|
Flapping
Flapping or tapping, also known as alveolar flapping, intervocalic flapping, or ''t''-voicing, is a phonological process involving a voiced alveolar tap or flap; it is found in many varieties of English, especially North American, Cardiff, Ulster, Australian and New Zealand English, where the voiceless alveolar stop consonant phoneme is pronounced as a voiced alveolar flap , a sound produced by briefly tapping the alveolar ridge with the tongue, when placed between vowels. In London English, the flapped is perceived as a casual pronunciation intermediate between the affricate , with higher class associations, and the glottal stop , with lower class associations. In these named varieties, outside of Britain, , the voiced counterpart of , is also frequently pronounced as a flap in such positions, making pairs of words like ''latter'' and ''ladder'' sound similar or identical. In similar positions, the combination may be pronounced as a nasalized flap , making ''winter'' soun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoneme
A phoneme () is any set of similar Phone (phonetics), speech sounds that are perceptually regarded by the speakers of a language as a single basic sound—a smallest possible Phonetics, phonetic unit—that helps distinguish one word from another. All languages contain phonemes (or the spatial-gestural equivalent in sign languages), and all spoken languages include both consonant and vowel phonemes; phonemes are primarily studied under the branch of linguistics known as phonology. Examples and notation The English words ''cell'' and ''set'' have the exact same sequence of sounds, except for being different in their final consonant sounds: thus, versus in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), a writing system that can be used to represent phonemes. Since and alone distinguish certain words from others, they are each examples of phonemes of the English language. Specifically they are consonant phonemes, along with , while is a vowel phoneme. The spelling of Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American English
North American English (NAmE) encompasses the English language as spoken in both the United States and Canada. Because of their related histories and cultures, plus the similarities between the pronunciations (accents), vocabulary, and grammar of American English, U.S. English and Canadian English, linguists often group the two together. Canadians are generally tolerant of both British and American spellings, although certain words always take British spellings (e.g., ''cheque'') and others American spellings (e.g., ''tire'' rather than ''tyre''). Dialects of English spoken by United Empire Loyalists who fled the American Revolution (1775–1783) have had a large influence on Canadian English from its early roots. Some terms in North American English are used almost exclusively in Canada and the United States (for example, the terms ''diaper'' and ''gasoline'' are widely used instead of ''nappy'' and ''petrol''). Although many English speakers from outside North America regard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, migrated to Britain after its End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman occupiers left. English is the list of languages by total number of speakers, most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire (succeeded by the Commonwealth of Nations) and the United States. English is the list of languages by number of native speakers, third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish language, Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in list of countries and territories where English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiced Dental And Alveolar Taps And Flaps
The voiced alveolar tap or flap is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents a dental, alveolar, or postalveolar tap or flap is . The terms ''tap'' and ''flap'' are often used interchangeably. Peter Ladefoged proposed the distinction that a tap strikes its point of contact directly, as a very brief stop, and a flap strikes the point of contact tangentially: "Flaps are most typically made by retracting the tongue tip behind the alveolar ridge and moving it forward so that it strikes the ridge in passing." That distinction between the alveolar tap and flap can be written in the IPA with tap and flap , the 'retroflex' symbol being used for the one that starts with the tongue tip curled back behind the alveolar ridge. The distinction is noticeable in the speech of some American English speakers in distinguishing the words "potty" (tap ) and "party" (retroflex ). For linguists who do not make the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Received Pronunciation
Received Pronunciation (RP) is the Accent (sociolinguistics), accent of British English regarded as the Standard language, standard one, carrying the highest Prestige (sociolinguistics), social prestige, since as late as the beginning of the 20th century. It is also commonly referred to as the Queen's English or King's English. The study of RP is concerned only with matters of pronunciation, while other features of standard British English, such as vocabulary, grammar, and Style (sociolinguistics), style, are not considered. Language scholars have long disagreed on RP's exact definition, how geographically neutral it is, how many speakers there are, the nature and classification of its sub-varieties, how appropriate a choice it is as a standard, how the accent has changed over time, and even its name. Furthermore, RP has changed to such a degree over the last century that many of its early 20th-century traditions of transcription and analysis have become outdated or are no long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
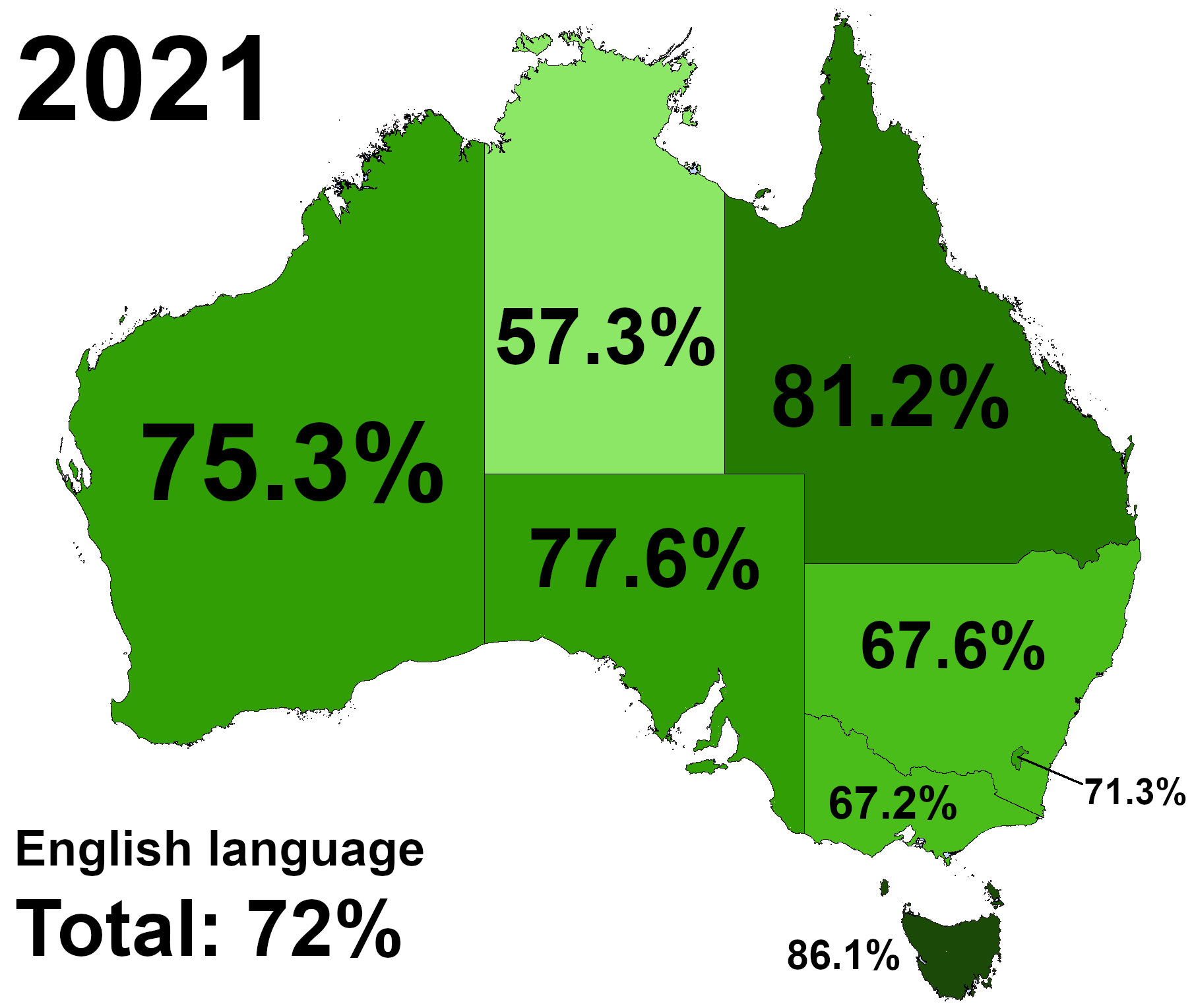
Australian English
Australian English (AusE, AusEng, AuE, AuEng, en-AU) is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to Australia. It is the country's common language and ''de facto'' national language. While Australia has no official language, English is the first language of Languages of Australia, the majority of the population, and has been entrenched as the ''de facto'' national language since the onset of History of Australia (1788–1850), British settlement, being the only language spoken in the home for 72% of Australians in 2021. It is also the main language used in compulsory education, as well as federal, state and territorial legislatures and courts. Australian English began to diverge from British English, British and Hiberno-English after the First Fleet established the Colony of New South Wales in 1788. Australian English arose from a Koiné language, dialectal melting pot created by the intermingling of early settlers who were from a variety of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronunciation Of English /r/
The pronunciation of the phoneme in the English language has many variations in different dialects. Variations Depending on dialect, has at least the following allophones in varieties of English around the world: *"Standard" R: postalveolar approximant (a common realization of the phoneme worldwide, Received Pronunciation and General American included). **"Bunched" or "Molar" R: velar bunched approximant (occurs in Southern American English and some Midwestern and Western American English most strongly); in fact, there is often a continuum of possible realizations for the postalveolar approximant within any single dialect from a more apical articulation to this more bunched articulation. *"Velarized" R: velarized alveolar approximant (occurs in conservative Irish English) *"Retroflex" R: retroflex approximant (occurs in West Country English, some American and Canadian English and Irish English, including Northern Irish English) *"Flapped" or "Tapped" R: alveolar fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress (linguistics)
In linguistics, and particularly phonology, stress or accent is the relative emphasis or prominence given to a certain syllable in a word or to a certain word in a phrase or Sentence (linguistics), sentence. That emphasis is typically caused by such properties as increased loudness and vowel length, full articulation of the vowel, and changes in Tone (linguistics), tone. The terms ''stress'' and ''accent'' are often used synonymously in that context but are sometimes distinguished. For example, when emphasis is produced through pitch alone, it is called ''Pitch-accent language, pitch accent'', and when produced through length alone, it is called ''quantitative accent''. When caused by a combination of various intensified properties, it is called ''stress accent'' or ''dynamic accent''; English uses what is called ''variable stress accent''. Since stress can be realised through a wide range of Phonetics, phonetic properties, such as loudness, vowel length, and pitch (which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockney
Cockney is a dialect of the English language, mainly spoken in London and its environs, particularly by Londoners with working-class and lower middle class roots. The term ''Cockney'' is also used as a demonym for a person from the East End, or, traditionally, born within earshot of Bow Bells. Estuary English is an intermediate accent between Cockney and Received Pronunciation, also widely spoken in and around London, as well as in wider South Eastern England. In multicultural areas of London, the Cockney dialect is, to an extent, being replaced by Multicultural London English—a new form of speech with significant Cockney influence. Words and phrases Etymology of ''Cockney'' The earliest recorded use of the term is 1362 in passus VI of William Langland's ''Piers Plowman'', where it is used to mean "a small, misshapen Egg as food, egg", from Middle English ''coken'' + ''ey'' ("a rooster, cock's egg"). Concurrently, the List of mythological places, mythical land of luxury Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonological
Phonology (formerly also phonemics or phonematics: "phonemics ''n.'' 'obsolescent''1. Any procedure for identifying the phonemes of a language from a corpus of data. 2. (formerly also phonematics) A former synonym for phonology, often preferred by the American Structuralists and reflecting the importance in structuralist work of phonemics in sense 1.": "phonematics ''n.'' 1. 'obsolete''An old synonym for phonemics (sense 2).") is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages systematically organize their phonemes or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a particular language variety. At one time, the study of phonology related only to the study of the systems of phonemes in spoken languages, but now it may relate to any linguistic analysis either: Sign languages have a phonological system equivalent to the system of sounds in spoken languages. The building blocks of signs are sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottal Stop
The glottal stop or glottal plosive is a type of consonantal sound used in many Speech communication, spoken languages, produced by obstructing airflow in the vocal tract or, more precisely, the glottis. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is . As a result of the obstruction of the airflow in the glottis, the glottal vibration either stops or becomes irregular with a low rate and sudden drop in intensity. Features Features of the glottal stop: * It has no phonation at all, as there is no airflow through the glottis. It is voiceless, however, in the sense that it is produced without vibrations of the vocal cords. Writing In the traditional romanization of many languages, such as Arabic, the glottal stop is transcribed with the Modifier letter apostrophe, apostrophe ʼ, or the symbol ʾ, , which is the source of the IPA character . In many Polynesian languages that use the Latin alphabet, however, the glottal stop is written wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betty Botter
Betty Botter is a tongue twister written by American author Carolyn Wells in her book "The Jingle Book" published in 1899. It was originally titled ''The Butter Betty Bought''. By the middle of the 20th century, it had become part of the Mother Goose collection of nursery rhymes. Construction The construction is based on alliteration, using the repeated two-syllable pattern with a range of vowels in the first, stressed syllable. The difficulty is in clearly and consistently differentiating all the vowels from each other. Except for (''bought a''), they are all short vowels: * (''batter'') * (''better'', ''Betty'') * (''bitter'', ''bit o’'') * (''Botta'') * (''butter'') Lyrics When it was first published in "The Jingle Book" in 1899, it read: Variations Elise isaacson's version Betty botter bought a bit of butter but the butter Betty bought was bitter so Betty bought a bit of better butter Bronte Alberts' version Betty Botter bought a bit of butter But the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |