|
Flageolet
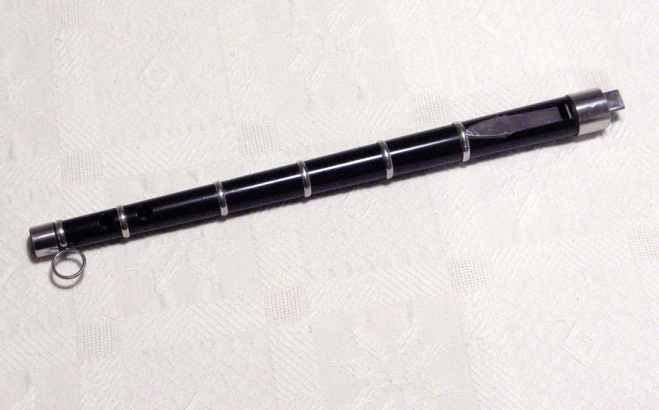
__NOTOC__ The flageolet is a woodwind instrument and a member of the family of fipple, duct flutes that includes Recorder (musical instrument), recorders and tin whistles. There are two basic forms of the instrument: the French, having four finger holes on the front and two thumb holes on the back; and the English, having six finger holes on the front and sometimes a single thumb hole on the back. The latter was developed by English instrument maker William Bainbridge, resulting in the "improved English flageolet" in 1803. There are also double and triple flageolets, having two or three bodies that allowed for a drone (music), drone and countermelody. Flageolets were made until the 19th century. Etymology Flageolet means "little flute". The name is the diminutive form of the Old French word ''flajol'' (flute). In Provençal dialect, flute is ''flaujol'' or ''flautol''. History Flageolets have varied greatly during the last 400 years. The first flageolets were called "French flag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flageolet ébène, Argent Et Nacre
__NOTOC__ The flageolet is a woodwind instrument and a member of the family of duct flutes that includes recorders and tin whistles. There are two basic forms of the instrument: the French, having four finger holes on the front and two thumb holes on the back; and the English, having six finger holes on the front and sometimes a single thumb hole on the back. The latter was developed by English instrument maker William Bainbridge, resulting in the "improved English flageolet" in 1803. There are also double and triple flageolets, having two or three bodies that allowed for a drone and countermelody. Flageolets were made until the 19th century. Etymology Flageolet means "little flute". The name is the diminutive form of the Old French word ''flajol'' (flute). In Provençal dialect">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... word ''flajol'' (flute). In Provençal dialect, flute is ''flaujol'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
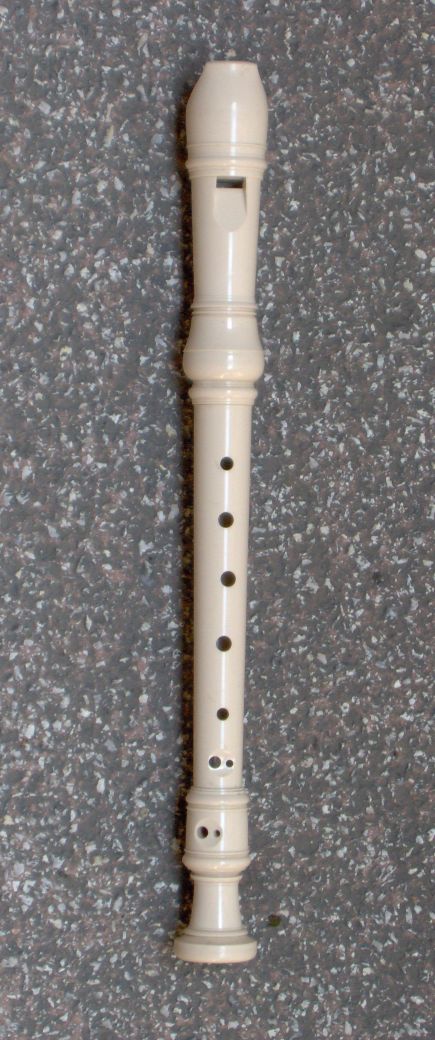
Recorder (musical Instrument)
The recorder is a family of woodwind musical instruments in the group known as ''internal duct flutes'': flutes with a whistle mouthpiece, also known as fipple flutes, although this is an archaic term. A recorder can be distinguished from other duct flutes by the presence of a thumb-hole for the upper hand and seven finger-holes: three for the upper hand and four for the lower. It is the most prominent duct flute in the western classical tradition. Recorders are made in various sizes with names and compasses roughly corresponding to various vocal ranges. The sizes most commonly in use today are the soprano (also known as descant, lowest note C5), alto (also known as treble, lowest note F4), tenor (lowest note C4), and bass (lowest note F3). Recorders were traditionally constructed from wood or ivory. Modern professional instruments are almost invariably of wood, often boxwood; student and scholastic recorders are commonly of moulded plastic. The recorders' internal and ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin Whistle
The tin whistle, also known as the penny whistle, is a simple six-holed woodwind instrument. It is a type of fipple flute, a class of instrument which also includes the recorder and Native American flute. A tin whistle player is called a whistler. The tin whistle is closely associated with Irish traditional music and Celtic music. Other names for the instrument are the flageolet, English flageolet, Scottish penny whistle, tin flageolet, or Irish whistle (also ). History The tin whistle in its modern form is from a wider family of fipple flutes which have been seen in many forms and cultures throughout the world. In Europe, such instruments have a long and distinguished history and take various forms, of which the most widely known are the recorder, tin whistle, Flabiol, Txistu and tabor pipe. Predecessors Almost all early cultures had a type of fipple flute, and it is most likely the first pitched flute-type instrument in existence. Examples found to date include a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Purkis
John Purkis (1781 – 10 April 1849), was an English organist and teacher. He was blind at birth. A child prodigy, Purkis studied with Thomas Grenville (circa 1744–1827), also blind, and the organist at the Foundling Hospital in London. He became organist at St Margaret's Chapel at the age of nine, and then, aged 12, at St Olave Southwark, after a public competition and three day poll. His salary there was £30. From 1804 until his death Purkis was organist at St Clement Danes, and also (after 1825) at St Peter's Walworth.'Purkis, John', in ''Historical Dictionary of English Music ca. 1400–1958'' ed. by Charles Edward McGuire, Steven E. Plank (2012), p. 246 He was consultant to the organ building firm Flight and Robinson during the construction of the Apollonicon a self-playing barrel organ A barrel organ (also called roller organ or crank organ) is a France, French mechanical musical instrument consisting of bellows and one or more ranks of organ pipe, pipes housed in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fipple
The term fipple specifies a variety of end-blown flute that includes the flageolet, recorder, and tin whistle. The Hornbostel–Sachs system for classifying musical instruments places this group under the heading "Flutes with duct or duct flutes." The label "fipple flute" is frequently applied to members of the subgroup but there is no general agreement about the structural detail of the sound-producing mechanism that constitutes the fipple itself. Nomenclature The accompanying illustration of the mouthpiece of a recorder shows a wooden block (A) with a channel carved into the body of the instrument (B), together forming a duct that directs a ribbon of air across an opening toward a sharp edge (C). The edge splits the air in a manner that alternately directs it into and outside of the tube, setting the contained column of air into periodic vibration. This flow-controlled "air reed" is a definitive characteristic of all flutes, which therefore all have an edge or equivalent air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipe And Tabor
Pipe and tabor is a pair of instruments played by a single player, consisting of a three-hole pipe played with one hand, and a small drum played with the other. The tabor hangs on the performer's left arm or around the neck, leaving the hands free to beat the drum with a stick in the right hand and play the pipe with thumb and first two fingers of the left hand. The pipe is made out of wood, metal or plastic and consists of a cylindrical tube of narrow bore (1:40 diameter:length ratio) pierced with three holes near one end, two in front and one in back. At the opposite end is a fipple or block, similar to that used in a recorder. Tabor pipes are widespread throughout the globe, found on most continents and in many countries. Each culture has developed a different style of pipe, so a different method of playing and a different range of notes. The smallest of the family is the Picco pipe, while the largest is the fujara. In Europe there are many variations of instrument. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin Whistles
Tin is a chemical element; it has symbol Sn () and atomic number 50. A silvery-colored metal, tin is soft enough to be cut with little force, and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, a bar of tin makes a sound, the so-called "tin cry", as a result of twinning in tin crystals. Tin is a post-transition metal in group 14 of the periodic table of elements. It is obtained chiefly from the mineral cassiterite, which contains stannic oxide, . Tin shows a chemical similarity to both of its neighbors in group 14, germanium and lead, and has two main oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4. Tin is the 49th most abundant element on Earth, making up 0.00022% of its crust, and with 10 stable isotopes, it has the largest number of stable isotopes in the periodic table, due to its magic number of protons. It has two main allotropes: at room temperature, the stable allotrope is β-tin, a silvery-white, malleable metal; at low temperatures it is l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffet Crampon
Buffet Crampon SAS is a French manufacturer of wind instruments based in Mantes-la-Ville, in the Yvelines department. The company is the world market leader in the production of Boehm system clarinets. Its subsidiary, Buffet Crampon Deutschland GmbH, founded in 2010 and based in Markneukirchen, Vogtland, Sachsen, is the world market leader in the manufacture of brass instruments. To manufacture and sell its products, the BC Group employed approximately 1,000 people worldwide at the beginning of 2021, 470 of whom were employed by BC Germany alone. The management of the group has been led by Jérôme Perrod since 2014. Products and brands The following brands / labels, with the exception of the Buffet Crampon brand, were formerly independent companies whose essential assets, including the name and trademark rights, are owned by other companies and ultimately were acquired partly by Buffet Crampon SAS partly by BC Deutschland GmbH, and which were then dissolved as companie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It shares Anglo-Scottish border, a land border with Scotland to the north and England–Wales border, another land border with Wales to the west, and is otherwise surrounded by the North Sea to the east, the English Channel to the south, the Celtic Sea to the south-west, and the Irish Sea to the west. Continental Europe lies to the south-east, and Ireland to the west. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the population was 56,490,048. London is both List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, the largest city and the Capital city, capital. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic. It takes its name from the Angles (tribe), Angles, a Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe who settled du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodwind
Woodwind instruments are a family of musical instruments within the greater category of wind instruments. Common examples include flute, clarinet, oboe, bassoon, and saxophone. There are two main types of woodwind instruments: flutes and Reed aerophones, reed instruments (otherwise called reed pipes). The main distinction between these instruments and other wind instruments is the way in which they produce sound. All woodwinds produce sound by splitting the air blown into them on a sharp edge, such as a reed (mouthpiece), reed or a fipple. Despite the name, a woodwind may be made of any material, not just wood. Common examples of other materials include brass, silver, cane, and other metals such as gold and platinum. The saxophone, for example, though made of brass, is considered a woodwind because it requires a reed to produce sound. Occasionally, woodwinds are made of earthen materials, especially ocarinas. Flutes Flutes produce sound by directing a focused stream of air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |