|
Ethyl Trifluoroacetate
Ethyl trifluoroacetate is a chemical compound from the trifluoroacetate group. Production Ethyl trifluoroacetate can be obtained by reacting 2,4,6-tris-(trifluoromethyl)-1,3,5-triazine with ethanol in the presence of hydrochloric acid. The former, in turn, can be prepared by a two-step reaction starting from trichloroacetonitrile by reaction with hydrogen chloride and fluorination of the intermediate with antimony trifluoride. The compound can also be obtained by reacting trifluoroacetic acid or sodium trifluoroacetate with ethanol.Google PatentsUS4879407A - Process for the preparation of ethyl trifluoroacetate - Google Patents retrieved 7 August 2022 Properties Ethyl trifluoroacetate is a colorless and odorless liquid that is sparingly soluble in water but miscible with chloroform and methanol. The compound exists in the gas phase in two more conformal forms. Use Ethyl trifluoroacetate is used as an intermediate in organic synthesis to prepare organic fluorine compounds such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichloroacetonitrile
Trichloroacetonitrile is an organic compound with the formula CCl3CN. It is a colourless liquid, although commercial samples often are brownish. It is used commercially as a precursor to the fungicide etridiazole. It is prepared by dehydration of trichloroacetamide. As a bifunctional compound, trichloroacetonitrile can react at both the trichloromethyl and the nitrile group. The Electrophilic aromatic directing groups, electron-withdrawing effect of the trichloromethyl group activates the nitrile group for nucleophilic additions. The high Reactivity (chemistry), reactivity makes trichloroacetonitrile a versatile reagent, but also causes its susceptibility towards hydrolysis. Synthesis The production of trichloroacetonitrile by dehydration of trichloroacetamide was first described in 1873 by L. Bisschopinck at the KU Leuven, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven. : Trichloroacetonitrile can be obtained by Chlorination reaction, chlorination of acetonitrile on a zinc, copper and alkali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimony Trifluoride
Antimony trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula SbF3. Sometimes called Swarts' reagent, it is one of two principal fluorides of antimony, the other being SbF5. It appears as a white solid. As well as some industrial applications, it is used as a reagent in inorganic and organofluorine chemistry. Preparation and structure In solid SbF3, the Sb centres have octahedral molecular geometry and are linked by bridging fluoride ligands. Three Sb–F bonds are short (192 pm) and three are long (261 pm). Because it is a polymer, SbF3 is far less volatile than related compounds AsF3 and SbCl3. SbF3 is prepared by treating antimony trioxide with hydrogen fluoride: :Sb2O3 + 6 HF → 2 SbF3 + 3 H2O The compound is a mild Lewis acid, hydrolyzing slowly in water. With fluorine, it is oxidized to give antimony pentafluoride. :SbF3 + F2 → SbF5 Applications It is used as a fluorination reagent in organic chemistry. This application was reported by the Belgian c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifluoroacetic Acid
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is a synthetic organofluorine compound with the chemical formula CF3CO2H. It belongs to the subclass of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) known as ultrashort-chain perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs). TFA is not produced biologically or abiotically and is commonly used in organic chemistry for various purposes. It is the most abundant PFAS found in the environment. It is a haloacetic acid, with all three of the acetyl group's hydrogen atoms replaced by fluorine atoms. It is a colorless liquid with a vinegar-like odor. TFA is a stronger acid than acetic acid, having an acid ionisation constant, ''K''a, that is approximately 34,000 times higher, as the highly electronegative fluorine atoms and consequent electron-withdrawing nature of the trifluoromethyl group weakens the oxygen-hydrogen bond (allowing for greater acidity) and stabilises the anionic conjugate base. Synthesis TFA is prepared industrially by the electrofluorination of ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifluoroacetate
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is a synthetic organofluorine compound with the chemical formula CF3CO2H. It belongs to the subclass of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) known as ultrashort-chain perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs). TFA is not produced biologically or abiotically and is commonly used in organic chemistry for various purposes. It is the most abundant PFAS found in the environment. It is a haloacetic acid, with all three of the acetyl group's hydrogen atoms replaced by fluorine atoms. It is a colorless liquid with a vinegar-like odor. TFA is a stronger acid than acetic acid, having an acid ionisation constant, ''K''a, that is approximately 34,000 times higher, as the highly electronegative fluorine atoms and consequent electron-withdrawing nature of the trifluoromethyl group weakens the oxygen-hydrogen bond (allowing for greater acidity) and stabilises the anionic conjugate base. Synthesis TFA is prepared industrially by the electrofluorination of acetyl chlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane (often abbreviated as TCM), is an organochloride with the formula and a common solvent. It is a volatile, colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to refrigerants and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Chloroform was once used as an inhalational anesthetic between the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century. It is miscible with many solvents but it is only very slightly soluble in water (only 8 g/L at 20°C). Structure and name The molecule adopts a tetrahedral molecular geometry with C3v symmetry. The chloroform molecule can be viewed as a methane molecule with three hydrogen atoms replaced with three chlorine atoms, leaving a single hydrogen atom. The name "chloroform" is a portmanteau of ''terchloride'' (tertiary chloride, a trichloride) and ''formyle'', an obsolete name for the methylylidene radical (CH) derived from formic acid. Natural occurrence Many kinds of seaweed produce chlor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
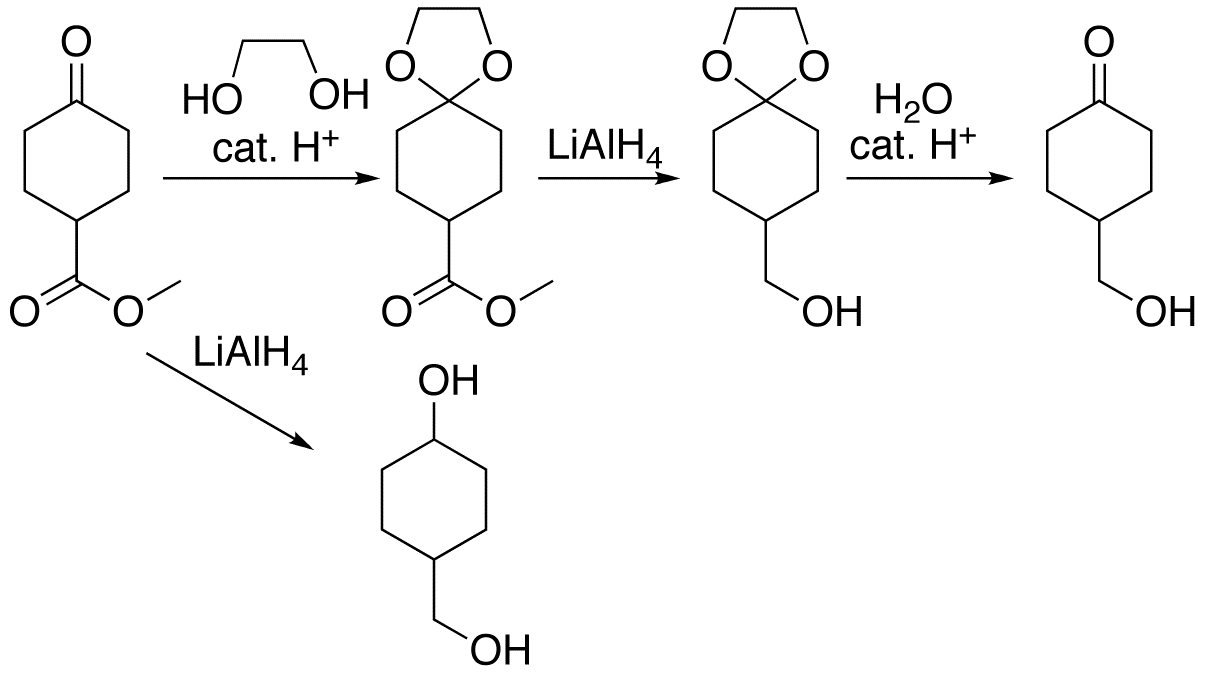
Protecting Group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, specific parts of the molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. These parts (functional groups) must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive reagent that usefully reduces esters to alcohols. It always reacts with carbonyl groups, and cannot be discouraged by any means. When an ester must be reduced in the presence of a carbonyl, hydride attack on the carbonyl must be prevented. One way to do so converts the carbonyl into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the hydride step is complete, aqueous acid removes the acetal, restoring the carbonyl. This step ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Synthesis
Organic synthesis is a branch of chemical synthesis concerned with the construction of organic compounds. Organic compounds are molecules consisting of combinations of covalently-linked hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. Within the general subject of organic synthesis, there are many different types of synthetic routes that can be completed including total synthesis, Enantioselective synthesis, stereoselective synthesis, automated synthesis, and many more. Additionally, in understanding organic synthesis it is necessary to be familiar with the methodology, techniques, and applications of the subject. Total synthesis A total synthesis refers to the complete chemical synthesis of molecules from simple, Precursor (chemistry), natural precursors. Total synthesis is accomplished either via a linear or convergent approach. In a Linear synthesis, ''linear'' synthesis—often adequate for simple structures—several steps are performed sequentially until the molecule is com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifluoromethyl Compounds
The trifluoromethyl group is a functional group that has the formula In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' in science refers to the general construct of a relationship betwe ... . The naming of is group is derived from the methyl group (which has the formula ), by replacing each hydrogen atom by a fluorine atom. Some common examples are trifluoromethane , 1,1,1-trifluoroethane , and hexafluoroacetone . Compounds with this group are a subclass of the organofluorines. Properties The trifluoromethyl group has a significant electronegativity that is often described as being intermediate between the electronegativities of fluorine and chlorine. For this reason, trifluoromethyl-substituted compounds are often strong acids, such as trifluoromethanesulfonic acid and trifluoroacetic acid. Conversely, the trifluoromethyl group lowers the basicity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |