|
Fungicide Resistance
Fungicides are pesticides used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in losses of yield and quality. Fungicides are used both in agriculture and to fight fungal infections in animals, including humans. Fungicides are also used to control oomycetes, which are not taxonomically/genetically fungi, although sharing similar methods of infecting plants. Fungicides can either be contact, translaminar or systemic. Contact fungicides are not taken up into the plant tissue and protect only the plant where the spray is deposited. Translaminar fungicides redistribute the fungicide from the upper, sprayed leaf surface to the lower, unsprayed surface. Systemic fungicides are taken up and redistributed through the xylem vessels. Few fungicides move to all parts of a plant. Some are locally systemic, and some move upward. Most fungicides that can be bought retail are sold in liquid form, the active ingredient being present at 0.08% i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all pesticide use globally. Most pesticides are used as plant protection products (also known as crop protection products), which in general protect plants from weeds, fungi, or insects. In general, a pesticide is a chemical or biological agent (such as a virus, bacterium, or fungus) that deters, incapacitates, kills, or otherwise discourages pests. Target pests can include insects, plant pathogens, weeds, molluscs, birds, mammals, fish, nematodes (roundworms), and microbes that destroy property, cause nuisance, spread disease, or are disease vectors. Along with these benefits, pesticides also have drawbacks, such as potential toxicity to humans and other species. Definition The word pesticide derives from the Latin ''pestis'' (plagu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agricultural Chemistry
Agricultural chemistry is the chemistry, especially organic chemistry and biochemistry, as they relate to agriculture. Agricultural chemistry embraces the structures and chemical reactions relevant in the production, protection, and use of Crop, crops and livestock. Its applied science and technology aspects are directed towards increasing yields and improving quality, which comes with multiple advantages and disadvantages. Agricultural and environmental chemistry This aspect of agricultural chemistry deals with the role of molecular chemistry in agriculture as well as the negative consequences. Plant biochemistry Plant biochemistry encompasses the chemical reactions that occur within plants. In principle, knowledge at a molecular level informs technologies for providing food. Particular focus is on the biochemical differences between plants and other organisms as well as the differences within the plant kingdom, such as dicotyledons vs monocotyledons, gymnosperms vs angiosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
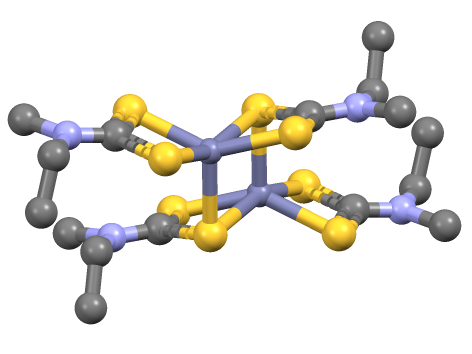
Mancozeb
Mancozeb is a dithiocarbamate non-systemic agricultural fungicide with multi-site, protective action on contact. It is a combination of two other dithiocarbamates: maneb and zineb. The mixture controls many fungal diseases in a wide range of field crops, fruits, nuts, vegetables, and ornamentals. It is marketed as Penncozeb, Trimanoc, Vondozeb, Dithane, Manzeb, Nemispot, and Manzane. In Canada, a mixture of zoxamide and mancozeb was registered for control of the mildew named Gavel as early as 2008. Mechanism Mancozeb reacts with, and inactivates, the sulfhydryl groups of amino acids and enzymes within fungal cells, resulting in disruption of lipid metabolism, respiration, and production of adenosine triphosphate. Mancozeb is listed under FRAC code M:03 The "M:" refers to Chemicals with Multi-Site Activity. "M:" FRAC groups are defined as generally considered as a low risk group without any signs of resistance developing to the fungicides. Toxicology A major toxicological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maneb
Maneb (manganese ethylene-bis-dithiocarbamate) is a fungicide and a polymeric complex of manganese with the ethylene bis (dithiocarbamate) anionic ligand. Health effects Exposure to maneb can occur when breathed in; it can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat as well as cause headache, fatigue, nervousness, dizziness, seizures and even unconsciousness. Prolonged or long-term exposure may interfere with the function of the thyroid. Exposure to maneb is also shown to induce a Parkinson's disease like neurotoxicity in mice. It is still challenged whether maneb, along with Paraquat, is an environmental risk factor for Parkinson's disease. Production Manganese(II) ethylenebis(dithiocarbamate) of low ethylenethiourea (ETU) content is prepared by mixing disodium ethylenebis (dithiocarbamate) with formaldehyde in aqueous medium then mixing a water-soluble manganese(II) salt to precipitate the maneb. The product can be further formulated with a metal salt and also with paraforma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zineb
Zineb is the chemical compound with the formula n. Structurally, it is classified as a coordination polymer and a dithiocarbamate complex. This pale yellow solid is used as fungicide. Production and applications It is produced by treating ethylene bis(dithiocarbamate) sodium salt, "nabam", with zinc sulfate. This procedure can be carried out by mixing nabam and zinc sulfate in a spray tank.Michael A. Kamrin, (1997) Pesticide Profiles: Toxicity, Environmental Impact, and Fate, CRC Press, Its uses include control of downy mildews, rusts, and redfire disease. In the US it was once registered as a "General Use Pesticide", however all registrations were voluntarily cancelled following an EPA special review. It continues to be used in many other countries. Structure Zineb is a polymeric complex of zinc with a dithiocarbamate. The polymer is composed of Zn(dithiocarbamate)2 subunits linked by an ethylene (-CH2CH2-) backbone. A reference compound is n(S2CNEt2)2sub>2, which features ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ziram
Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate is a coordination complex of zinc with dimethyldithiocarbamate. It is a pale yellow solid that is used as a fungicide, the sulfur vulcanization of rubber, and other industrial applications. Applications Known as ziram in agriculture, it was introduced in the United States in 1960 as a broad-spectrum fungicide. It was used to address List of pear diseases#Fungal diseases, scab on apples and pears, leaf curl in peaches, and anthracnose and blight in tomatoes. In 1981, additional uses for ziram were approved, including the prevention of leaf blight and scab on almonds, shot-hole in apricots, Monilinia fructicola, brown rot and leaf spot in cherries, and scab and anthracnose in pecans. Ziram also began to be used on residential ornaments as a bird and mammal repellent. As a protectant fungicide, it is active on the plant’s surface where it forms a chemical barrier between the plant and a fungus. A protectant fungicide is not absorbed into the plant and mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferbam
Iron tris(dimethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex of iron with dimethyldithiocarbamate with the formula Fe(S2CNMe2)3 (Me = methyl). It is marketed as a fungicide. Synthesis, structure, bonding Iron tris(dithiocarbamate)s are typically are prepared by salt metathesis reactions. Iron tris(dimethyldithiocarbamate) is an octahedral coordination complex of iron(III) with D3 symmetry. Spin crossover (SCO) was first observed in 1931 by Cambi ''et al.'' who discovered anomalous magnetic behavior for the tris(N,N-dialkyldithiocarbamatoiron(III) complexes. The spin states of these complexes are sensitive to the nature of the amine substituents. Reactions Iron tris(dithiocarbamate)s react with nitric oxide to give a nitrosyl complex: : This efficient chemical trapping reaction provides a means to detect NO. Reflecting the strongly donating properties of dithiocarbamate ligands, iron tris(dithiocarbamate)s oxidize at relatively mild potentials to give isolable iron(IV) d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dithiocarbamate
In organic chemistry, a dithiocarbamate is a chemical compound with the general formula . It contains the functional group with the Chemical structure, structure . It is the analog of a carbamate in which both oxygen atoms are replaced by sulfur atoms (when only one oxygen is replaced the result is thiocarbamate). Dithiocarbamate also refers to the dithiocarbamate ion and its salts. A common example is sodium diethyldithiocarbamate . Dithiocarbamates and their derivatives are widely used in the vulcanization of rubber. Formation Many secondary amines react with carbon disulfide and sodium hydroxide to form dithiocarbamate salts: : Ammonia reacts with carbon disulfide, similarly, to give ammonium dithiocarbamate: : Dithiocarbamate salts are pale colored solids that are soluble in water and Solvent, polar organic solvents. Dithiocarbamic acid A primary amine and carbon disulfide react to give a dithiocarbamic acid: : In the presence of diimides or pyridine, these acids convert t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulocladium
''Ulocladium'' is a genus of fungi. Species of this genus contain both plant pathogens and food spoilage agents. Other species contain enzymes that are biological control agents. Some members of the genus can invade homes and are a sign of moisture because the mold requires water to thrive. They can cause plant diseases or hay fever and more serious infections in immuno-suppressed individuals. Species of ''Ulocladium'' resemble those of genus ''Alternaria'' with which they were once included. Several DNA-based phylogenetic studies place ''Ulocladium'' convincingly within ''Alternaria'', suggesting that the latter is the correct classification for these species. However, ''Ulocladium'', unlike ''Alternaria'', do not produce alternariols, tenuazonic acid, altersolanols, or macrosporin. The species ''Ulocladium oudemansii'' is utilised as a biocontrol agent against ''Botrytis cinerea''. The New Zealand companBotryzen (2010) Ltduses it to control Botrytis bunch rot in the NZ vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Subtilis
''Bacillus subtilis'' (), known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus ''Bacillus'', ''B. subtilis'' is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. ''B. subtilis'' has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. ''B. subtilis'' is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies. Description ''Bacillus subtilis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, rod-shaped and catalase-positive. It was originally named ''Vibrio subtilis'' by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jojoba Oil
Jojoba oil () is the liquid produced in the seed of the ''Simmondsia chinensis'' ( jojoba) plant, a shrub, which is native to southern Arizona, southern California, and northwestern Mexico. The oil makes up approximately 50% of the jojoba seed by weight. The terms "jojoba oil" and "jojoba wax" are often used interchangeably because the wax visually appears to be a mobile oil, but as a wax it is composed almost entirely (~97%) of mono-esters of long-chain fatty acids ''(wax ester)'' and alcohols ( isopropyl jojobate), accompanied by only a tiny fraction of triglyceride esters. This composition accounts for its extreme shelf-life stability and extraordinary resistance to high temperatures, compared with true vegetable oils. History The O'odham Native American tribe extracted the oil from jojoba seeds to treat sores and wounds. The collection and processing of the seed from naturally occurring stands marked the beginning of jojoba domestication in the early 1970s. In 1943, natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosemary
''Salvia rosmarinus'' (), commonly known as rosemary, is a shrub with fragrant, evergreen, needle-like leaves and white, pink, purple, or blue flowers. It is a member of the sage family, Lamiaceae. The species is native to the Mediterranean region, as well as Portugal and Spain. It has a number of cultivars and its leaves are commonly used as a flavoring. Description Rosemary has a fibrous root system. It forms an aromatic evergreen shrub with leaves similar to '' Tsuga'' needles. Forms range from upright to trailing; the upright forms can reach between tall. The leaves are evergreen, long and broad, green above, and white below, with dense, short, woolly hair. The plant flowers in spring and summer in temperate climates, but the plants can be in constant bloom in warm climates; flowers are white, pink, purple or deep blue. The branches are dotted with groups of 2 to 3 flowers down its length. Rosemary also has a tendency to flower outside its normal flowering season; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |