|
Geonic Period
''Geonim'' (; ; also transliterated Gaonim, singular Gaon) were the presidents of the two great Babylonian Talmudic Academies of Sura and Pumbedita, in the Abbasid Caliphate. They were generally accepted as the spiritual leaders of the Jewish community worldwide in the early medieval era, in contrast to the ''Resh Galuta'' (exilarch) who wielded secular authority over the Jews in Islamic lands. ''Geonim'' is the plural of (''Ga'on'') , which means "pride" or "splendor" in Biblical Hebrew and since the 19th century "genius" as in modern Hebrew. As a title of a Babylonian college president it meant something like "His Excellency". The ''Geonim'' played a prominent and decisive role in the transmission and teaching of Torah and Jewish law. They taught Talmud and decided on issues on which no ruling had been rendered during the period of the Talmud. Era The period of the Geonim began in 589 CE ( Hebrew date: 4349), after the period of the Sevora'im, and ended in 1038 (Hebrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanization Of Hebrew
The Hebrew language uses the Hebrew alphabet with optional vowel diacritics. The romanization of Hebrew is the use of the Latin alphabet to transliterate Hebrew words. For example, the Hebrew name () can be romanized as or . Romanization includes any use of the Latin alphabet to transliterate Hebrew words. Usually, it is to identify a Hebrew word in a non-Hebrew language that uses the Latin alphabet, such as German, Spanish, Turkish, and so on. Transliteration uses an alphabet to represent the letters and sounds of a word spelled in another alphabet, whereas transcription uses an alphabet to represent the sounds only. Romanization can refer to either. To go the other way, that is from English to Hebrew, see Hebraization of English. Both Hebraization of English and Romanization of Hebrew are forms of transliteration. Where these are formalized these are known as ''transliteration systems'', and, where only some words, not all, are transliterated, this is known as ''trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hezekiah Gaon
Hezekiah Gaon or Hezekiah ben David () was the last Gaon of the Talmudic academy in Pumbedita from 1038 to 1040. Hezekiah ben David was a member of the House of Exilarchs; his father David was the son of Zakkai. Some scholars believe Hezekiah was great-grandson of David ben Zakai (not the grandson of David). Hezekiah was elected to the office of principal after the death of Hai Gaon at the age of 99, but was denounced to a fanatical government of the Buyid dynasty, who then imprisoned and tortured him to death. However, the '' Jewish Quarterly Review'' mentioned that Hezekiah was liberated from prison, and became head of the academy, and is mentioned as such by a contemporary in 1046. With him ended his family except two sons who escaped to the Iberian Peninsula, where they found a home with Joseph ibn Naghrela, son of Samuel ibn Naghrillah. The death of Hezekiah ended the line of the Geonim, which had begun four centuries earlier (see Hanan of Iskiya), and with it, Pumbedit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siddur
A siddur ( ''sīddūr'', ; plural siddurim ) is a Jewish prayer book containing a set order of daily prayers. The word comes from the Hebrew root , meaning 'order.' Other terms for prayer books are ''tefillot'' () among Sephardi Jews, ''tefillah'' among German Jews, and ''tiklāl'' () among Yemenite Jews. History The earliest parts of Jewish prayer books are the '' Shema Yisrael'' ("Hear O Israel") (Deuteronomy 6:4 ''et seq'') and the Priestly Blessing ( Numbers 6:24-26), which are in the Torah. A set of eighteen (currently nineteen) blessings called the ''Shemoneh Esreh'' or the ''Amidah'' (Hebrew, "standing rayer), is traditionally ascribed to the Great Assembly in the time of Ezra, at the end of the biblical period. The name ''Shemoneh Esreh'', literally "eighteen", is a historical anachronism, since it now contains nineteen blessings. It was only near the end of the Second Temple period that the eighteen prayers of the weekday Amidah became standardized. Even at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semicha
''Semikhah'' () is the traditional term for rabbiinic ordination in Judaism. The original ''semikhah'' was the formal "transmission of authority" from Moses through the generations. This form of ''semikhah'' ceased between 360 and 425 CE. Since then, ''semikhah'' has continued in a less formal way; throughout Jewish history, there have been several attempts to reestablish the classical ''semikhah''. The title of "rabbi" has "proliferated greatly over the last century". Nowadays, ''semikhah'' is also granted for a comparatively limited form of ordination, bestowing the authority to apply ''Halakha'' in specific Jewish settings rather than across the Jewish people writ large. In non- Orthodox Jewish religious movements, rabbinical education often emphasizes the modern roles of rabbis, such as preaching, teaching, counseling, and pastoral work. In recent times, relatedly, some institutions grant ordination for the role of ''hazzan'' (cantor), extending the "investiture" grante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Responsa
''Responsa'' (plural of Latin , 'answer') comprise a body of written decisions and rulings given by legal scholars in response to questions addressed to them. In the modern era, the term is used to describe decisions and rulings made by scholars in historic religious law. In the Roman Empire Roman law recognised , i.e., the responses and thoughts of jurists, as one of the sources of (written law), along with laws originating from magistrates, from the Senate, or from the emperor. A particularly well-known and highly influential example of such ''responsa'' was the ''Digesta'' (or ''Digests''), in 90 books, the principal work of the prominent second century jurist Salvius Julianus. This was a systematic treatise on civil and praetorian law, consisting of responsa on real and hypothetical cases, cited by many later Roman legal writers. In the Catholic Church In the Catholic Church, ''responsa'' are answers of the competent executive authority to specific questions (in Latin, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
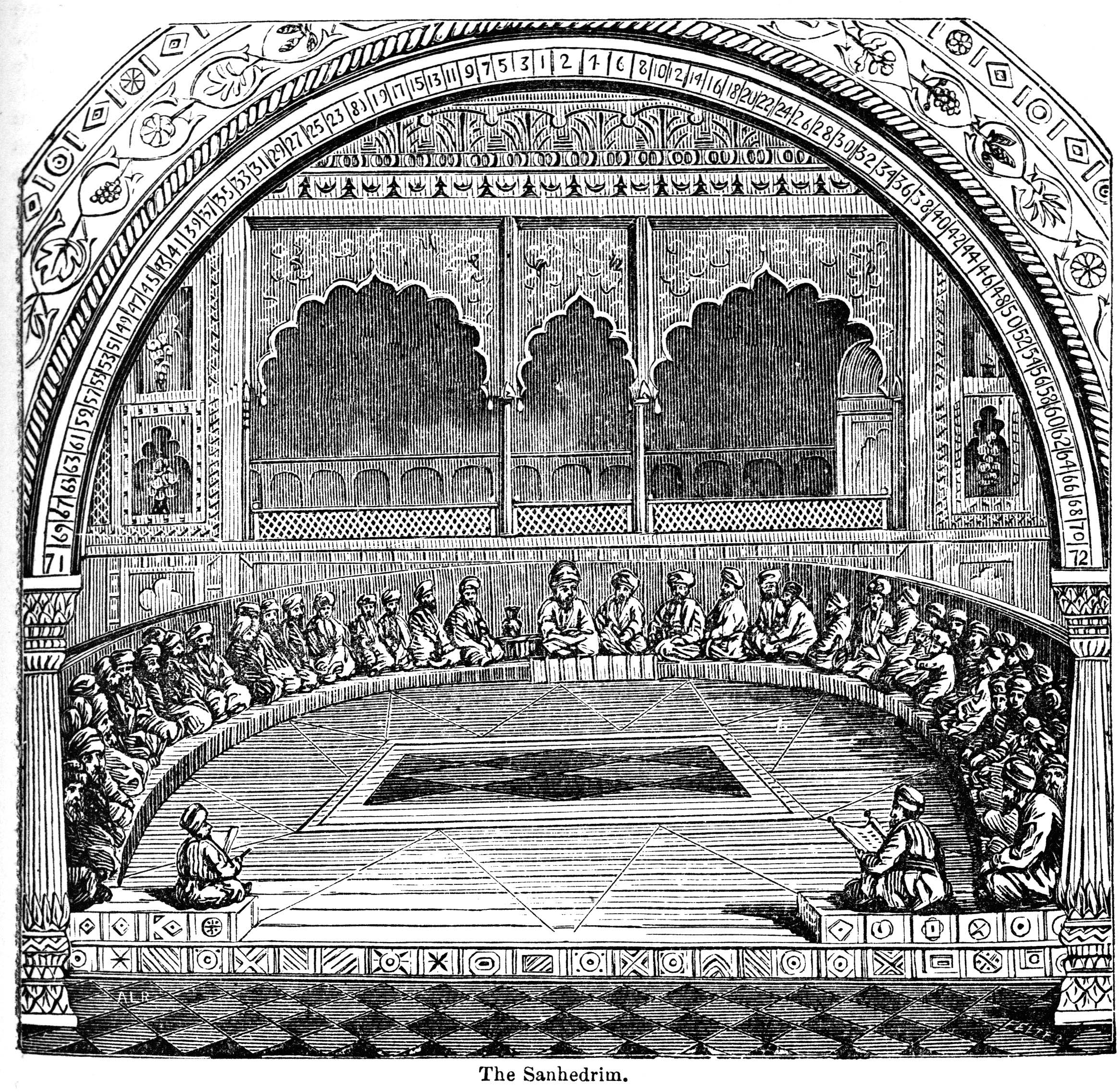
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Middle Aramaic , a loanword from , 'assembly,' 'sitting together,' hence ' assembly' or 'council') was a Jewish legislative and judicial assembly of either 23 or 70 elders, existing at both a local and central level in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite courts called sanhedrins: Greater and Lesser. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city. There was only one Great Sanhedrin of 70 judges, which, among other roles, acted as a supreme court, taking appeals from cases that lesser courts decided. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier usually refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the Nasi, who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the Av Beit Din or the chief of the court, who was second to the Nasi and 69 general members. In the Second Temple period, the Great Sanhedrin met in the Temple in Jerusalem, in a bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramaic Language
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient Syria (region), region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai Peninsula, Sinai, Southeastern Anatolia Region, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written and spoken in different variety (linguistics), varieties for over three thousand years. Aramaic served as a language of public life and administration of ancient kingdoms and empires, particularly the Neo-Assyrian Empire, Neo-Babylonian Empire, and Achaemenid Empire, and also as a language of divine worship and religious study within Judaism, Christianity, and Gnosticism. Several Neo-Aramaic languages, modern varieties of Aramaic are still spoken. The modern Eastern Aramaic, eastern branch is spoken by Assyrian people, Assyrians, Mandaeans, Mandeans, and Mizrahi Jews.{{cite book , last1=Huehnergard , first1=John , author-link1=John Huehnergard , last2=Rub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosh Yeshiva
Rosh yeshiva or Rosh Hayeshiva (, plural, pl. , '; Anglicized pl. ''rosh yeshivas'') is the title given to the dean of a yeshiva, a Jewish educational institution that focuses on the study of traditional religious texts, primarily the Talmud and the Torah, and ''halakha'' (Jewish law). The general role of the rosh yeshiva is to oversee the Talmudic studies and halakha, practical matters. The rosh yeshiva will often give the highest ''Shiur (Torah), shiur'' (class) and is also the one to decide whether to grant permission for students to undertake classes for rabbinical ordination, known as ''semicha''. The term is a compound word, compound of the Hebrew words ''rosh'' ("head") and ''yeshiva'' (a school of religious Jewish education). The rosh yeshiva is required to have a comprehensive knowledge of the Talmud and the ability to analyse and present new perspectives, called ''chidushim'' (wikt:novellae, novellae) verbally and often in print. In some institutions, such as YU's Rabbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaon (Hebrew)
Gaon (, ''gā'ōn'', , plural geonim, , ''gĕ'ōnīm'') was originally a formal title for the Geonim, heads of Talmudic academies in the 6th–11th century. Since the rishonic period, many great rabbis, whether or not they head academies, are often lauded with this honorific as a mark of respect; for example, one may refer to Ovadia Yosef as "HaGaon Ovadia Yosef". Modern Hebrew reuses the word as an equivalent for "genius" based on phonetic similarity. Etymology It may have originated as a shortened version of "Rosh Yeshivat Ge'on Ya'akov", although there are alternative explanations. In Ancient Hebrew, it referred to arrogance and haughty pride ( – "I abhor the pride of Jacob and detest his fortresses; I will deliver up the city and everything in it.") and, according to another explanation, it later became known as a general term for pride, and the title was used as "Pride f. Examples One of the Geonim during the period 589–1040. Prominent Geonim include: * Yehudai Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; , from the verb ''šānā'', "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first written collection of the Jewish oral traditions that are known as the Oral Torah. Having been collected in the 3rd century CE, it is the first work of rabbinic literature, written primarily in Mishnaic Hebrew but also partly in Jewish Palestinian Aramaic. The oldest surviving physical fragments of it are from the 6th to 7th centuries. The Mishnah was literary redaction, redacted by Judah ha-Nasi probably in Beit She'arim (Roman-era Jewish village), Beit Shearim or Sepphoris between the ending of the second century CE and the beginning of the third century. Heinrich Graetz, dissenting, places the Mishnah's compilation in 189 CE (see: H. Graetz, ''History of the Jews'', vol. 6, Philadelphia 1898, p105), and which date follows that penned by Rabbi Abraham ben David in his "Sefer HaKabbalah le-Ravad", or what was then ''anno'' 500 of the Seleucid era. in a time when the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saboraim
''Savora'' (; Aramaic: סבורא, "a reasoner", plural ''Savora'im'', ''Sabora'im'' , סבוראים) is a term used in Jewish law and history to signify one among the leading rabbis living from the end of period of the ''Amoraim'' (around 500 CE) to the beginning of the ''Geonim'' (around 600 CE). As a group they are also referred to as the Rabbeinu Sevorai or Rabanan Saborai, and may have played a large role in giving the Talmud its current structure. Modern scholars also use the plural term Stammaim (Hebrew; "closed, vague or unattributed sources") for the authors of unattributed statements in the Gemara. Role in the formation of the Talmud Much of classical rabbinic literature generally holds that the Babylonian Talmud was redacted into more or less its final form around 550 CE. The Talmud states that Ravina and Rav Ashi (two amoraim) were the "end of instruction", which many understand to mean they compiled the Babylonian Talmud.R' Meir TriebitzHistory & Development of Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoraim
''Amoraim'' ( , singular ''Amora'' ; "those who say" or "those who speak over the people", or "spokesmen") refers to Jewish scholars of the period from about 200 to 500 CE, who "said" or "told over" the teachings of the Oral Torah. They were primarily located in Babylonia and the Land of Israel. Their legal discussions and debates were eventually codified in the Gemara. The ''Amoraim'' followed the '' Tannaim'' in the sequence of ancient Jewish scholars. The ''Tannaim'' were direct transmitters of uncodified oral tradition; the ''Amoraim'' expounded upon and clarified the oral law after its initial codification. The Amoraic era The first Babylonian ''Amoraim'' were Abba Arikha, respectfully referred to as ''Rav'', and his contemporary and frequent debate partner, Shmuel. Among the earliest ''Amoraim'' in Israel were Johanan bar Nappaha and Shimon ben Lakish. Traditionally, the Amoraic period is reckoned as seven or eight generations (depending on where one begins and en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |