|
Falsetto
Falsetto ( , ; Italian language, Italian diminutive of , "false") is the vocal register occupying the frequency range just above the modal voice register and overlapping with it by approximately one octave. It is produced by the vibration of the ligamentous edges of the vocal cords, in whole or in part. Commonly cited in the context of singing, falsetto, a characteristic of phonation by both sexes, is also one of four main spoken vocal registers recognized by speech pathology. The term ''falsetto'' is most often used in the context of singing to refer to a type of vocal phonation that enables the singer to sing notes beyond the vocal range of the normal, or modal, voice (M1). The typical tone of falsetto register, or M2, usually has a characteristic breathy and flute-like sound relatively free of overtones—which is more limited than its modal counterpart in both dynamic variation and tone quality. However, William Vennard points out that while most untrained people can sound co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Registers
A vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice (or normal voice), vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register. Registers originate in laryngeal function. They occur because the vocal folds are capable of producing several different vibratory patterns. Each of these vibratory patterns appears within a particular range of pitches and produces certain characteristic sounds. In speech pathology, the vocal register has three components: a certain vibratory pattern of the vocal folds, a certain series of pitches, and a certain type of sound. Although this view is also adopted by many vocal pedagogists, others define vocal registration more loosely than in the sciences, using the term to denote various theories of how the human voice changes, both subjectively and objectively, as it moves through its pitch range. There are many divergent theories on vocal registers within vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Register
A vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice (or normal voice), vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register. Registers originate in larynx, laryngeal function. They occur because the vocal folds are capable of producing several different vibratory patterns. Each of these vibratory patterns appears within a particular range of Pitch (music), pitches and produces certain characteristic sounds. In speech pathology, the vocal register has three components: a certain vibratory pattern of the vocal folds, a certain series of pitches, and a certain type of sound. Although this view is also adopted by many vocal pedagogy, vocal pedagogists, others define vocal registration more loosely than in the sciences, using the term to denote various theories of how the human voice changes, both subjectively and objectively, as it moves through its pitch range. There are many divergent theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countertenor
A countertenor (also contra tenor) is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range is equivalent to that of the female contralto or mezzo-soprano voice types, generally extending from around G3 to D5 or E5, although a sopranist (a specific kind of countertenor) may match the soprano's range of around C4 to C6.A sopranist is a term, widely used falsely, used to describe a countertenor whose vocal range is so high it is equivalent to that of a soprano. Countertenors often have tenor or baritone chest voices, but sing in falsetto or head voice much more often than they do in their chest voice. The nature of the countertenor voice has radically changed throughout musical history, from a modal voice, to a modal and falsetto voice, to the primarily falsetto voice that is denoted by the term today. This is partly because of changes in human physiology ( increase in body height) and partly because of fluctuations in pitch. The term first came into use in England during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Range
Vocal range is the range of pitches that a human voice can phonate. A common application is within the context of singing, where it is used as a defining characteristic for classifying singing voices into voice types. It is also a topic of study within linguistics, phonetics, and speech-language pathology, particularly in relation to the study of tonal languages and certain types of vocal disorders, although it has little practical application in terms of speech. Singing and the definition of vocal range While the broadest definition of "vocal range" is simply the span from the lowest to the highest note a particular voice can produce, this broad definition is often not what is meant when "vocal range" is discussed in the context of singing. Vocal pedagogists tend to define the vocal range as the total span of "musically useful" pitches that a singer can produce. This is because some of the notes a voice can produce may not be considered usable by the singer within performan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
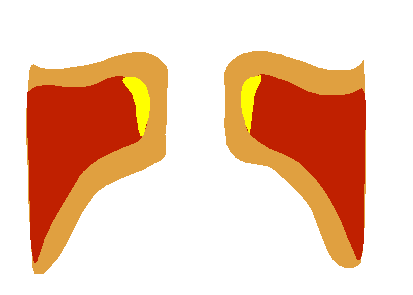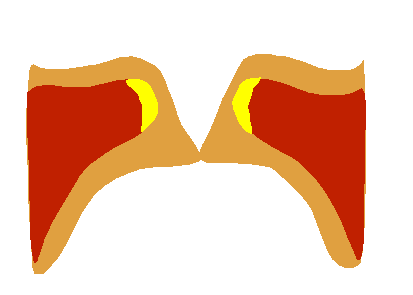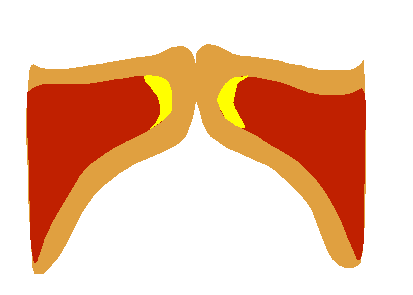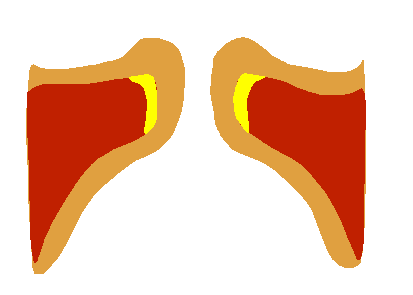
Vocal Fold Scheme
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production in which the vocal folds (vocal cords) are the primary sound source. (Other sound production mechanisms produced from the same general area of the body involve the production of unvoiced consonants, clicks, whistling and whispering.) Generally speaking, the mechanism for generating the human voice can be subdivided into three parts; the lungs, the vocal folds within the larynx (voice box), and the articulators. The lungs, the "pump" must produce adequate airflow and air pressure to vibrate vocal folds. The vocal folds (vocal cords) then vibrate to use airflow from the lungs to create audible pulses that form the laryngeal sound source. The muscles of the larynx adjust the length and tension of the vocal folds to 'fine-tune' pitch and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Register (music)
A register is the range (music), range within pitch space of some music or often musical speech. It may describe a given pitch or pitch class (or set theory (music), set of them), a human voice or musical instrument (or group of them), or both, as in a melody or part (music), part. It is also often related to timbre and musical form. In musical compositions, it may be fixed or "frozen". Relation to other musical elements or parameters Register is often understood in relation to other elements of music, sometimes called parameters. Relation to pitch A "higher" register may be said to indicate a "higher" pitch. For example, violins may be said to be in a "higher" register than cellos. This is often denoted concisely using subscripted numerals in scientific pitch notation. Relation to timbre The register in which an instrument plays, or in which a part is written, affects the quality of sound, or its timbre. Relation to form Register is also used structurally in musical form, with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Fold Falsett Animated
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production in which the vocal folds (vocal cords) are the primary sound source. (Other sound production mechanisms produced from the same general area of the body involve the production of unvoiced consonants, clicks, whistling and whispering.) Generally speaking, the mechanism for generating the human voice can be subdivided into three parts; the lungs, the vocal folds within the larynx (voice box), and the articulators. The lungs, the "pump" must produce adequate airflow and air pressure to vibrate vocal folds. The vocal folds (vocal cords) then vibrate to use airflow from the lungs to create audible pulses that form the laryngeal sound source. The muscles of the larynx adjust the length and tension of the vocal folds to 'fine-tune' pitch and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modal Voice
Modal voice is the vocal register used most frequently in speech and singing in most languages. It is also the term used in linguistics for the most common phonation of vowels. The term "modal" refers to the resonant mode of vocal folds; that is, the optimal combination of airflow and glottal tension that yields maximum vibration. In linguistics, modal voice is the only phonation found in the vowels and other sonorants (consonants such as ''m, n, l,'' and ''r)'' of most of the languages of the world, but a significant minority contrasts modal voice with other phonations. Among obstruents (consonants such as ''k, g, t͡ʃ/ch, d͡ʒ/j, s,'' and ''z),'' it is very common for languages to contrast modal voice with voicelessness, but in English, many supposedly-voiced obstruents do not usually have modal voice. In speech pathology, the modal register is one of the four identifiable registers within the human voice. It is above the vocal fry register and overlapping the lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the definition used among those who study laryngeal anatomy and physiology and speech production in general. Phoneticians in other subfields, such as linguistic phonetics, call this process '' voicing'', and use the term ''phonation'' to refer to any oscillatory state of any part of the larynx that modifies the airstream, of which voicing is just one example. Voiceless and supra-glottal phonations are included under this definition. Voicing The phonatory process, or voicing, occurs when air is expelled from the lungs through the glottis, creating a pressure drop across the larynx. When this drop becomes sufficiently large, the vocal folds start to oscillate. The minimum pressure drop required to achieve phonation is called the phonation thres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch (music), pitch and sound pressure, volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word 'larynx' (: larynges) comes from the Ancient Greek word ''lárunx'' ʻlarynx, gullet, throatʼ. Structure The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a respiratory epithelium, ciliated columnar epithelium except for the vocal folds. The laryngeal cavity, cavity of the larynx extends from its tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (music)
Pitch is a perception, perceptual property that allows sounds to be ordered on a frequency-related scale (music), scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melody, melodies. Pitch is a major auditory system, auditory attribute of musical tones, along with duration (music), duration, loudness, and timbre. Pitch may be quantified as a frequency, but pitch is not a purely objective physical property; it is a subjective Psychoacoustics, psychoacoustical attribute of sound. Historically, the study of pitch and pitch perception has been a central problem in psychoacoustics, and has been instrumental in forming and testing theories of sound representation, processing, and perception in the auditory system. Perception Pitch and frequency Pitch is an auditory sensation in which a listener assigns musical tones to relative positions on a musical scale based primarily on their percep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Folds
In humans, the vocal cords, also known as vocal folds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through Speech, vocalization. The length of the vocal cords affects the pitch of voice, similar to a violin string. Open when breathing and vibrating for speech or singing, the folds are controlled via the recurrent laryngeal nerve, recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve. They are composed of twin infoldings of mucous membrane stretched horizontally, from back to front, across the larynx. They vibration, vibrate, modulating the flow of air being expelled from the lungs during phonation. The 'true vocal cords' are distinguished from the 'false vocal folds', known as vestibular folds or ''ventricular folds'', which sit slightly superior to the more delicate true folds. These have a minimal role in normal phonation, but can produce deep sonorous tones, screams and growls. The length of the vocal fold at birth is approximately six to eight millimeters and grows t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |