|
False Bottom (sea Ice)
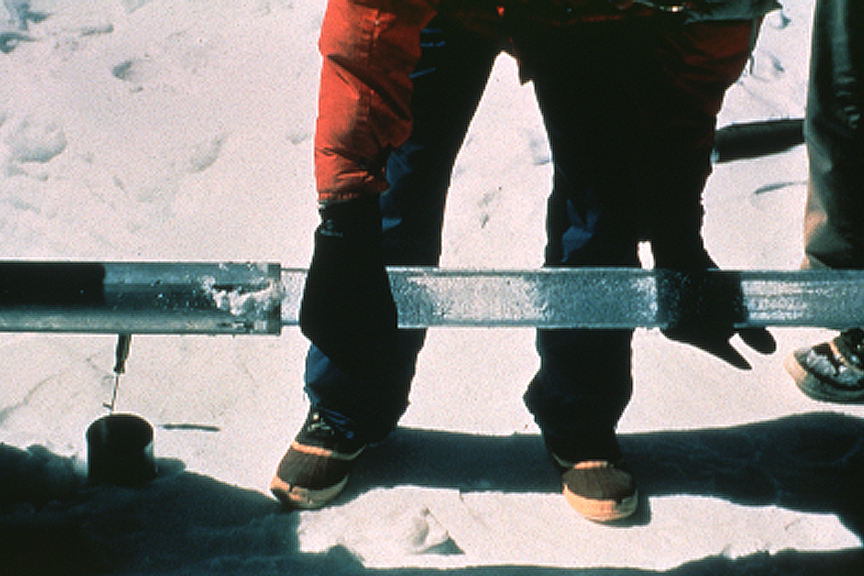
False bottom is a form of sea ice that forms at the interface between meltwater and seawater via the process of Double diffusive convection, double-diffusive convection of heat and salt. Characteristics False bottoms have been observed under drifting Arctic sea ice, under land-fast ice in Greenland, and at Ward Hunt Ice Shelf. Being located under ice, false bottoms are not easy to investigate, and the current observations are quite variable. For example, the areal coverage of false bottoms was 50% at the drifting station Charlie in 1959, 15% during Surface Heat Budget of the Arctic Ocean, SHEBA expedition in 1998 and 20% during MOSAiC Expedition, MOSAiC expedition in 2020. Both physical modelling and in situ observations suggest that false bottoms may decrease Arctic sea ice decline, sea ice melt up to 8%. Meanwhile, measurements from manual ice thickness gauges in Fram Strait in the summer of 2020 showed a nearly 50% reduction in bottom ice melt due to false bottoms. The sali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheme Of False Bottom
A scheme is a systematic plan for the implementation of a certain idea. Scheme or schemer may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''The Scheme'' (TV series), a BBC Scotland documentary series * The Scheme (band), an English pop band * ''The Scheme'', an action role-playing video game for the PC-8801, made by Quest Corporation * Schemer (comics), Richard Fisk, a Marvel Comics villain turned antihero * Horace Schemer, a fictional character in the TV series ''Shining Time Station'' * Schemee, a fictional child character and Schemer's nephew in the TV Series ''Shining Time Station'' * ''Schemers'' (film), a Scottish film Other uses * Classification scheme, eg a thesaurus, a taxonomy, a data model, or an ontology * Scheme (programming language), a minimalist dialect of Lisp * Scheme (mathematics), a concept in algebraic geometry * Scheme (linguistics), a figure of speech that changes a sentence's structure * Scam, an attempt to swindle or cheat people through deception **Get-rich-quic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Bottom Salinity , falsehood in Hindu mythology
{{Disambiguation ...
False or falsehood may refer to: *False (logic), the negation of truth in classical logic *Lie or falsehood, a type of deception in the form of an untruthful statement *false (Unix), a Unix command * ''False'' (album), a 1992 album by Gorefest *Matthew Dear or False (born 1979), American DJ and producer * ''Falsehood'' (1952 film), an Italian melodrama film * ''Falsehood'' (2001 film), an American short film See also * *Anrita Adharma is the Sanskrit antonym of dharma. It means "that which is not in accord with the dharma". Connotations include betrayal, discord, disharmony, unnaturalness, wrongness, evil, immorality, unrighteousness, wickedness, and vice..In Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Mass Balance Buoy
An ice mass balance buoy (IMB) allows scientists studying sea ice to measure its temperature and the evolution of its interfaces remotely. The autonomous mass balance buoys usually consist of a data controller module and a temperature string. Some ice mass balance buoys also include Echo sounding, acoustic sounders above and below ice measuring the positions of the snow-ice and ice-water interfaces. Types The main types of ice mass balance buoys include * The Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, CRREL-Dartmouth College, Dartmouth Ice Mass Balance (IMB) Buoy * Snow and Ice Mass Balance Array (SIMBA) from Scottish Association for Marine Science, SAMS * Seasonal Ice Mass Balance buoy (SIMB-1,2,3) The CRREL-Dartmouth Ice Mass Balance Buoy (IMB) includes two ice-facing acoustic rangefinders, a vertical temperature string, and air temperature and pressure sensors. These sensors are connected to a non-floating satellite-connected transmission package. Seasonal Ice Mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances ( ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. "Sonar" can refer to one of two types of technology: ''passive'' sonar means listening for the sound made by vessels; ''active'' sonar means emitting pulses of sounds and listening for echoes. Sonar may be used as a means of acoustic location and of measurement of the echo characteristics of "targets" in the water. Acoustic location in air was used before the introduction of radar. Sonar may also be used for robot navigation, and SODAR (an upward-looking in-air sonar) is used for atmospheric investigations. The term ''sonar'' is also used for the equipment used to generate and receive the sound. The acoustic frequencies used in sonar systems vary from very low ( infrasonic) to ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Drilling
Ice drilling allows scientists studying glaciers and ice sheets to gain access to what is beneath the ice, to take measurements along the interior of the ice, and to retrieve samples. Instruments can be placed in the drilled holes to record temperature, pressure, speed, direction of movement, and for other scientific research, such as neutrino detection. Many different methods have been used since 1840, when the first scientific ice drilling expedition attempted to drill through the Unteraargletscher in the Alps. Two early methods were percussion, in which the ice is fractured and pulverized, and rotary drilling, a method often used in mineral exploration for rock drilling. In the 1940s, thermal drills began to be used; these drills melt the ice by heating the drill. Drills that use jets of hot water or steam to bore through ice soon followed. A growing interest in ice cores, used for palaeoclimatological research, led to ice coring drills being developed in the 1950s and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Core
An ice core is a core sample that is typically removed from an ice sheet or a high mountain glacier. Since the ice forms from the incremental buildup of annual layers of snow, lower layers are older than upper ones, and an ice core contains ice formed over a range of years. Cores are drilled with hand augers (for shallow holes) or powered drills; they can reach depths of over two miles (3.2 km), and contain ice up to 800,000 years old. The physical properties of the ice and of material trapped in it can be used to reconstruct the climate over the age range of the core. The proportions of different oxygen and hydrogen isotopes provide information about ancient temperatures, and the air trapped in tiny bubbles can be analysed to determine the level of atmospheric gases such as carbon dioxide. Since heat flow in a large ice sheet is very slow, the borehole temperature is another indicator of temperature in the past. These data can be combined to find the climate m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wandel Sea
The Wandel Sea ( da, Wandelhavet; also known as McKinley Sea) is a body of water in the Arctic Ocean, stretching from northeast of Greenland to Svalbard. It is obstructed by ice most of the year. This sea is named after Danish polar explorer and hydrographer, Vice Admiral Carl Frederick Wandel, who in the years 1895–96 explored the coastal waters of Greenland as part of the Danish Ingolf Expedition. Geography This arctic sea is located at 82° north longitude and 21° west latitude. Seas farther north and northwest of the Wandel Sea were once frozen year-round but now may have open water in late summer, as of August 2018.ftp://ftp-projects.cen.uni-hamburg.de/seaice/AMSR2/3.125km/ The Wandel Sea stretches westward as far as Cape Morris Jesup. Further west is the Lincoln Sea. In the south, it stretches to Nordostrundingen. The Wandel Sea connects to the Greenland Sea in the south through the Fram Strait. Independence Fjord and Frederick E. Hyde Fjord are two great fjor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Ice
Fast ice (also called ''land-fast ice'', ''landfast ice'', and ''shore-fast ice'') is sea ice that is "fastened" to the coastline, to the sea floor along shoals or to grounded icebergs.Leppäranta, M. 2011. The Drift of Sea Ice. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. Fast ice may either grow in place from the sea water or by freezing pieces of drifting ice to the shore or other anchor sites.Kovacs, A.and M. Mellor. 1974. "Sea ice morphology and ice as a geologic agent in the Southern Beaufort Sea." pp. 113-164, in: ''The Coast and Shelf of the Beaufort Sea'', J.C. Reed and J.E. Sater (Eds.), Arlington, Va.: U.S.A. Unlike drift (or pack) ice, fast ice does not move with currents and winds. The width (and the presence) of this ice zone is usually seasonal and depends on ice thickness, topography of the sea floor and islands. It ranges from a few meters to several hundred kilometers. Seaward expansion is a function of a number of factors, notably water depth, shoreline protection, time of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaufort Sea
The Beaufort Sea (; french: Mer de Beaufort, Iñupiaq: ''Taġiuq'') is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of the Northwest Territories, the Yukon, and Alaska, and west of Canada's Arctic islands. The sea is named after Sir Francis Beaufort, a hydrographer. The Mackenzie River, the longest in Canada, empties into the Canadian part of the Beaufort Sea west of Tuktoyaktuk, which is one of the few permanent settlements on the sea's shores. The sea, characterized by severe climate, is frozen over most of the year. Historically, only a narrow pass up to opened in August–September near its shores, but recently due to climate change in the Arctic the ice-free area in late summer has greatly enlarged. Until recently, the Beaufort Sea was known as an important reservoir for the replenishment of Arctic sea ice. Sea ice would often rotate for several years in the Beaufort Gyre, the dominant ocean current of the Beaufort Sea, growing into sturdy and thick multi-ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
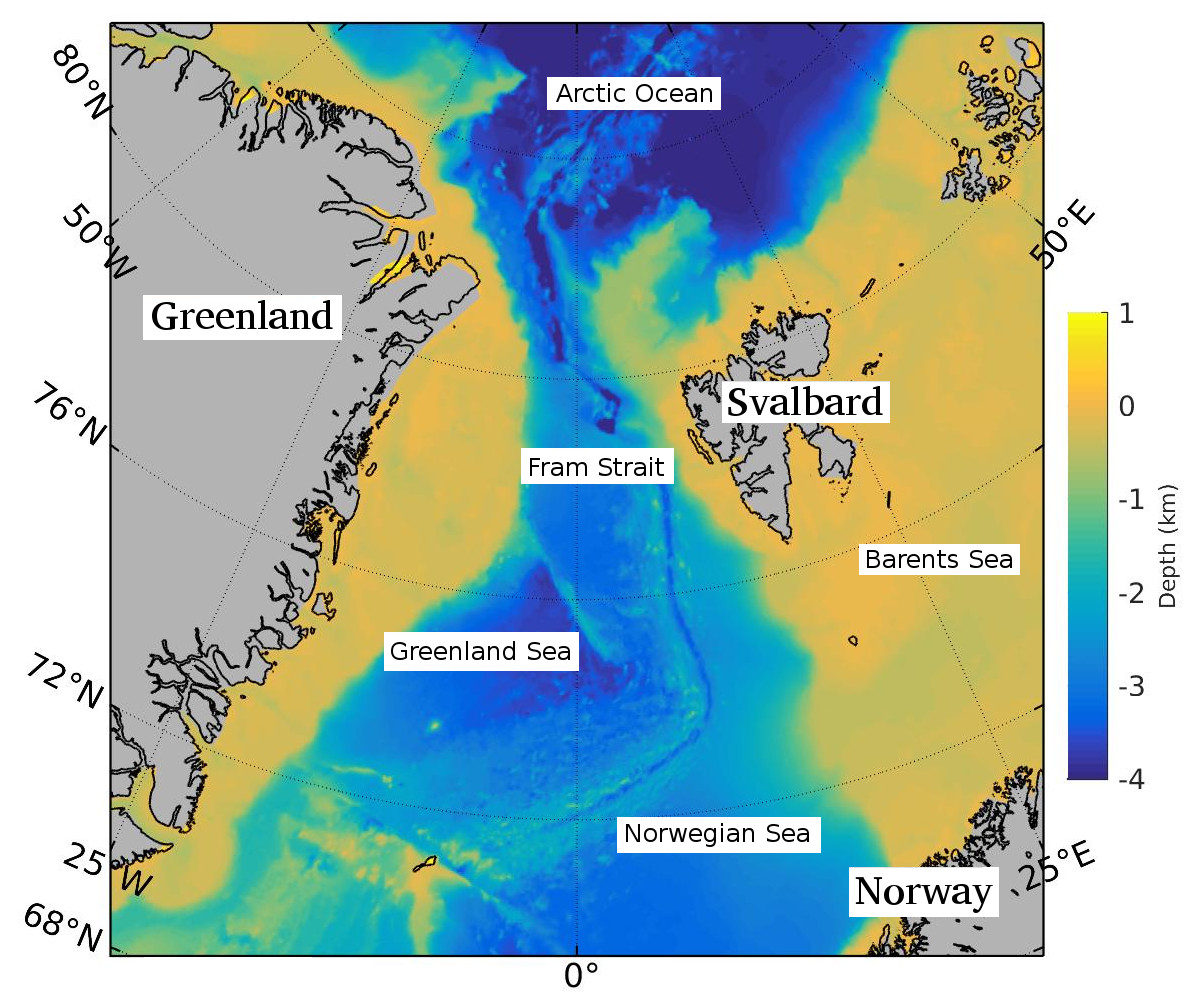
Fram Strait
The Fram Strait is the passage between Greenland and Svalbard, located roughly between 77°N and 81°N latitudes and centered on the prime meridian. The Greenland and Norwegian Seas lie south of Fram Strait, while the Nansen Basin of the Arctic Ocean lies to the north. Fram Strait is noted for being the only deep connection between the Arctic Ocean and the World Oceans. The dominant oceanographic features of the region are the West Spitsbergen Current on the east side of the strait and the East Greenland Current on the west. Description Fram Strait is the northernmost ocean area having ice-free conditions throughout the year. The width of the strait is about 450 km, but because of the wide continental shelves of Greenland and Spitsbergen, the deep portion of Fram Strait is only about 300 km wide. The ocean over the Greenland continental shelf is often covered with ice. Within Fram Strait, the sill connecting the Arctic and Fram Strait is 2545 m deep. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Ridge (ice)
A pressure ridge, when consisting of ice, is a linear pile-up of sea ice fragments formed in pack ice by accumulation in the convergence between floes. Such a pressure ridge develops in an ice cover as a result of a stress regime established within the plane of the ice. Within sea ice expanses, pressure ridges originate from the interaction between floes,A ''floe'' is any individual piece of sea ice larger than . as they collide with each other.http://nsidc.org/cryosphere/seaice/index.html .Weeks, W. F. (2010) ''On sea ice''. University of Alaska Press, Fairbanks, 664 p. Currents and winds are the main driving forces, but the latter are particularly effective when they have a predominant direction. Pressure ridges are made up of angular ice blocks of various sizes that pile up on the floes. The part of the ridge that is above the water surface is known as the ''sail''; that below it as the ''keel''.These terms also apply for any floating ice feature, such as icebergs. Pressure rid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melt Pond
Melt ponds are pools of open water that form on sea ice in the warmer months of spring and summer. The ponds are also found on glacial ice and ice shelves. Ponds of melted water can also develop under the ice. Melt ponds are usually darker than the surrounding ice, and their distribution and size is highly variable. They absorb solar radiation rather than reflecting it as ice does and, thereby, have a significant influence on Earth's radiation balance. This differential, which had not been scientifically investigated until recently, has a large effect on the rate of ice melting and the extent of ice cover. Melt ponds can melt through to the ocean's surface. Seawater entering the pond increases the melt rate because the salty water of the ocean is warmer than the fresh water of the pond. The increase in salinity also depresses the water's freezing point. Water from melt ponds over land surface can run into crevasses or moulins – tubes leading under ice sheets or glacier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |