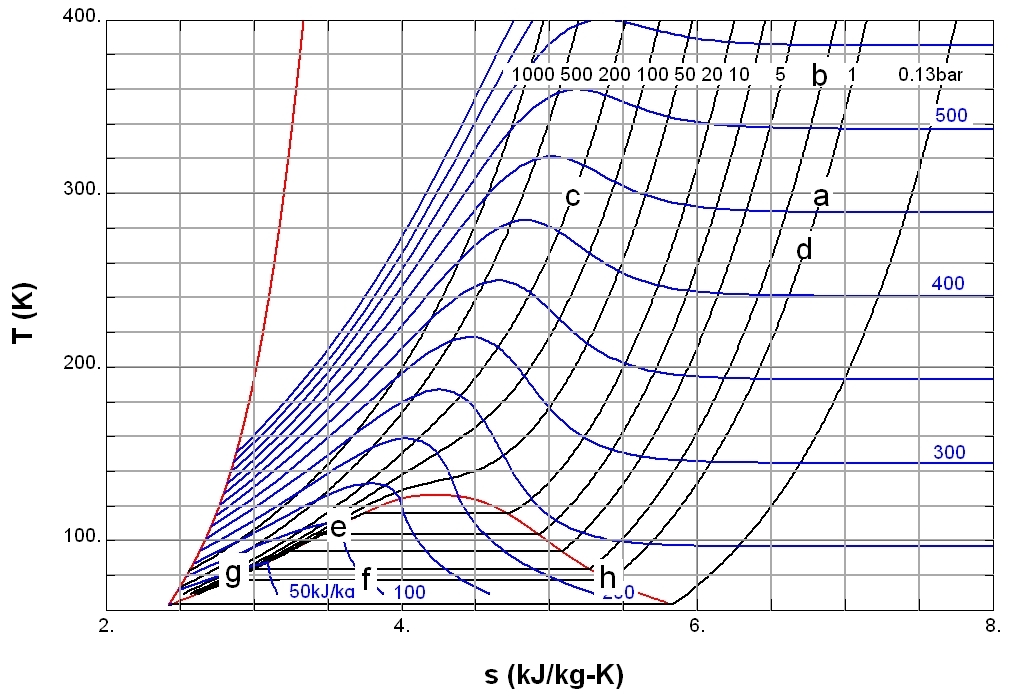
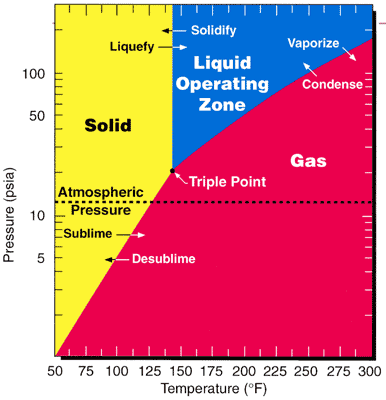
|
Gaseous Fission Reactor
A gas core reactor, and the very closely related vapor core reactor, is a proposed kind of nuclear reactor in which the nuclear fuel would be in a gaseous state rather than liquid or solid. In this type of reactor, the only temperature-limiting materials would be the reactor walls, and with appropriate cooling of the walls, the reactor can run at much higher temperatures. Conventional reactors have stricter limitations because the core would melt if the fuel temperature were to rise too high. There are two proposed roles for the concept, for nuclear power electrical generation, and as an advanced rocket engine. In the former, the advantage to the design is that it directly produces a high-velocity stream of partially ionized gas. This can be used to power a magnetohydrodynamic generator (MHD), which can operate with efficiencies roughly double that of the traditional liquid-cooled reactors which use the Rankine cycle and reach about 35% efficiency. The complexity of the design and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons production and Research reactor, research. Fissile material, Fissile nuclei (primarily uranium-235 or plutonium-239) absorb single neutron, neutrons and split, releasing energy and multiple neutrons, which can induce further fission. Reactors stabilize this, regulating Neutron absorber, neutron absorbers and neutron moderator, moderators in the core. Fuel efficiency is exceptionally high; Enriched uranium#Low-enriched uranium (LEU), low-enriched uranium is 120,000 times more energy dense than coal. Heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid Nuclear reactor#By coolant, coolant. In commercial reactors, this drives Turbine, turbines and electrical generator shafts. Some reactors are used for district heating, and isotopes, isoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthalpy
Enthalpy () is the sum of a thermodynamic system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function in thermodynamics used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant external pressure, which is conveniently provided by the large ambient atmosphere. The pressure–volume term expresses the work (physics), work W that was done against constant external pressure P_\text to establish the system's physical dimensions from V_\text=0 to some final volume V_\text (as W=P_\text\Delta V), i.e. to make room for it by displacing its surroundings. The pressure-volume term is very small for solids and liquids at common conditions, and fairly small for gases. Therefore, enthalpy is a stand-in for energy in chemical systems; Bond energy, bond, Lattice energy, lattice, solvation, and other chemical "energies" are actually enthalpy differences. As a state function, enthalpy depends only on the final configuration of internal e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Power Reactor Types
Nuclear may refer to: Physics Relating to the nucleus of the atom: *Nuclear engineering Nuclear engineering is the engineering discipline concerned with designing and applying systems that utilize the energy released by nuclear processes. The most prominent application of nuclear engineering is the generation of electricity. Worldwide ... *Nuclear physics *Nuclear power *Nuclear reactor *Nuclear weapon *Nuclear medicine *Radiation therapy *Nuclear warfare Mathematics *Nuclear space *Nuclear operator *Nuclear congruence *Nuclear C*-algebra Biology Relating to the Cell nucleus, nucleus of the cell: * Nuclear DNA Society *Nuclear family, a family consisting of a pair of adults and their children Music *Nuclear (band), "Nuclear" (band), chilean thrash metal band *Nuclear (Ryan Adams song), "Nuclear" (Ryan Adams song), 2002 *"Nuclear", a song by Mike Oldfield from his ''Man on the Rocks'' album *Nu.Clear (EP), ''Nu.Clear'' (EP) by South Korean girl group CLC Films *Nuclear (fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Propulsion
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. In-space propulsion exclusively deals with propulsion systems used in the vacuum of space and should not be confused with space launch or atmospheric entry. Several methods of pragmatic spacecraft propulsion have been developed, each having its own drawbacks and advantages. Most satellites have simple reliable chemical thrusters (often monopropellant rockets) or resistojet rockets for orbital station-keeping, while a few use Reaction wheel, momentum wheels for attitude control. Russian and antecedent Soviet bloc satellites have used Spacecraft electric propulsion, electric propulsion for decades, and newer Western geo-orbiting spacecraft are starting to use them for north–south station-keeping and orbit raising. Interplanetary vehicles mostly use chemical rockets as well, although a few have used electric propulsion such as ion thrusters and Hall-effect thrusters. Various technologies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Core Reactor Rocket
Gas core reactor rockets are a conceptual type of rocket that is propelled by the exhausted coolant of a gaseous fission reactor. The nuclear fission reactor core may be either a gas or plasma. They may be capable of creating specific impulses of 3,000–5,000 s (30 to 50 kN·s/kg, effective exhaust velocities 30 to 50 km/s) and thrust which is enough for relatively fast interplanetary travel. Heat transfer to the working fluid (propellant) is by thermal radiation, mostly in the ultraviolet, given off by the fission gas at a working temperature of around 25,000 °C. Theory of operation Nuclear gas-core-reactor rockets can provide much higher specific impulse than solid core nuclear rockets because their temperature limitations are in the nozzle and core wall structural temperatures, which are distanced from the hottest regions of the gas core. Consequently, nuclear gas core reactors can provide much higher temperatures to the propellant. Solid core nuclea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Hexafluoride
Uranium hexafluoride, sometimes called hex, is the inorganic compound with the formula . Uranium hexafluoride is a volatile, white solid that is used in enriching uranium for nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons. Preparation Uranium dioxide is converted with hydrofluoric acid (HF) to uranium tetrafluoride: : The resulting is subsequently oxidized with fluorine to give the hexafluoride: : In samples contaminated with uranium trioxide, uranyl fluoride, an oxyfluoride compound is produced in the HF step: : which can be fluorinated to produce the same product, uranium hexafluoride. : The fluorination step in both reactions above are highly exothermic. Properties Physical properties At atmospheric pressure, sublimes at 56.5 °C. The solid-state structure was determined by neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K.J. C. Taylor, P. W. Wilson, J. W. Kelly: „The structures of fluorides. I. Deviations from ideal symmetry in the structure of crystalline UF6: a neutron diffract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Impulse
Specific impulse (usually abbreviated ) is a measure of how efficiently a reaction mass engine, such as a rocket engine, rocket using propellant or a jet engine using fuel, generates thrust. In general, this is a ratio of the ''Impulse (physics), impulse'', i.e. change in momentum, ''per mass'' of propellant. This is equivalent to "thrust per massflow". The resulting unit is equivalent to velocity. If the engine expels mass at a constant exhaust velocity v_e then the thrust will be \mathbf = v_e \frac . If we integrate over time to get the total change in momentum, and then divide by the mass, we see that the specific impulse is equal to the exhaust velocity v_e . In practice, the specific impulse is usually lower than the actual physical exhaust velocity inefficiencies in the rocket, and thus corresponds to an "effective" exhaust velocity. That is, the specific impulse I_ in units of velocity *is defined by* : \mathbf = I_ \frac , where \mathbf is the average thrust. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalton (unit)
The dalton or unified atomic mass unit (symbols: Da or u, respectively) is a unit of mass defined as of the mass of an Bound state, unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state and invariant mass, at rest. It is a Non-SI units mentioned in the SI, non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. The word "unified" emphasizes that the definition was accepted by both IUPAP and IUPAC. The atomic mass constant, denoted , is defined identically. Expressed in terms of , the atomic mass of carbon-12: . Its value in International System of Units, SI units is an experimentally determined quantity. The 2022 CODATA recommended value of the atomic mass constant expressed in the SI base unit kilogram is:This value serves as a Conversion of units, conversion factor of mass from daltons to kilograms, which can easily be converted to Gram, grams and other metric units of mass. The 2019 revision of the SI redefined the kilogram by fixing the value of the Planck constant (), i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tritium
Tritium () or hydrogen-3 (symbol T or H) is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen with a half-life of ~12.33 years. The tritium nucleus (t, sometimes called a ''triton'') contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of the common isotope hydrogen-1 (''protium'') contains one proton and no neutrons, and that of non-radioactive hydrogen-2 ('' deuterium'') contains one proton and one neutron. Tritium is the heaviest particle-bound isotope of hydrogen. It is one of the few nuclides with a distinct name. The use of the name hydrogen-3, though more systematic, is much less common. Naturally occurring tritium is extremely rare on Earth. The atmosphere has only trace amounts, formed by the interaction of its gases with cosmic rays. It can be produced artificially by irradiation of lithium or lithium-bearing ceramic pebbles in a nuclear reactor and is a low-abundance byproduct in normal operations of nuclear reactors. Tritium is used as the energy source in radio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterium
Deuterium (hydrogen-2, symbol H or D, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen; the other is protium, or hydrogen-1, H. The deuterium nucleus (deuteron) contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common H has no neutrons. The name ''deuterium'' comes from Greek '' deuteros'', meaning "second". American chemist Harold Urey discovered deuterium in 1931. Urey and others produced samples of heavy water in which the H had been highly concentrated. The discovery of deuterium won Urey a Nobel Prize in 1934. Nearly all deuterium found in nature was synthesized in the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago, forming the primordial ratio of H to H (~26 deuterium nuclei per 10 hydrogen nuclei). Deuterium is subsequently produced by the slow stellar proton–proton chain, but rapidly destroyed by exothermic fusion reactions. The deuterium–deuterium reaction has the second-lowest energy threshold, and is the most astrophysically acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokamak
A tokamak (; ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field generated by external magnets to confine plasma (physics), plasma in the shape of an axially symmetrical torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement fusion, magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. The tokamak concept is currently one of the leading candidates for a practical fusion reactor for providing minimally polluting electrical power. The proposal to use controlled thermonuclear fusion for industrial purposes and a specific scheme using thermal insulation of high-temperature plasma by an electric field was first formulated by the Soviet physicist Oleg Lavrentiev in a mid-1950 paper. In 1951, Andrei Sakharov and Igor Tamm modified the scheme by proposing a theoretical basis for a thermonuclear reactor, where the plasma would have the shape of a torus and be held by a magnetic field. The first tokamak was built in the Soviet Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel up to 99% of the speed of light, and the electromagnetic waves are on the high-energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma rays, X-rays, and the higher energy vacuum ultraviolet, ultraviolet part of the electromagnetic spectrum are ionizing radiation; whereas the lower energy ultraviolet, visible light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves are non-ionizing radiation. Nearly all types of laser light are non-ionizing radiation. The boundary between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation in the ultraviolet area cannot be sharply defined, as different molecules and atoms ionize at Ionization energies of the elements (data page), different energies. The energy of ionizing radiation starts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |