|
Gluteal Tuberosity
The gluteal tuberosity is the lateral one of the three upward prolongations of the linea aspera of the femur, extending to the base of the greater trochanter. It serves as the principal insertion site for the gluteus maximus muscle. Structure The gluteal tuberosity is the lateral prolongation of three prolongations of the linea aspera that extending superior-ward from the superior extremity of the linea aspera on the posterior surface of the femur The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg. The Femo .... The gluteal tuberosity takes the form of either an elongated depression or a rough ridge. It extends from the linea aspera nearly vertically superior-ward to the base of the greater trochanter. Its superior part is often elongated to form a roughened crest, upon which a more or less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linea Aspera
The linea aspera () is a ridge of roughened surface on the posterior surface of the shaft of the femur. It is the site of attachments of muscles and the intermuscular septum. Its margins diverge above and below. The linea aspera is a prominent longitudinal ridge or crest, on the middle third of the bone, presenting a medial and a lateral lip, and a narrow rough, intermediate line. It is an important insertion point for the adductors and the lateral and medial intermuscular septa that divides the thigh into three compartments. The tension generated by muscle attached to the bones is responsible for the formation of the ridges. Structure Above Above, the linea aspera is prolonged by three ridges. * The lateral ridge is very rough, and runs almost vertically upward to the base of the greater trochanter. It is termed the gluteal tuberosity, and gives attachment to part of the gluteus maximus: its upper part is often elongated into a roughened crest, on which a more or less wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg. The Femoral head, top of the femur fits into a socket in the pelvis called the hip joint, and the bottom of the femur connects to the shinbone (tibia) and kneecap (patella) to form the knee. In humans the femur is the largest and thickest bone in the body. Structure The femur is the only bone in the upper Human leg, leg. The two femurs converge Anatomical terms of location, medially toward the knees, where they articulate with the Anatomical terms of location, proximal ends of the tibiae. The angle at which the femora converge is an important factor in determining the femoral-tibial angle. In females, thicker pelvic bones cause the femora to converge more than in males. In the condition genu valgum, ''genu valgum'' (knock knee), the femurs conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
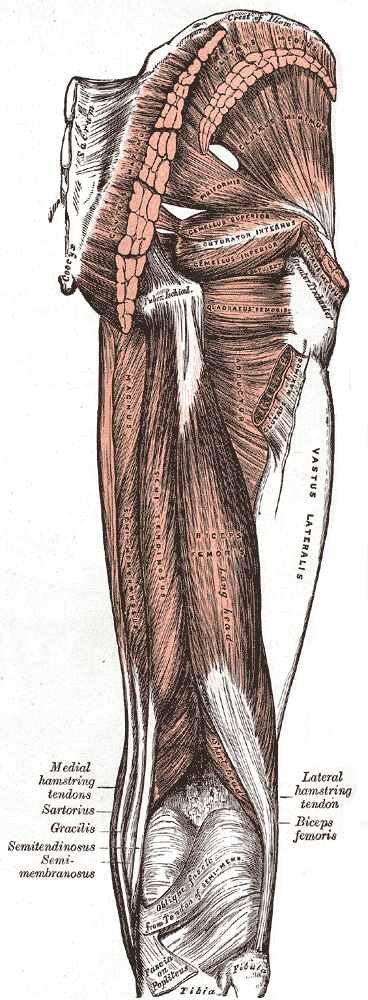
Greater Trochanter
The greater trochanter of the femur is a large, irregular, quadrilateral eminence and a part of the skeletal system. It is directed lateral and medially and slightly posterior. In the adult it is about 2–4 cm lower than the femoral head.Standring, Susan, editor. ''Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice''. Forty-First edition, Elsevier Limited, 2016, p. 1327. Because the pelvic outlet in the female is larger than in the male, there is a greater distance between the greater trochanters in the female. It has two surfaces and four borders. It is a traction epiphysis. Surfaces The ''lateral surface'', quadrilateral in form, is broad, rough, convex, and marked by a diagonal impression, which extends from the postero-superior to the antero-inferior angle, and serves for the insertion of the tendon of the gluteus medius. Above the impression is a triangular surface, sometimes rough for part of the tendon of the same muscle, sometimes smooth for the interp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluteus Maximus
The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle in the human body. Its thick fleshy mass, in a quadrilateral shape, forms the prominence of the buttocks. The other gluteal muscles are the medius and minimus, and sometimes informally these are collectively referred to as the glutes. Its large size is one of the most characteristic features of the muscular system in humans,Norman Eizenberg et al., ''General Anatomy: Principles and Applications'' (2008), p. 17. connected as it is with the power of maintaining the trunk in the erect posture. Other primates have much flatter hips and cannot sustain standing erectly. The muscle is made up of muscle fascicles lying parallel with one another, and are collected together into larger bundles separated by fibrous septa. Structure The gluteus maxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Trochanter
In human anatomy, the third trochanter is a bony projection occasionally present on the proximal femur near the superior border of the gluteal tuberosity. When present, it is oblong, rounded, or conical in shape and sometimes continuous with the gluteal ridge. It generally occurs bilaterally without significant side to side dimorphism. A structure of minor importance in humans, the incidence of the third trochanter varies from 17 to 72% between ethnic groups and it is frequently reported as more common in females than in males. Structures analogous to the third trochanter are present in other mammals, including some primates, but also in horses. It is called the third trochanter in reference to the greater and lesser trochanters that are always present on the femur. Function Its function is to provide an attachment for the ascending tendon of the gluteus maximus muscle. It may function as (1) a reinforcement mechanism for the proximal femoral diaphysis in response to incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliotibial Tract
The iliotibial tract or iliotibial band (ITB; also known as Maissiat's band or the IT band) is a longitudinal fibrous reinforcement of the fascia lata. The action of the muscles associated with the ITB ( tensor fasciae latae and some fibers of gluteus maximus) flex, extend, abduct, and laterally and medially rotate the hip. The ITB contributes to lateral knee stabilization. During knee extension the ITB moves anterior to the lateral condyle of the femur, while ~30 degrees knee flexion, the ITB moves posterior to the lateral condyle. However, it has been suggested that this is only an illusion due to the changing tension in the anterior and posterior fibers during movement. It originates at the anterolateral iliac tubercle portion of the external lip of the iliac crest and inserts at the lateral condyle of the tibia at Gerdy's tubercle. The figure shows only the proximal part of the iliotibial tract. The part of the iliotibial band which lies beneath the tensor fasciae latae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bones Of The Lower Limb
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions. Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the uncountable sense of that word, is hard tissue, a type of specialised connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are involved in the formation and mineralisation of bone; osteoclasts are involved in the resorption of bone tissue. Modified (flattened) osteoblasts become the lining cells that form a protective layer on the bone surface. The mineralised ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |