|
Gilliflower
A gilliflower or gillyflower () is the carnation or a similar plant of the genus ''Dianthus'', especially the Clove Pink ''Dianthus caryophyllus''. Its botanical name is ''Matthiola incana'', also known as stock. The same name also describes other plants, such as the wallflower, which have fragrant flowers. The name derives from the French ''giroflée'' from Greek ''karyophyllon'' = " nut-leaf" = the spice called clove, the association deriving from the flower's scent. Gilliflowers were allegedly referenced as payment for peppercorn rent in medieval feudal-tenure contracts.Cuttino, G. P. “King’s Clerks and the Community of the Realm.” ''Speculum'' 29, no. 2 (1954): 395–409. https://doi.org/10.2307/2853958. For example, in 1262 in Bedfordshire a tenant held an area of land called The Hyde "for the rent of one clove of gilliflower", and Elmore Court in Gloucester was granted to the Guise family by John De Burgh for the rent of "The clove of one Gillyflower" each year. In K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
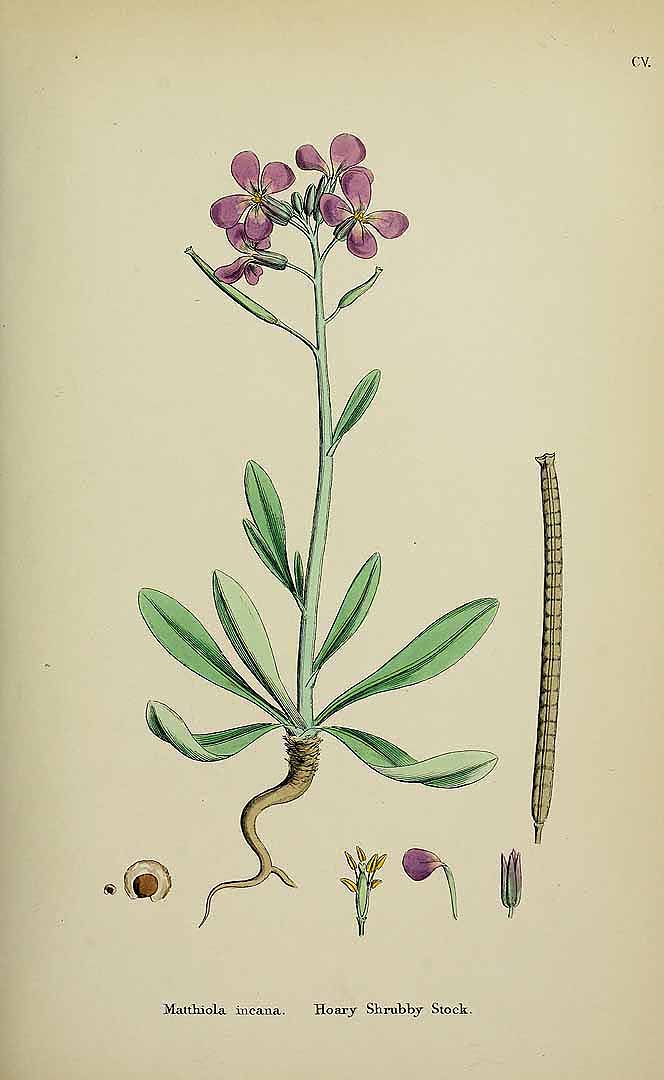
Matthiola Incana Illustration
''Matthiola'' () is a genus of flowering plant in the mustard family Brassicaceae. It is named after Italian naturalist Pietro Andrea Mattioli (1501–1577). The genus contains about 50 species of annual, biennial and perennial herbaceous plants and subshrubs.Jaén-Molina, R., et al. (2009The molecular phylogeny of ''Matthiola'' R. Br.(Brassicaceae) inferred from ITS sequences, with special emphasis on the Macaronesian endemics. ''Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution'' 53(3) 972–81.''Matthiola''. Flora of China.Sanchez, J. L., et al. (2005) Genetic diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal allegiance, services or payments. The fees were often lands, land revenue or revenue-producing real property like a watermill, held in feudal land tenure: these are typically known as fiefs or fiefdoms. However, not only land but anything of value could be held in fee, including governmental office, rights of exploitation such as hunting, fishing or felling trees, monopolies in trade, money rents and tax farms. There never existed a standard feudal system, nor did there exist only one type of fief. Over the ages, depending on the region, there was a broad variety of customs using the same basic legal principles in many variations. Terminology In ancient Rome, a " benefice" (from the Latin noun , meaning "benefit") was a gift of land () f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brideshead Revisited
''Brideshead Revisited: The Sacred & Profane Memories of Captain Charles Ryder'' is a novel by the English writer Evelyn Waugh, first published in 1945. It follows, from the 1920s to the early 1940s, the life and romances of Charles Ryder, especially his friendship with the Flytes, a family of wealthy English Catholics who live in a palatial mansion, Brideshead Castle. Ryder has relationships with two of the Flytes: Lord Sebastian and Lady Julia. The novel explores themes including Catholicism and nostalgia for the age of English aristocracy. A well-received television adaptation of the novel was produced in an 11-part miniseries by Granada Television in 1981. In 2008, it was adapted as a film. Plot The novel is divided into three parts, framed by a prologue and epilogue. ''Prologue'' The prologue takes place during the final years of the Second World War. Charles Ryder and his battalion are sent to a country estate called Brideshead, which prompts his recollections of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Les Rougon-Macquart
''Les Rougon-Macquart'' () is the collective title given to a cycle of twenty novels by France, French writer Émile Zola. Subtitled ''Histoire naturelle et sociale d'une famille sous le Second Empire'' (''Natural and social history of a family under the Second Empire''), it follows the lives of the members of the two titular branches of a fictional family living during the Second French Empire (1852–1870) and is one of the most prominent works of the French Naturalism (literature), naturalism literary movement. Influences Early in his life, Zola discovered the work of Honoré de Balzac and his famous cycle ''La Comédie humaine''. This had a profound impact on Zola, who decided to write his own, unique cycle. However, in 1869, he explained in ''Différences entre Balzac et moi'', why he would not make the same kind of book as Balzac: In one word, his work wants to be the mirror of the contemporary society. My work, mine, will be something else entirely. The scope will be narr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Émile Zola
Émile Édouard Charles Antoine Zola (, ; ; 2 April 184029 September 1902) was a French novelist, journalist, playwright, the best-known practitioner of the literary school of Naturalism (literature), naturalism, and an important contributor to the development of Naturalism (theatre), theatrical naturalism. He was a major figure in the political liberalization of France and in the exoneration of the falsely accused and convicted army officer Alfred Dreyfus, which is encapsulated in his renowned newspaper opinion headlined ''J'Accuse...!'' Zola was nominated for the first and second Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Prizes in Literature in 1901 and 1902. Early life Zola was born in Paris in 1840 to François Zola (originally Francesco Zolla) and Émilie Aubert. His father was an Italian engineer with some Greeks, Greek ancestry, who was born in Venice in 1795, and engineered the Zola Dam in Aix-en-Provence; his mother was French. The family moved to Aix-en-Provence in the Provence, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Faute De L'Abbé Mouret
(1875) is the fifth novel in Émile Zola's twenty-volume series ''Les Rougon-Macquart''. Viciously anticlericalism, anticlerical in tone, it follows on from the horrific events at the end of , focussing this time on a remote Provence, Provençal backwater village. Unusually for Zola, the novel contains very few characters and locations, and its use of amnesia as a plot device gives it an unusually fantastical tone. Plot summary The plot centres on the neurotic young priest Serge Mouret, first seen in , as he takes his orders and becomes the parish priest for the uninterested village of Artauds. The inbred villagers have no interest in religion and Serge is portrayed giving several wildly enthusiastic Masses to his completely empty, near-derelict church. Serge not only seems unperturbed by this state of affairs but actually appears to have positively sought it out especially, for it gives him time to contemplate religious affairs and to fully experience the fervour of his faith. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Demon Barber Of Fleet Street
''Sweeney Todd: The Demon Barber of Fleet Street'' (often referred to simply as ''Sweeney Todd'') is a 1979 musical with music and lyrics by Stephen Sondheim and book by Hugh Wheeler. It is based on the 1970 play ''Sweeney Todd'' by Christopher Bond. The character of Sweeney Todd first appeared in a Victorian penny dreadful titled ''The String of Pearls''. ''Sweeney Todd'' opened on Broadway in 1979 and in the West End in 1980. It won the Tony Award for Best Musical and Olivier Award for Best New Musical. It has been revived in many productions and inspired a film adaptation. The original logo for the musical is a modified version of an advertising image from the 19th century, with the sign replaced by a straight razor. There is also a woman wearing a blood-stained dress and holding a rolling pin next to the man. Background The character Sweeney Todd originated in serialized Victorian popular fiction, known as penny dreadfuls. A story called ''The String of Pearls'' was pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Sondheim
Stephen Joshua Sondheim (; March22, 1930November26, 2021) was an American composer and lyricist. Regarded as one of the most important figures in 20th-century musical theater, he is credited with reinventing the American musical. He received List of awards and nominations received by Stephen Sondheim, numerous accolades, including eight Tony Awards, an Academy Award, eight Grammy Awards, an Olivier Award, and the Pulitzer Prize. He was inducted into the American Theater Hall of Fame in 1982, and awarded the Kennedy Center Honor in 1993 and the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 2015. Sondheim was mentored at an early age by Oscar Hammerstein II and later frequently collaborated with Harold Prince and James Lapine. His Broadway theatre, Broadway musicals tackle themes that range beyond the genre's traditional subjects, while addressing darker elements of the human experience. His music and lyrics are tinged with complexity, sophistication, and ambivalence about various aspects of li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterbeach Abbey
{{UK-Christian ...
Waterbeach Abbey was an abbey at Waterbeach in Cambridgeshire, England. It was established in 1294 by nuns from the Second Order of St. Francis who had come from Longchamp Abbey in France, which also at least inspired the Abbey of the Minoresses of St. Clare without Aldgate. By 1351, the flood-prone abbey had become disused, the nuns having moved to the nearby Denny Abbey. The site is a scheduled monument. References Monasteries in Cambridgeshire 1294 establishments in England Christian monasteries established in the 1290s Scheduled monuments in Cambridgeshire Roman Catholic monasteries in England Franciscan monasteries in England Women in England England Poor Clare monasteries in England Abbey An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christians, Christian monks and nun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corps Of Royal Engineers
The Corps of Royal Engineers, usually called the Royal Engineers (RE), and commonly known as the ''Sappers'', is the engineering arm of the British Army. It provides military engineering and other technical support to the British Armed Forces and is headed by the Chief Royal Engineer. The Corps Headquarters and the Royal School of Military Engineering are in Chatham in Kent, England. The corps is divided into several regiments, barracked at various places in the United Kingdom and around the world. History The Royal Engineers trace their origins back to the military engineers brought to England by William the Conqueror, specifically Bishop Gundulf of Rochester Cathedral, and claim over 900 years of unbroken service to the crown. Engineers have always served in the armies of the Crown; however, the origins of the modern corps, along with those of the Royal Artillery, lie in the Board of Ordnance established in the 15th century. In Woolwich in 1716, the Board formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
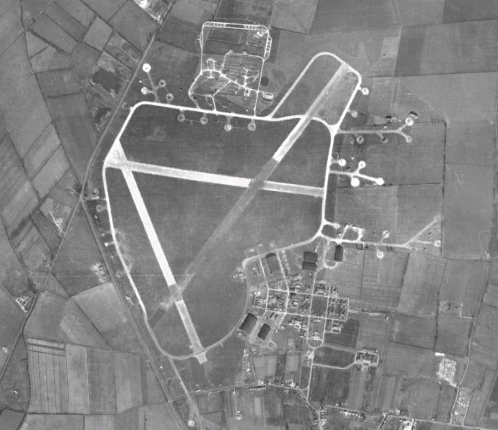
RAF Waterbeach
Royal Air Force Waterbeach or more simply RAF Waterbeach is a former Royal Air Force station located in Waterbeach, Cambridgeshire which is about north of Cambridge, England. The site was transferred to the Royal Engineers, part of the British Army, in 1966, as Waterbeach Barracks. History Royal Air Force The airfield was built in 1940 on the northern edge of Waterbeach village and operated under the control of RAF Bomber Command. The original control tower and many RAF buildings, including several hangars, are still present. RAF units and aircraft – Bomber Command, WW2 Transport Command, 1945-1949 After the Second World War, Consolidated Liberators and Douglas Dakotas from RAF Transport Command flew from RAF Waterbeach. RAF units and aircraft – Transport Command Fighter Command, 1950-1963 RAF Fighter Command took over the base on 1 March 1950 and used Gloster Meteors, Supermarine Swifts, de Havilland Venoms, de Havilland Vampires and Gloster Javelins. In addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungal microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular and cell biology, much like '' Escherichia coli'' as the model bacterium. It is the microorganism which causes many common types of fermentation. ''S. cerevisiae'' cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding. Many proteins important in human biology were first discovered by studying their homologs in yeast; these proteins include cell cycle proteins, signaling proteins, and protein-processing enzymes. ''S. cerevisiae'' is currently the only yeast cell known to have Berkeley bodies present, which are involved in particular secretory pathways. Antibodies again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |