two pairs of jointed legs on most body segments; they are known scientifically as the class Diplopoda, the name derived from this feature. Each double-legged segment is a result of two single segments fused together. Most millipedes have very elongated cylindrical or flattened bodies with more than 20 segments, while pill millipedes are shorter and can roll into a tight ball. Although the name "millipede" derives from Latin for "thousand feet", no species was known to have 1,000 or more until the discovery in 2020 of '' Eumillipes persephone'', which can have over 1,300 legs. There are approximately 12,000 named species classified into 16 orders and around 140 families, making Diplopoda the largest class of myriapods, an arthropod group which also includes centipedes and other multi-legged creatures. Most millipedes are slow-moving detritivores, eat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod Mouthparts
The mouthparts of arthropods have evolved into a number of forms, each adapted to a different style or mode of feeding. Most mouthparts represent modified, paired appendages, which in ancestral forms would have appeared more like legs than mouthparts. In general, arthropods have mouthparts for cutting, chewing, piercing, sucking, shredding, siphoning, and filtering. This article outlines the basic elements of four arthropod groups: insects, myriapods, crustaceans and chelicerates. Insects are used as the model, with the novel mouthparts of the other groups introduced in turn. Insects are not, however, the ancestral form of the other arthropods discussed here. Insects Insect mouthparts exhibit a range of forms. The earliest insects had chewing mouthparts. Specialisation includes mouthparts modified for siphoning, piercing, sucking and sponging. These modifications have evolved a number of times. For example, mosquitoes and aphids both pierce and suck; however, female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Malacostracan En
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air and space forces, marines or naval infantry. In some usages, the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. French Revolutionary system Arab system Other variations Other nomenclatures for general officers include the titles and ranks: * Adjutant general * Commandant-general * Inspector general * General-in-chief * General of the Air Force (USAF only) * General of the Armies of the United States (of America), a title created for General John J. Pershing, and subsequently granted posthumously to George Washington and Ulysses S. Grant * (" general admiral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
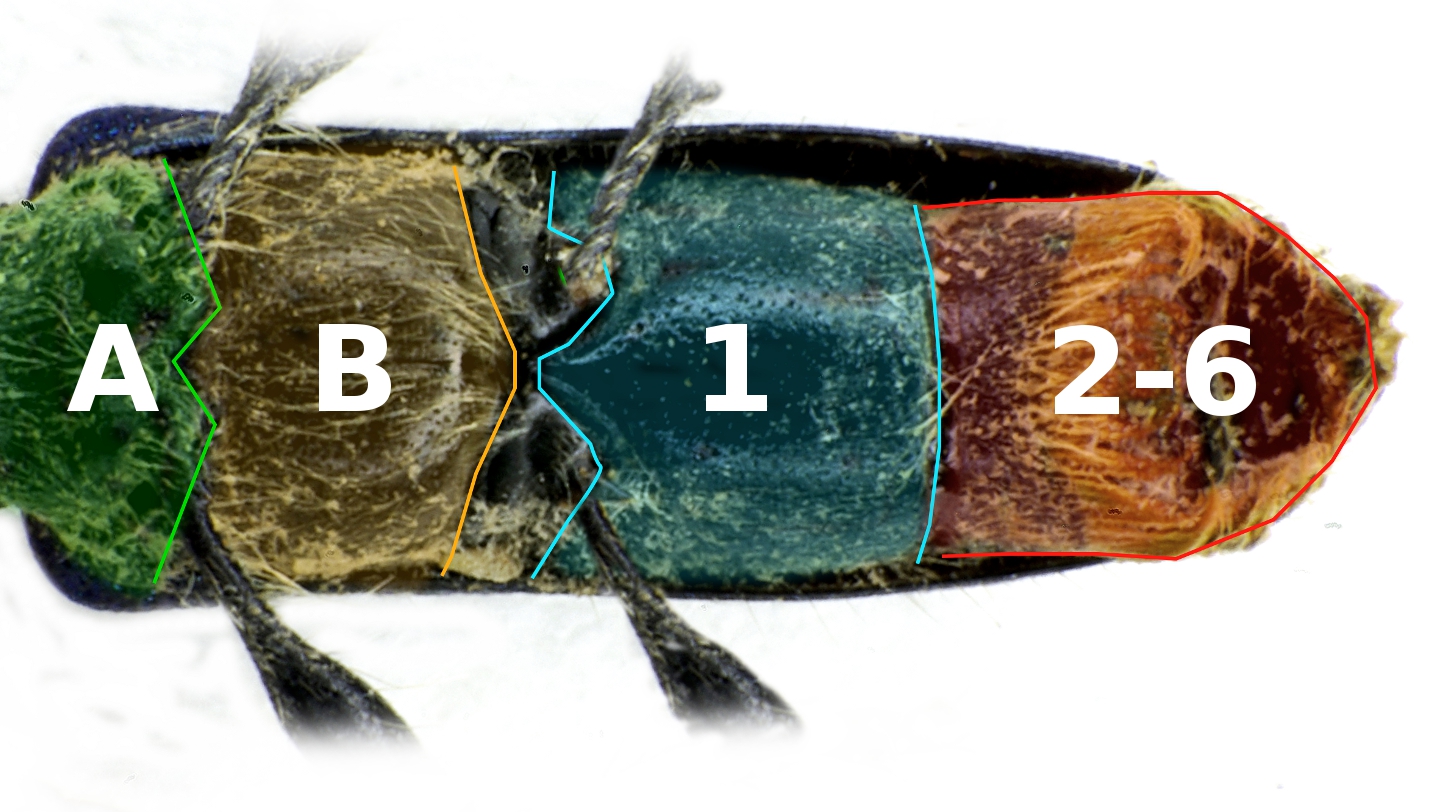
Sternite
The sternum (: sterna) is the ventral portion of a segment of an arthropod thorax or abdomen. In insects, the sterna are usually single, large sclerites, and external. However, they can sometimes be divided in two or more, in which case the subunits are called sternites, and may also be modified on the terminal abdominal segments so as to form part of the functional genitalia, in which case they are frequently reduced in size and development, and may become internalized and/or membranous. For a detailed explanation of the terminology, see Kinorhynchs have tergal and sternal plates too, though seemingly not homologous with those of arthropods.Sørensen, M. V. et al. Phylogeny of Kinorhyncha based on morphology and two molecular loci. PLoS One 10, 1–33 (2015). Ventrites are externally visible sternites. Usually the first sternite is covered up, so that ventrite numbers do not correspond to sternite numbers. The term is also used in other arthropod groups such as crustaceans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod Anatomy
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated ( metameric) segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired ventral nerve cords running through all segments and forming paired ganglia in each segment. Their heads are formed by fusion of varying numbers of segments, and their brains are formed by fusi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nymph (biology)
In biology, a nymph (from Ancient Greek wikt:νύμφα, νύμφα ''nūmphē'' meaning "bride") is the juvenile (organism), juvenile form of some invertebrates, particularly insects, which undergoes gradual metamorphosis (biology), metamorphosis (hemimetabolism) before reaching its adult stage. Unlike a typical larva, a nymph's overall form already resembles that of the adult, except for a lack of wings (in winged species) and the emergence of genitalia. In addition, while a nymph ecdysis, moults, it never enters a pupal stage. Instead, the final moult results in an adult insect. Nymphs undergo multiple stages of development called instars. Taxa with nymph stages Many species of Arthropod, arthropods have nymph stages. This includes the insect orders such as Orthoptera (cricket (insect), crickets, grasshoppers and locusts), Hemiptera (cicadas, shield bugs, Whitefly, whiteflies, aphids, leafhoppers, froghoppers, treehoppers), mayfly, mayflies, termites, cockroaches, mantises, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odonata
Odonata is an order of predatory flying insects that includes the dragonflies and damselflies (as well as the '' Epiophlebia'' damsel-dragonflies). The two major groups are distinguished with dragonflies (Anisoptera) usually being bulkier with large compound eyes together and wings spread up or out at rest, while damselflies (suborder Zygoptera) are usually more slender with eyes placed apart and wings folded together along body at rest. Adult odonates can land and perch, but rarely walk. All odonates have aquatic larvae called naiads or nymphs, and all of them, larvae and adults, are carnivorous and are almost entirely insectivorous, although at the larval stage they will eat anything that they can overpower, including small fish, tadpoles, and even adult newts. The adults are superb aerial hunters and their legs are specialised for catching prey in flight. Odonata in its narrow sense forms a subgroup of the broader Odonatoptera, which contains other dragonfly-like insects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidopterans
Lepidoptera ( ) or lepidopterans is an order (biology), order of winged insects which includes butterflies and moths. About 180,000 species of the Lepidoptera have been described, representing 10% of the total described species of living organisms, making it the second largest insect order (behind Coleoptera) with 126 family (biology), families and 46 Taxonomic rank, superfamilies, and one of the most widespread and widely recognizable insect orders in the world. Lepidopteran species are characterized by more than three derived features. The most apparent is the presence of scale (anatomy), scales that cover the torso, bodies, large triangular Insect wing, wings, and a proboscis for siphoning nectars. The scales are modified, flattened "hairs", and give butterflies and moths their wide variety of colors and patterns. Almost all species have some form of membranous wings, except for a few that have reduced wings or are wingless. Mating and the laying of eggs is normally performe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemiptera
Hemiptera (; ) is an order of insects, commonly called true bugs, comprising more than 80,000 species within groups such as the cicadas, aphids, planthoppers, leafhoppers, assassin bugs, bed bugs, and shield bugs. They range in size from to around , and share a common arrangement of piercing-sucking mouthparts. The name "true bugs" is sometimes limited to the suborder Heteroptera. Entomologists reserve the term ''bug'' for Hemiptera or Heteroptera,Gilbert Waldbauer. ''The Handy Bug Answer Book.'' Visible Ink, 1998p. 1. which does not include other arthropods or insects of other orders such as ants, bees, beetles, or butterflies. In some varieties of English, all terrestrial arthropods (including non-insect arachnids and myriapods) also fall under the colloquial understanding of ''bug''. Many insects with "bug" in their common name, especially in American English, belong to other orders; for example, the lovebug is a fly and the Maybug and ladybug are beetles. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect Mouthparts
Insects have arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts that may vary greatly across insect species, as they are adapted to particular modes of feeding. The earliest insects had chewing mouthparts. Most specialisation of mouthparts are for piercing and sucking, and this mode of feeding has evolved a number of times independently. For example, mosquitoes (which are true flies) and aphids (which are Hemiptera, true bugs) both pierce and suck, though female mosquitoes feed on animal blood whereas aphids feed on plant fluids. Evolution Like most external features of arthropods, the mouthparts of Hexapoda are highly derived. Insect mouthparts show a multitude of different functional mechanisms across the wide diversity of insect species. It is common for significant Homology (biology), homology to be conserved, with matching structures forming from matching Primordium, primordia, and having the same evolutionary origin. However, even if structures are almost physically and functionally identica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thysanura
Thysanura is the now Deprecation, deprecated name of what was, for over a century, recognised as an Order (biology), order in the Class (biology), class Insecta. The two constituent groups within the former order, the Archaeognatha (jumping bristletails) and the Zygentoma (silverfish and firebrats), share several characteristics, such as of having three long caudal filaments, the lateral ones being the Cercus, cerci, while the one between (telson) is a Anatomical terms of location#Medial and lateral, medial cerciform appendage, specifically an epiproct. They are also both wingless, and have bodies covered with fine scales, rather like the scales of the practically unrelated Lepidoptera. In the late 20th century, it was recognized that the two suborders were not sister taxa, therefore Thysanura was paraphyletic, and the two suborders were each raised to the status of an independent monophyletic order, with Archaeognatha sister taxon to the Dicondylia, including the Zygentoma. Althou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeognatha
The Archaeognatha are an order of apterygotes, known by various common names such as jumping bristletails. Among extant insect taxa they are some of the most evolutionarily primitive; they appeared in the Middle Devonian period at about the same time as the arachnids. Specimens that closely resemble extant species have been found as both body and trace fossils (the latter including body imprints and trackways) in strata from the remainder of the Paleozoic Era and more recent periods. For historical reasons an alternative name for the order is Microcoryphia. Until the late 20th century the suborders Zygentoma and Archaeognatha comprised the order Thysanura; both orders possess three-pronged tails comprising two lateral cerci and a medial epiproct or ''appendix dorsalis''. Of the three organs, the appendix dorsalis is considerably longer than the two cerci; in this the Archaeognatha differ from the Zygentoma, in which the three organs are subequal in length. In the late 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |