|
Generalized Wiener Filter
The Wiener filter as originally proposed by Norbert Wiener is a signal processing filter which uses knowledge of the statistical properties of both the signal and the noise to reconstruct an optimal estimate of the signal from a noisy one-dimensional time-ordered data stream. The generalized Wiener filter generalizes the same idea beyond the domain of one-dimensional time-ordered signal processing, with two-dimensional image processing being the most common application. Description Consider a data vector d which is the sum of independent signal and noise vectors d = s+n with zero mean and covariances \langle ss^T\rangle=S and \langle nn^T\rangle=N. The generalized Wiener Filter is the linear operator G which minimizes the expected residual between the estimated signal and the true signal, e = \langle(Gd-s)^T(Gd-s)\rangle. The G that minimizes this is G = S(S+N)^, resulting in the Wiener estimator \hat s = S(S+N)^d. In the case of Gaussian distributed signal and noise, this esti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiener Filter
In signal processing, the Wiener filter is a filter used to produce an estimate of a desired or target random process by linear time-invariant ( LTI) filtering of an observed noisy process, assuming known stationary signal and noise spectra, and additive noise. The Wiener filter minimizes the mean square error between the estimated random process and the desired process. Description The goal of the Wiener filter is to compute a statistical estimate of an unknown signal using a related signal as an input and filtering that known signal to produce the estimate as an output. For example, the known signal might consist of an unknown signal of interest that has been corrupted by additive noise. The Wiener filter can be used to filter out the noise from the corrupted signal to provide an estimate of the underlying signal of interest. The Wiener filter is based on a statistical approach, and a more statistical account of the theory is given in the minimum mean square error (MMSE) es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is : f(x) = \frac e^ The parameter \mu is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while the parameter \sigma is its standard deviation. The variance of the distribution is \sigma^2. A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a random variable with finite mean and variance is itself a random variable—whose distribution converges to a normal dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjugate Gradients
In mathematics, the conjugate gradient method is an algorithm for the numerical solution of particular systems of linear equations, namely those whose matrix is positive-definite. The conjugate gradient method is often implemented as an iterative algorithm, applicable to sparse systems that are too large to be handled by a direct implementation or other direct methods such as the Cholesky decomposition. Large sparse systems often arise when numerically solving partial differential equations or optimization problems. The conjugate gradient method can also be used to solve unconstrained optimization problems such as energy minimization. It is commonly attributed to Magnus Hestenes and Eduard Stiefel, who programmed it on the Z4, and extensively researched it. The biconjugate gradient method provides a generalization to non-symmetric matrices. Various nonlinear conjugate gradient methods seek minima of nonlinear optimization problems. Description of the problem address ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
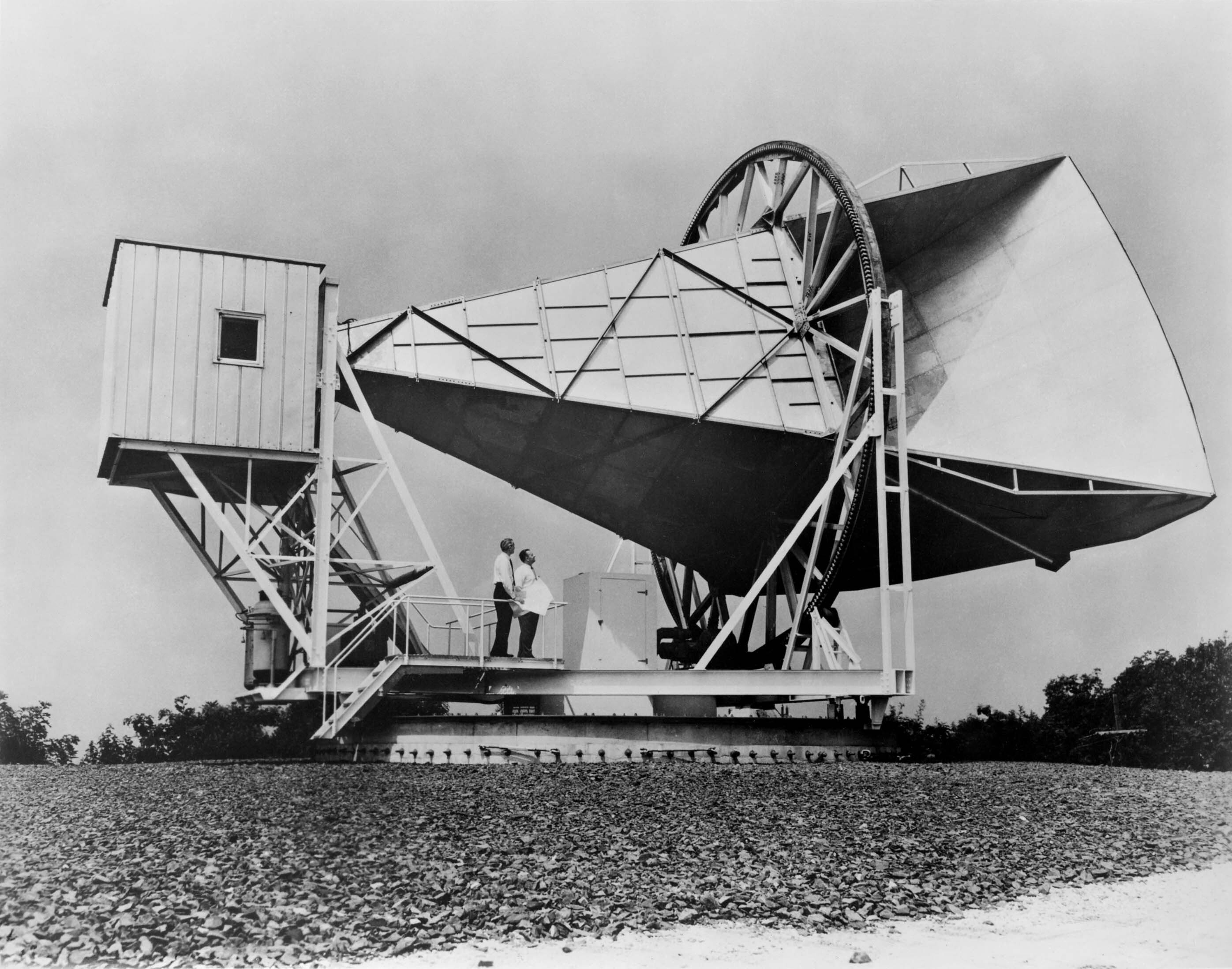
CMB Wiener Filter Example
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space. It is an important source of data on the early universe because it is the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination when the first atoms were formed. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark (see: Olbers' paradox). However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background brightness, or glow, almost uniform, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Harmonics
In mathematics and physical science, spherical harmonics are special functions defined on the surface of a sphere. They are often employed in solving partial differential equations in many scientific fields. Since the spherical harmonics form a complete set of orthogonal functions and thus an orthonormal basis, each function defined on the surface of a sphere can be written as a sum of these spherical harmonics. This is similar to periodic functions defined on a circle that can be expressed as a sum of circular functions (sines and cosines) via Fourier series. Like the sines and cosines in Fourier series, the spherical harmonics may be organized by (spatial) angular frequency, as seen in the rows of functions in the illustration on the right. Further, spherical harmonics are basis functions for irreducible representations of SO(3), the group of rotations in three dimensions, and thus play a central role in the group theoretic discussion of SO(3). Spherical harmonics originate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda-CDM Model
The ΛCDM (Lambda cold dark matter) or Lambda-CDM model is a parameterization of the Big Bang cosmological model in which the universe contains three major components: first, a cosmological constant denoted by Lambda (Greek Λ) associated with dark energy; second, the postulated cold dark matter (abbreviated CDM); and third, ordinary matter. It is frequently referred to as the ''standard model'' of Big Bang cosmology because it is the simplest model that provides a reasonably good account of the following properties of the cosmos: * the existence and structure of the cosmic microwave background * the large-scale structure in the distribution of galaxies * the observed abundances of hydrogen (including deuterium), helium, and lithium * the accelerating expansion of the universe observed in the light from distant galaxies and supernovae The model assumes that general relativity is the correct theory of gravity on cosmological scales. It emerged in the late 1990s as a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Microwave Background
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space. It is an important source of data on the early universe because it is the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination when the first atoms were formed. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark (see: Olbers' paradox). However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background brightness, or glow, almost uniform, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum A Posteriori Estimation
In Bayesian statistics, a maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) estimate is an estimate of an unknown quantity, that equals the mode of the posterior distribution. The MAP can be used to obtain a point estimate of an unobserved quantity on the basis of empirical data. It is closely related to the method of maximum likelihood (ML) estimation, but employs an augmented optimization objective which incorporates a prior distribution (that quantifies the additional information available through prior knowledge of a related event) over the quantity one wants to estimate. MAP estimation can therefore be seen as a regularization of maximum likelihood estimation. Description Assume that we want to estimate an unobserved population parameter \theta on the basis of observations x. Let f be the sampling distribution of x, so that f(x\mid\theta) is the probability of x when the underlying population parameter is \theta. Then the function: :\theta \mapsto f(x \mid \theta) \! is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Operator
In mathematics, and more specifically in linear algebra, a linear map (also called a linear mapping, linear transformation, vector space homomorphism, or in some contexts linear function) is a Map (mathematics), mapping V \to W between two vector spaces that preserves the operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication. The same names and the same definition are also used for the more general case of module (mathematics), modules over a ring (mathematics), ring; see Module homomorphism. If a linear map is a bijection then it is called a . In the case where V = W, a linear map is called a (linear) ''endomorphism''. Sometimes the term refers to this case, but the term "linear operator" can have different meanings for different conventions: for example, it can be used to emphasize that V and W are Real number, real vector spaces (not necessarily with V = W), or it can be used to emphasize that V is a function space, which is a common convention in functional analysis. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norbert Wiener
Norbert Wiener (November 26, 1894 – March 18, 1964) was an American mathematician and philosopher. He was a professor of mathematics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). A child prodigy, Wiener later became an early researcher in stochastic and mathematical noise processes, contributing work relevant to electronic engineering, electronic communication, and control systems. Wiener is considered the originator of cybernetics, the science of communication as it relates to living things and machines, with implications for engineering, systems control, computer science, biology, neuroscience, philosophy, and the organization of society. Norbert Wiener is credited as being one of the first to theorize that all intelligent behavior was the result of feedback mechanisms, that could possibly be simulated by machines and was an important early step towards the development of modern artificial intelligence. Biography Youth Wiener was born in Columbia, Missouri, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of the joint variability of two random variables. If the greater values of one variable mainly correspond with the greater values of the other variable, and the same holds for the lesser values (that is, the variables tend to show similar behavior), the covariance is positive. In the opposite case, when the greater values of one variable mainly correspond to the lesser values of the other, (that is, the variables tend to show opposite behavior), the covariance is negative. The sign of the covariance therefore shows the tendency in the linear relationship between the variables. The magnitude of the covariance is not easy to interpret because it is not normalized and hence depends on the magnitudes of the variables. The normalized version of the covariance, the correlation coefficient, however, shows by its magnitude the strength of the linear relation. A distinction must be made between (1) the covariance of two ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistically Independent
Independence is a fundamental notion in probability theory, as in statistics and the theory of stochastic processes. Two events are independent, statistically independent, or stochastically independent if, informally speaking, the occurrence of one does not affect the probability of occurrence of the other or, equivalently, does not affect the odds. Similarly, two random variables are independent if the realization of one does not affect the probability distribution of the other. When dealing with collections of more than two events, two notions of independence need to be distinguished. The events are called pairwise independent if any two events in the collection are independent of each other, while mutual independence (or collective independence) of events means, informally speaking, that each event is independent of any combination of other events in the collection. A similar notion exists for collections of random variables. Mutual independence implies pairwise independenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |