|
Frequently Asked Questions
A frequently asked questions (FAQ) list is often used in articles, websites, email lists, and online forums where common questions tend to recur, for example through posts or queries by new users related to common knowledge gaps. The purpose of a FAQ is generally to provide information on frequent questions or concerns; however, the format is a useful means of organizing information, and text consisting of questions and their answers may thus be called a FAQ regardless of whether the questions are actually ''frequently'' asked. Since the acronym ''FAQ'' originated in textual media, its pronunciation varies. FAQ can be pronounced as an initialism, "F-A-Q", or as an acronym, "FAQ". Web designers often label a single list of questions as a "FAQ", such as on Google Search, while using "FAQs" to denote multiple lists of questions such as on United States Treasury sites. Use of "FAQ" to refer to a single frequently asked question, in and of itself, is less common. Origins While the nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Mailing List
A mailing list is a collection of names and addresses used by an individual or an organization to send material to multiple recipients. Mailing lists are often rented or sold. If rented, the renter agrees to use the mailing list only at contractually agreed-upon times. The mailing list owner typically enforces this by " salting" (known as "seeding" in direct mail) the mailing list with fake addresses and creating new salts for each time the list is rented. Unscrupulous renters may attempt to bypass salts by renting several lists and merging them to find common, valid addresses. Mailing list brokers exist to help organizations rent their lists. For some list owners, such as specialized niche publications or charitable groups, their lists may be some of their most valuable assets, and mailing list brokers help them maximize the value of their lists. Transmission may be paper-based or electronic. Each has its strengths, although a 2022 article claimed that compared to email, " di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netlib
Netlib is a repository of software for scientific computing maintained by AT&T, Bell Laboratories, the University of Tennessee and Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Netlib comprises many separate programs and libraries. Most of the code is written in C and Fortran, with some programs in other languages. History The project began with email distribution on UUCP, ARPANET and CSNET in the 1980s. The code base of Netlib was written at a time when computer software was not yet considered merchandise. Therefore, no license terms or terms of use are stated for many programs. Before the Berne Convention Implementation Act of 1988 (and the earlier Copyright Act of 1976) works without an explicit copyright notice were public-domain software. Also, most of the Netlib code is work of US government employees and therefore in the public domain. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jargon File
The Jargon File is a glossary and usage dictionary of slang used by computer programmers. The original Jargon File was a collection of terms from technical cultures such as the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, MIT AI Lab, the Stanford University centers and institutes#Stanford Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, Stanford AI Lab (SAIL) and others of the old ARPANET Artificial intelligence, AI/Lisp programming language, LISP/PDP-10 communities, including BBN Technologies, Bolt, Beranek and Newman (BBN), Carnegie Mellon University, and Worcester Polytechnic Institute. It was published in paperback form in 1983 as ''The Hacker's Dictionary'' (edited by Guy L. Steele Jr., Guy Steele) and revised in 1991 as ''The New Hacker's Dictionary'' (ed. Eric S. Raymond; third edition published 1996). The concept of the file began with the Tech Model Railroad Club (TMRC) that came out of early TX-0 and PDP-1 hackers in the 1950s, where the term ''hacker'' emerged and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Digital Service
The Government Digital Service is a unit of the Government of the United Kingdom's Department for Science, Innovation and Technology, tasked with transforming the provision of online public services. It was formed in April 2011 by David Cameron's Conservative Party (UK) , Conservative government to implement the "Digital by Default" strategy proposed by a report produced for the Cabinet Office in 2010 called ''Directgov 2010 and beyond: revolution not evolution''. It is overseen by the Public Expenditure Executive (Efficiency & Reform). GDS is primarily based in the Whitechapel Building, London. the interim CEO is Christine Bellamy, who previously led digital transformation and delivery at the BBC and had been managing director at Johnston Press, Johnston Media. Originally part of the Cabinet Office since inception, in July 2024, it was announced by the Starmer ministry that the GDS would be moving to become part of the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology. In Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subject Heading
In information retrieval, an index term (also known as subject term, subject heading, descriptor, or keyword) is a term that captures the essence of the topic of a document. Index terms make up a controlled vocabulary for use in bibliographic records. They are an integral part of bibliographic control, which is the function by which libraries collect, organize and disseminate documents. They are used as keywords to retrieve documents in an information system, for instance, a catalog or a search engine. A popular form of keywords on the web are tags, which are directly visible and can be assigned by non-experts. Index terms can consist of a word, phrase, or alphanumerical term. They are created by analyzing the document either manually with subject indexing or automatically with automatic indexing or more sophisticated methods of keyword extraction. Index terms can either come from a controlled vocabulary or be freely assigned. Keywords are stored in a search index. Common words ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Search Engine Optimization
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of improving the quality and quantity of Web traffic, website traffic to a website or a web page from web search engine, search engines. SEO targets unpaid search traffic (usually referred to as "Organic search, organic" results) rather than direct traffic, referral traffic, social media traffic, or Online advertising, paid traffic. Unpaid search engine traffic may originate from a variety of kinds of searches, including image search, video search, academic databases and search engines, academic search, news search, and industry-specific vertical search engines. As an Internet marketing strategy, SEO considers how search engines work, the computer-programmed algorithms that dictate search engine results, what people search for, the actual search queries or Keyword research, keywords typed into search engines, and which search engines are preferred by a target audience. SEO is performed because a website will receive more visito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossposting
Crossposting, also known as x-posting or xposting, is the act of posting one message to multiple information channels; forums, mailing lists, or newsgroups. This is distinct from multiposting, which is the posting of separate identical messages, individually, to each channel, (a forum, a newsgroup, an email list, or topic area). Enforcement actions against crossposting individuals vary from simple admonishments up to total lifetime bans. In some cases, on email lists and forums, an individual is put under a stealth ban where their posts are distributed back to them as if they were being distributed normally, but the rest of the subscribers are not sent the messages. This is easily detected if the Stealthed individual has two different, and totally non-associated identities in the channel, such that the non-stealthed identity will see a different set of messages, lacking the posts of the stealthed individual, in their view of the channel. Crossposting to groups that are irrelevan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurogamer
''Eurogamer'' is a British video game journalism website launched in 1999 alongside parent company Gamer Network. In 2008, it started in the formerly eponymous trade fair EGX (Eurogamer Expo until 2013) organised by its parent company. From 2013 to 2020, sister site ''USGamer'' ran independently under its parent company. History ''Eurogamer'' (initially stylised as ''EuroGamer'' was launched on 4 September 1999 under company Eurogamer Network. The founding team included John Bye, the webmaster for the PlanetQuake website and a writer for British magazine '' PC Gaming World''; Patrick Stokes, a contributor for the website Warzone; and Rupert Loman, who had organised the EuroQuake esports event for the game '' Quake''. It became the official online media partner of the 2002 European Computer Trade Show. ''Eurogamer'' hosts content from media outlet ''Digital Foundry'' since 2007, which was founded in 2004. By the end of 2012, visits to the ''Eurogamer'' website and its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Videogame
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, controller, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual feedback from a display device, most commonly shown in a video format on a television set, computer monitor, flat-panel display or touchscreen on handheld devices, or a virtual reality headset. Most modern video games are audiovisual, with audio complement delivered through speakers or headphones, and sometimes also with other types of sensory feedback (e.g., haptic technology that provides tactile sensations). Some video games also allow microphone and webcam inputs for in-game chatting and livestreaming. Video games are typically categorized according to their hardware platform, which traditionally includes arcade video games, console games, and computer games (which includes LAN games, online games, and browser games). More recently, the video game industry has expande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jef Poskanzer
Jeffrey A. Poskanzer is a computer programmer. He was the first person to post a weekly FAQ to Usenet. He developed the portable pixmap file format and pbmplus (the precursor to the Netpbm package) to manipulate it. He has also worked on the team that ported A/UX. He has shared in two USENIX#USENIX Lifetime Achievement Award, USENIX Lifetime Achievement Awards – in 1993 for Berkeley Unix, and in 1996 for the Software Tools Project. He owns the Internet address acme.com (which is notable for receiving over one million e-mail spams a day), which is the home page for ACME Laboratories. It hosts a number of open source software projects; major projects maintained include both pbmplus and thttpd, an open source web server. Notes External links ACME Laboratories A/UX people Living people Year of birth missing (living people) {{compu-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
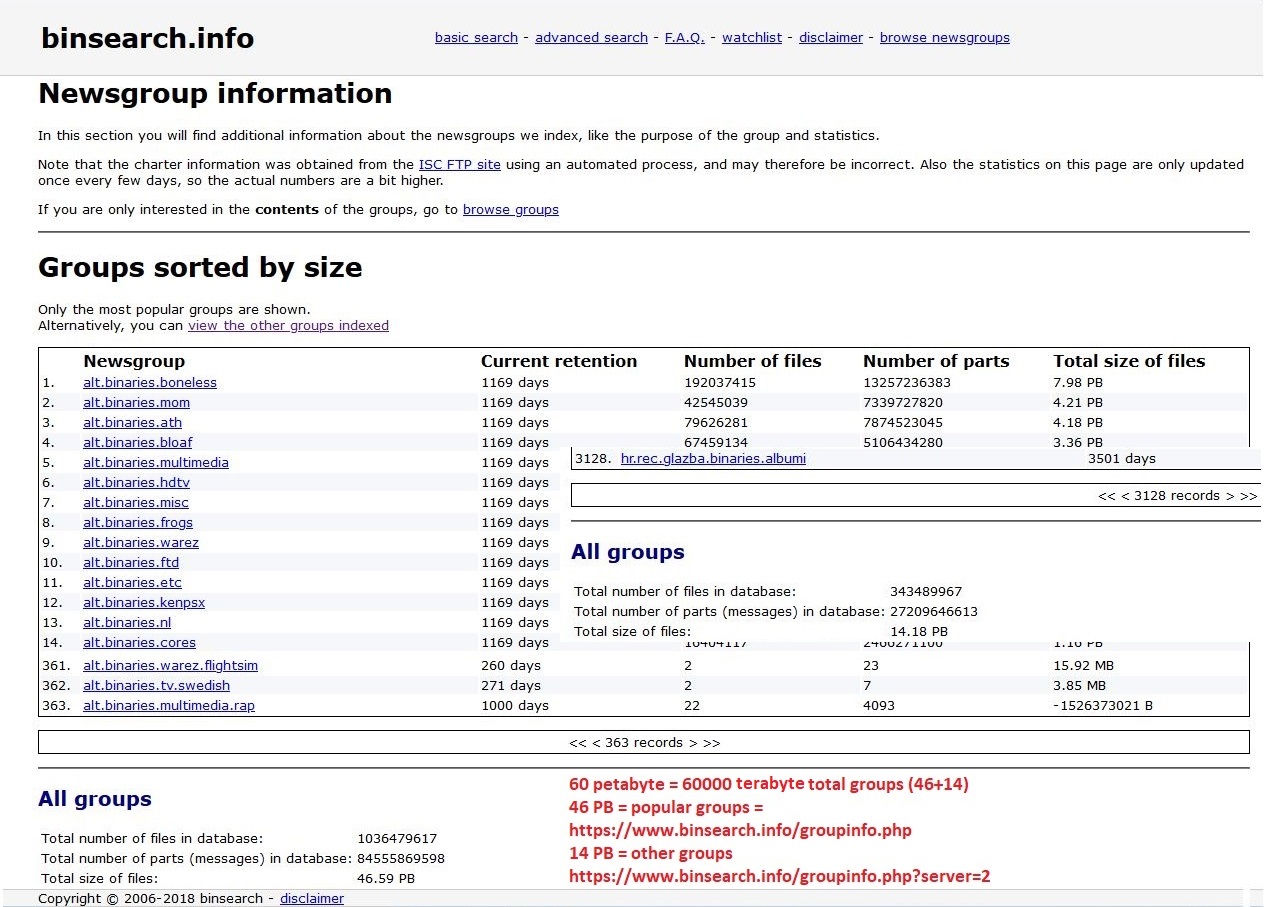
Newsgroup
A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system for messages posted from users in different locations using the Internet. They are not only discussion groups or conversations, but also a repository to publish articles, start developing tasks like creating Linux, sustain mailing lists and file uploading. That’s thank to the protocol that poses no article size limit, but are to the providers to decide. In the late 1980s, Usenet articles were often limited by the providers to 60,000 characters, but in time, Usenet groups have been split into two types: ''text'' for mainly discussions, conversations, articles, limited by most providers to about 32,000 characters, and ''binary'' for file transfer, with providers setting limits ranging from less than 1 MB to about 4 MB. Newsgroups are technically distinct from, but functionally similar to, discussion forums on the World Wide Web. Newsreader software is used to read the content of newsgroups. Before the adoption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usenet
Usenet (), a portmanteau of User's Network, is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose UUCP, Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis (computing), Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was established in 1980.''From Usenet to CoWebs: interacting with social information spaces'', Christopher Lueg, Danyel Fisher, Springer (2003), , Users read and post messages (called ''articles'' or ''posts'', and collectively termed ''news'') to one or more topic categories, known as Usenet newsgroup, newsgroups. Usenet resembles a bulletin board system (BBS) in many respects and is the precursor to the Internet forums that have become widely used. Discussions are Threaded discussion, threaded, as with web forums and BBSes, though posts are stored on the server sequentially. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |