|
Esophageal Dysphagia
Esophageal dysphagia is a form of dysphagia where the underlying cause arises from the body of the esophagus, lower esophageal sphincter, or cardia of the stomach, usually due to mechanical causes or motility problems. Signs and symptoms Patients usually complain of dysphagia (the feeling of food getting stuck ''several seconds'' after swallowing), and will point to the suprasternal notch or behind the sternum as the site of obstruction. Causes If there is dysphagia to both solids and liquids, then it is most likely a motility problem. If there is dysphagia initially to solids but progresses to also involve liquids, then it is most likely a mechanical obstruction. Once a distinction has been made between a motility problem and a mechanical obstruction, it is important to note whether the dysphagia is intermittent or progressive. An intermittent motility dysphagia likely can be diffuse esophageal spasm (DES) or nonspecific esophageal motility disorder (NEMD). Progressive motility d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology (from the Greek gastḗr- "belly", -énteron "intestine", and -logía "study of") is the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. The digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes referred to as the ''GI tract,'' which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine as well as the accessory organs of digestion which include the pancreas, gallbladder, and liver. The digestive system functions to move material through the GI tract via peristalsis, break down that material via digestion, absorb nutrients for use throughout the body, and remove waste from the body via defecation. Physicians who specialize in the medical specialty of gastroenterology are called gastroenterologists or sometimes ''GI doctors''. Some of the most common conditions managed by gastroenterologists include gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal bleeding, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer (American English) or oesophageal cancer (British English) is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include dysphagia, difficulty in swallowing and weight loss. Other symptoms may include odynophagia, pain when swallowing, a hoarseness, hoarse voice, Lymphadenopathy, enlarged lymph nodes ("glands") around the clavicle, collarbone, a dry cough, and possibly hemoptysis, coughing up or hematemesis, vomiting blood. The two main Histopathology, sub-types of the disease are esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma (often abbreviated to ESCC), which is more common in the developing world, and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), which is more common in the developed world. A number of less common types also occur. Squamous-cell carcinoma arises from the squamous epithelium, epithelial cells that line the esophagus. Adenocarcinoma arises from glandular cells present in the lower third of the esophagus, ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple-A Syndrome
Triple-A syndrome or AAA syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive congenital disorder. In most cases, there is no family history of AAA syndrome. The syndrome was first identified by Jeremy Allgrove and colleagues in 1978; since then just over 100 cases have been reported. The syndrome is called Triple-A due to the manifestation of the illness which includes achalasia (a dysfunction of the esophagus), addisonianism (adrenal insufficiency of primary type), and alacrima (insufficiency of tears). Alacrima is usually the earliest manifestation. Neurodegeneration or atrophy of the nerve cells and autonomic dysfunction may be seen in the disorder; therefore, some have suggested the disorder be called 4A syndrome. It is a progressive disorder that can take years to develop the full-blown clinical picture. The disorder also has variability and heterogeneity in presentation. Presentation Individuals affected by AAA have adrenal insufficiency/Addison's disease due to ACTH resistance, alac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
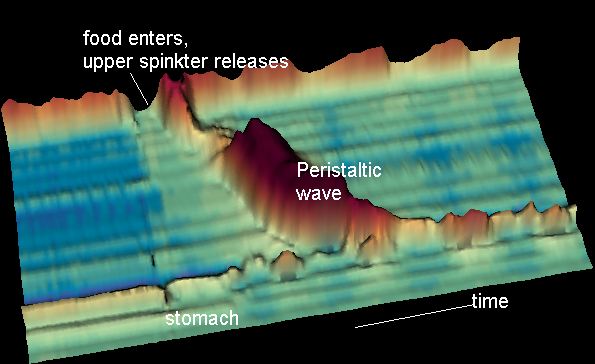
Peristalsis
Peristalsis ( , ) is a type of intestinal motility, characterized by symmetry in biology#Radial symmetry, radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an wikt:anterograde, anterograde direction. Peristalsis is progression of coordinated contraction of involuntary circular muscles, which is preceded by a simultaneous contraction of the longitudinal muscle and relaxation of the circular muscle in the lining of the gut. In much of a digestive tract, such as the human gastrointestinal tract, smooth muscle tissue contracts in sequence to produce a peristaltic wave, which propels a ball of food (called a bolus (digestion), bolus before being transformed into chyme in the stomach) along the tract. The peristaltic movement comprises relaxation of circular smooth muscles, then their contraction behind the chewed material to keep it from moving backward, then longitudinal contraction to push it forward. Earthworms use a similar mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin available for oxygen transport, or abnormalities in hemoglobin that impair its function. The name is derived . When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as Fatigue, tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a Exercise intolerance, reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, lightheadedness, feeling like one is going to pass out, Syncope (medicine), loss of consciousness, and polydipsia, increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably Pallor, pale. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe. Anemia can be caused by blood loss, decreased red blood cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Deficiency
Iron deficiency, or sideropenia, is the state in which a body lacks enough iron to supply its needs. Iron is present in all cells in the human body and has several vital functions, such as carrying oxygen to the tissues from the lungs as a key component of the hemoglobin protein, acting as a transport medium for electrons within the cells in the form of cytochromes, and facilitating oxygen enzyme reactions in various tissues. Too little iron can interfere with these vital functions and lead to morbidity and death. Total body iron averages approximately 3.8 g in men and 2.3 g in women. In blood plasma, iron is carried tightly bound to the protein transferrin. Several mechanisms control iron metabolism and safeguard against iron deficiency. The main regulatory mechanism is situated in the gastrointestinal tract. Most iron absorption occurs in the duodenum, the first section of the small intestine. Several dietary factors may affect iron absorption. Iron deficiency develops when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plummer–Vinson Syndrome
Plummer–Vinson syndrome (also known as Paterson–Kelly syndrome or Paterson–Brown-Kelly syndrome in the UK) is a rare disease characterized by dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), iron-deficiency anemia, atrophic glossitis (inflammation of the tongue), angular cheilitis or cheilosis (crackings at the corners of the mouth, respectively associated or not with inflammation), and upper esophageal webs (thin membranes in the esophagus that can cause obstruction). Treatment with iron supplementation and mechanical widening of the esophagus generally leads to excellent outcomes. While exact epidemiological data are lacking, Plummer–Vinson syndrome has become extremely rare. The reduction in prevalence has been hypothesized to result from improvements in nutritional status and iron availability in countries where the syndrome was previously more common. The syndrome generally occurs in perimenopausal women. Identification and follow-up of affected individuals are important due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cricoid
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the Vertebrate trachea, trachea. It forms the back part of the larynx, voice box and functions as an attachment site for muscles, cartilages, and ligaments involved in opening and closing the airway and in producing speech. Anatomy The cricoid cartilage is the only laryngeal cartilage to form a complete circle around the airway. It is smaller yet thicker and tougher than the thyroid cartilage above. It articulates superiorly with the thyroid cartilage, and the paired arytenoid cartilage. Inferiorly, the trachea attaches onto it. It occurs at the level of the cervical vertebrae, C6 vertebra. Structure The Anatomical terms of location, posterior part of the cricoid cartilage (cricoid lamina) is somewhat broader than the anterior and lateral part (cricoid arch). Its shape is said to resemble a signet ring. Cricoid arch T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an allergic inflammatory condition of the esophagus that involves eosinophils, a type of white blood cell. In healthy individuals, the esophagus is typically devoid of eosinophils. In EoE, eosinophils migrate to the esophagus in large numbers. When a trigger food is eaten, the eosinophils contribute to tissue damage and inflammation. Symptoms include swallowing difficulty, food impaction, vomiting, and heartburn. Eosinophilic esophagitis was first described in children but also occurs in adults. The condition is poorly understood, but food allergy may play a significant role. The treatment may consist of removing known or suspected triggers and medication to suppress the immune response. In severe cases, it may be necessary to enlarge the esophagus with an endoscopy procedure. While knowledge about EoE has been increasing rapidly, diagnosing it can be challenging because the symptoms and histopathologic findings are not specific. Signs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
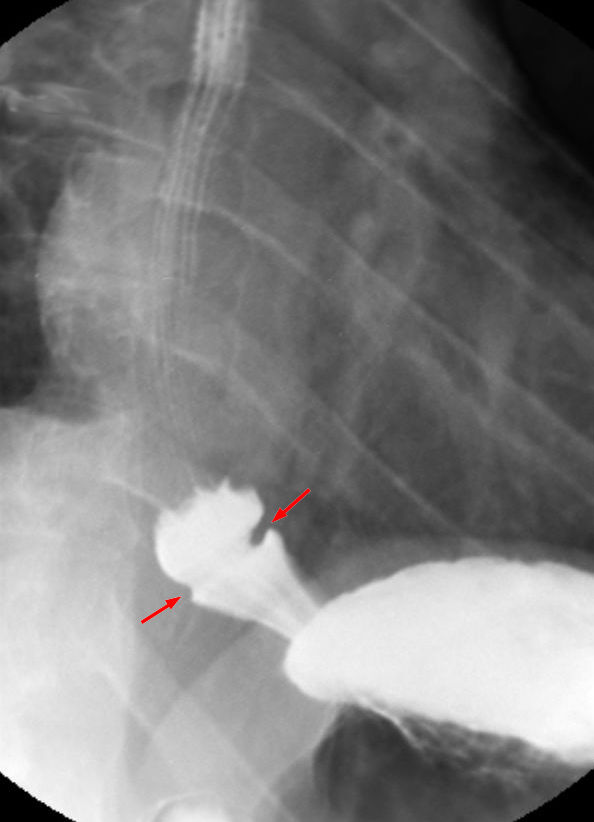
Schatzki Ring
A Schatzki ring or Schatzki–Gary ring is a narrowing of the lower esophagus that can cause difficulty swallowing (dysphagia). The narrowing is caused by a ring of mucosal tissue (which lines the esophagus) or muscular tissue. A Schatzki ring is a specific type of "esophageal ring", and Schatzki rings are further subdivided into those above the esophagus/stomach junction (A rings), and those found at the squamocolumnar junction in the lower esophagus (B rings). Patients with Schatzki rings can develop intermittent difficulty swallowing or, more seriously, a completely blocked esophagus. The ring is named after the German-American physician Richard Schatzki. Signs and symptoms Not all patients with Schatzki rings have symptoms; barium swallow tests of the esophagus sometimes show Schatzki rings in patients with no swallowing difficulties. When Schatzki rings cause symptoms, they usually result in episodic difficulties with swallowing (dysphagia) solid foods, or a sensation th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Web
Esophageal webs are thin membranes occurring anywhere along the esophagus. Presentation Its main symptoms are pain and difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia). Esophageal webs are thin membranes of normal esophageal tissue consisting of mucosa and submucosa that can partially protrude/obstruct the esophagus. They can be congenital or acquired. Congenital webs commonly appear in the middle and inferior third of the esophagus, and they are more likely to be circumferential with a central or eccentric orifice. Acquired webs are much more common than congenital webs and typically appear in the cervical area (postcricoid). Clinical symptoms of this condition are selective (solid more than liquids) dysphagia, thoracic pain, nasopharyngeal reflux, aspiration, perforation and food impaction (the last two are very rare). file:Zervikales Web.jpg, Esophageal web stenosis in barium swallow examination lateral view. file:Web mit Jet-Phaenomen.jpg, Web with "jet-phenomenon". Arrowhead on inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Ring
A Schatzki ring or Schatzki–Gary ring is a narrowing of the lower esophagus that can cause difficulty swallowing (dysphagia). The narrowing is caused by a ring of mucosal tissue (which lines the esophagus) or muscular tissue. A Schatzki ring is a specific type of "esophageal ring", and Schatzki rings are further subdivided into those above the esophagus/stomach junction (A rings), and those found at the squamocolumnar junction in the lower esophagus (B rings). Patients with Schatzki rings can develop intermittent difficulty swallowing or, more seriously, a completely blocked esophagus. The ring is named after the German-American physician Richard Schatzki. Signs and symptoms Not all patients with Schatzki rings have symptoms; barium swallow tests of the esophagus sometimes show Schatzki rings in patients with no swallowing difficulties. When Schatzki rings cause symptoms, they usually result in episodic difficulties with swallowing (dysphagia) solid foods, or a sensation that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |