|
Fluid Mosaic Model
The fluid mosaic model explains various characteristics regarding the structure of functional cell membranes. According to this Scientific model, biological model, there is a lipid bilayer (two molecules thick layer consisting primarily of Amphiphile, amphipathic phospholipids) in which protein molecules are embedded. The phospholipid bilayer gives Membrane fluidity, fluidity and Elasticity (physics), elasticity to the membrane. Small amounts of carbohydrates are also found in the cell membrane. The biological model, which was devised by Seymour Jonathan Singer and Garth L. Nicolson in 1972, describes the cell membrane as a two-dimensional liquid where embedded proteins are generally randomly distributed. For example, it is stated that "A prediction of the fluid mosaic model is that the two-dimensional long-range distribution of any integral protein in the plane of the membrane is essentially random." Chemical makeup Experimental evidence The fluid property of functional biolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane Detailed Diagram En
Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life * Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network * Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization * Electrochemical cell, a device used to convert chemical energy to electrical energy * Prison cell, a room used to hold people in prisons Cell may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Cell (comics), a Marvel comic book character * Cell (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the manga series ''Dragon Ball'' Literature * ''Cell'' (novel), a 2006 horror novel by Stephen King * "Cells", poem, about a hungover soldier in gaol, by Rudyard Kipling * ''The Cell'' (play), an Australian play by Robert Wales Music * Cell (music), a small rhythmic and melodic design that can be isolated, or can make up one part of a thematic context * Cell (American band) * Cell (Japanese band) * ''Cell'' (album), a 2004 album by Plastic Tree * ''Cells'', a 199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
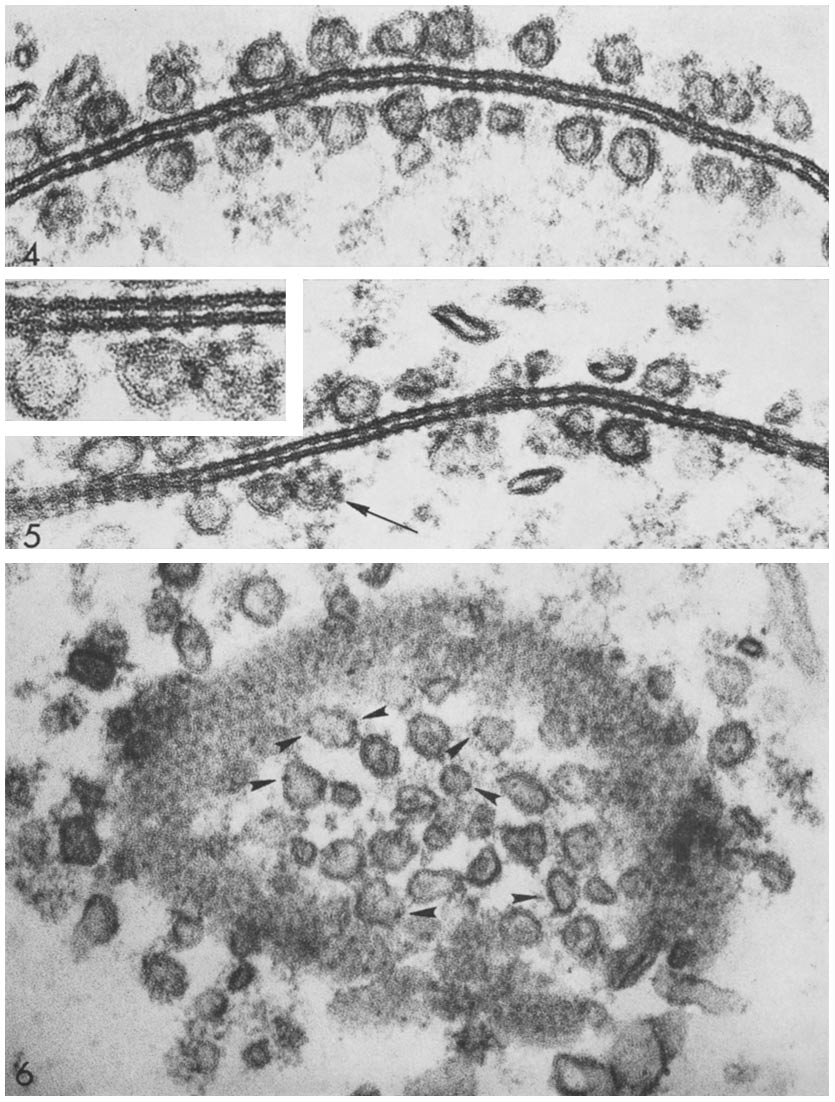
Davson–Danielli Model
The Davson–Danielli model (or paucimolecular model) was a model of the plasma membrane of a cell, proposed in 1935 by Hugh Davson and James Danielli. The model describes a phospholipid bilayer that lies between two layers of globular proteins, which is both trilaminar and lipoprotinious. The phospholipid bilayer had already been proposed by Gorter and Grendel in 1925; however, the flanking proteinaceous layers in the Davson–Danielli model were novel and intended to explain Danielli's observations on the surface tension of lipid bi-layers (It is now known that the phospholipid head groups are sufficient to explain the measured surface tension). Evidence for the model included electron microscopy, in which high-resolution micrographs showed three distinct layers within a cell membrane, with an inner white core and two flanking dark layers. Since proteins usually appear dark and phospholipids white, the micrographs were interpreted as a phospholipid bilayer sandwiched between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesicle (biology And Chemistry)
In cell biology, a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion ( exocytosis), uptake (endocytosis), and the transport of materials within the plasma membrane. Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes (not to be confused with lysosomes). If there is only one phospholipid bilayer, the vesicles are called ''unilamellar liposomes''; otherwise they are called ''multilamellar liposomes''. The membrane enclosing the vesicle is also a lamellar phase, similar to that of the plasma membrane, and intracellular vesicles can fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell. Vesicles can also fuse with other organelles within the cell. A vesicle released from the cell is known as an extracellular vesicle. Vesicles perform a variety of functions. Because it is separated from the cytosol, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatidylinositol
Phosphatidylinositol or inositol phospholipid is a biomolecule. It was initially called "inosite" when it was discovered by Léon Maquenne and Johann Joseph von Scherer in the late 19th century. It was discovered in bacteria but later also found in eukaryotes, and was found to be a signaling molecule. The biomolecule can exist in 9 different isomers. It is a lipid which contains a phosphate group, two fatty acid chains, and one inositol sugar molecule. Typically, the phosphate group has a negative charge (at physiological pH values). As a result, the molecule is amphiphilic. The production of the molecule is limited to the endoplasmic reticulum. History of phospatidylinositol Phosphatidylinositol (PI) and its derivatives have a rich history dating back to their discovery by Johann Joseph von Scherer and Léon Maquenne in the late 19th century. Initially known as " inosite" based on its sweet taste, the isolation and characterization of inositol laid the groundwork for und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BAR Domain
In molecular biology, BAR domains are highly conserved protein dimerisation domains that occur in many proteins involved in membrane dynamics in a cell. The BAR domain is banana-shaped and binds to membrane via its concave face. It is capable of sensing membrane curvature by binding preferentially to curved membranes. BAR domains are named after three proteins that they are found in: Bin, Amphiphysin and Rvs. BAR domains occur in combinations with other domains Many BAR family proteins contain alternative lipid specificity domains that help target these protein to particular membrane compartments. Some also have SH3 domains that bind to dynamin and thus proteins like amphiphysin and endophilin are implicated in the orchestration of vesicle scission. N-BAR domain Some BAR domain containing proteins have an N-terminal amphipathic helix preceding the BAR domain. This helix inserts (like in the epsin ENTH domain) into the membrane and induces curvature, which is stabilise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gap Junction
Gap junctions are membrane channels between adjacent cells that allow the direct exchange of cytoplasmic substances, such small molecules, substrates, and metabolites. Gap junctions were first described as ''close appositions'' alongside tight junctions, however, electron microscopy studies in 1967 led to gap junctions being named as such to be distinguished from tight junctions. They bridge a 2-4 nm gap between cell membranes. Gap junctions use protein complexes known as connexons, composed of connexin proteins to connect one cell to another. Gap junction proteins include the more than 26 types of connexin, as well as at least 12 non-connexin components that make up the gap junction complex or ''nexus,'' including the tight junction protein ZO-1—a protein that holds membrane content together and adds structural clarity to a cell, sodium channels, and aquaporin. More gap junction proteins have become known due to the development of next-generation sequencing. Connexins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrophobic Mismatch
Hydrophobic mismatch is the difference between the thicknesses of hydrophobic regions of a transmembrane protein and of the biological membrane it spans. In order to avoid unfavorable exposure of hydrophobic surfaces to water, the hydrophobic regions of transmembrane proteins are expected to have approximately the same thickness as the hydrophobic (lipid acyl chain) region of the surrounding lipid bilayer. Nevertheless, the same membrane protein can be encountered in bilayers of different thickness. In eukaryotic cells, the plasma membrane is thicker than the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum. Yet all proteins that are abundant in the plasma membrane are initially integrated into the endoplasmic reticulum upon synthesis on ribosomes. Transmembrane peptides or proteins and surrounding lipids can adapt to the hydrophobic mismatch by different means. Possible adaptations to mismatch In order to avoid unfavorable exposure of hydrophobic surfaces to a hydrophilic environment, bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils. Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all animal Cell (biology)#Eukaryotic cells, cells and is an essential structural and cholesterol signaling, signaling component of animal cell membranes. In vertebrates, hepatocyte, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. In the brain, astrocytes produce cholesterol and transport it to neurons. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as ''Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. Cholesterol also serves as a Precursor (chemistry), precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood, especially when bound to low-density lipoprotein (LDL, often referred to as "bad cholesterol"), may increase the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Biology
Structural biology deals with structural analysis of living material (formed, composed of, and/or maintained and refined by living cells) at every level of organization. Early structural biologists throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries were primarily only able to study structures to the limit of the naked eye's visual acuity and through magnifying glasses and light microscopes. In the 20th century, a variety of experimental techniques were developed to examine the 3D structures of biological molecules. The most prominent techniques are X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance, and Electron microscope, electron microscopy. Through the discovery of X-ray, X-rays and its applications to protein crystals, structural biology was revolutionized, as now scientists could obtain the three-dimensional structures of biological molecules in atomic detail. Likewise, Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, NMR spectroscopy allowed information about protein structure and dynamic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence Microscopy
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. A fluorescence microscope is any microscope that uses fluorescence to generate an image, whether it is a simple setup like an epifluorescence microscope or a more complicated design such as a confocal microscope, which uses optical sectioning to get better resolution of the fluorescence image. Principle The specimen is illuminated with light of a specific wavelength (or wavelengths) which is absorbed by the fluorophores, causing them to emit light of longer wavelengths (i.e., of a different color than the absorbed light). The illumination light is separated from the much weaker emitted fluorescence through the use of a spectral emission filter. Typical components of a fluorescence microscope are a light source (xenon arc lamp or mercury-vapor lamp are com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunostaining
In biochemistry, immunostaining is any use of an antibody-based method to detect a specific protein in a sample. The term "immunostaining" was originally used to refer to the immunohistochemical staining of tissue sections, as first described by Albert Coons in 1941. However, immunostaining now encompasses a broad range of techniques used in histology, cell biology, and molecular biology that use antibody-based staining methods. Techniques Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemistry or IHC staining of tissue sections (or immunocytochemistry, which is the staining of cells), is perhaps the most commonly applied immunostaining technique. While the first cases of IHC staining used fluorescent dyes (see ''immunofluorescence''), other non-fluorescent methods using enzymes such as peroxidase (see '' immunoperoxidase staining'') and alkaline phosphatase are now used. These enzymes are capable of catalysing reactions that give a coloured product that is easily detectable by ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterokaryon
In biology, a heterokaryon is a multinucleate cell that contains genetically different nuclei. This is a special type of syncytium. This can occur naturally, such as in the mycelium of fungi during sexual reproduction, or artificially as formed by the experimental fusion of two genetically different cells, as e.g., in hybridoma technology. Etymology The term ''heterokaryosis'' for the property of having genetically unlike nuclei is borrowed from the German ''Heterokaryosis'', which was coined by the German botanist Hans Burgeff in a 1912 paper about his work on the fungus '' Phycomyces nitens''. It is based on Greek ''hetero'', meaning "different," and ''karyon'', meaning "kernel" or in this case "nucleus.". Occurrence Heterokaryons are found in the life cycle of yeasts, for example ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', a genetic model organism. The heterokaryon stage is produced from the fusion of two haploid cells. This ''transient'' heterokaryon can produce further haploid buds, or c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |