Schatzki ring on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A Schatzki ring or Schatzki–Gary ring is a narrowing of the lower
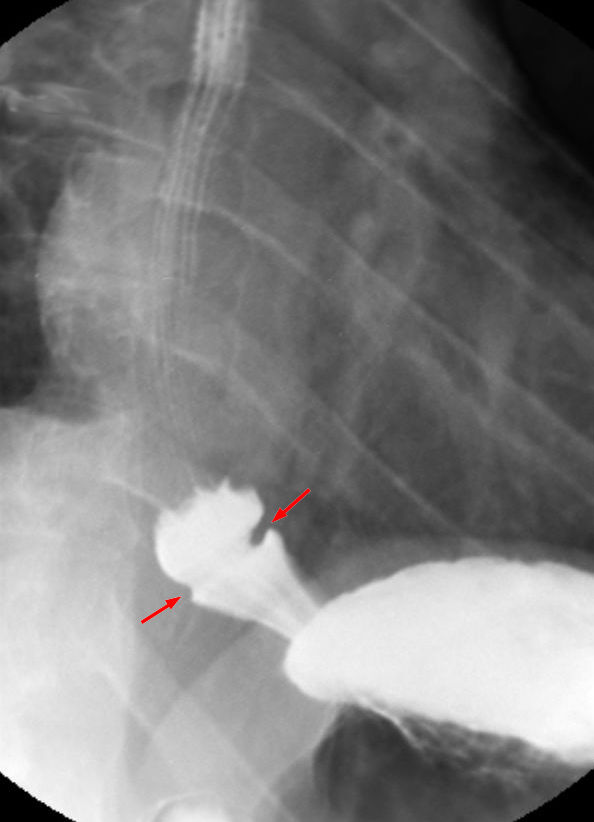 A Schatzki ring is usually diagnosed by
A Schatzki ring is usually diagnosed by
esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the ...
that can cause difficulty swallowing (dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liqu ...
). The narrowing is caused by a ring of mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
l tissue (which lines the esophagus) or muscular tissue. A Schatzki ring is a specific type of "esophageal ring", and Schatzki rings are further subdivided into those above the esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the ...
/stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
junction (A rings), and those found at the squamocolumnar junction in the lower esophagus (B rings).
Patients with Schatzki rings can develop intermittent difficulty swallowing
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liqu ...
or, more seriously, a completely blocked esophagus. The ring is named after the German-American physician Richard Schatzki.
Signs and symptoms
Not all patients with Schatzki rings have symptoms;barium swallow
An upper gastrointestinal series, also called a barium swallow, barium study, or barium meal, is a series of radiographs used to examine the gastrointestinal tract for abnormalities. A contrast medium, usually a radiocontrast agent such as bariu ...
tests of the esophagus sometimes show Schatzki rings in patients with no swallowing difficulties.
When Schatzki rings cause symptoms, they usually result in episodic difficulties with swallowing (dysphagia) solid foods, or a sensation that the food "sticks" while swallowing, especially if the food is not chewed thoroughly. Patients usually are able to regurgitate or force through the food material and resume eating. However, complete obstruction of the esophagus by a bolus
Bolus may refer to:
Geography
* Bolus, Iran, a village in Ardabil Province, Iran
* Bolus, or Baulus, an Anatolian village on the site of ancient Berissa
Medicine
* Bolus (digestion), a ball-shaped mass moving through the digestive tract
* Bolus ...
of food (often called steakhouse syndrome) can occur. This can cause crushing chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with ...
and may need immediate treatment with endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are inse ...
, which is the use of a specialized fibre-optic
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means ...
camera in order to remove the lodged food. After the obstruction is located, snares or forceps
Forceps (plural forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural ''forcipes'' is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Fo ...
are inserted to pull the food out of the esophagus or to push it into the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
. The latter is done with caution, usually when the anatomy of the structures around the obstruction is already known.Other associations
* Schatzki rings can be associated with ''swallow syncope'', a rare variety of syncope. * Schatzki rings are associated with lesser incidence ofBarrett's esophagus
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal ( metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cel ...
, which is considered to be a pre-cancerous condition of the esophagus in some cases.
Cause
Although many hypotheses have been proffered, the cause of Schatzki rings remains uncertain; bothcongenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities c ...
and acquired factors may be involved.
Diagnosis
 A Schatzki ring is usually diagnosed by
A Schatzki ring is usually diagnosed by esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) or oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD), also called by various other names, is a diagnostic endoscopic procedure that visualizes the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract down to the duodenum. It is considere ...
or barium swallow
An upper gastrointestinal series, also called a barium swallow, barium study, or barium meal, is a series of radiographs used to examine the gastrointestinal tract for abnormalities. A contrast medium, usually a radiocontrast agent such as bariu ...
. Endoscopy usually shows a ring within the lumen of the esophagus which can be of variable size (see picture). The ring is usually located a few centimetres above the gastro-esophageal junction
The stomach is a muscular, Organ (anatomy), hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the Digestion, dige ...
, where the esophagus joins the stomach. Schatzki rings can often resemble a related entity called an esophageal web. Esophageal webs also contain extra mucosal tissue, but do not completely encircle the esophagus.
Endoscopies and barium swallows done for other reasons often reveal unsuspected Schatzki rings, meaning that many Schatzki rings are asymptomatic.
Two varieties of Schatzki rings have been described. The original description by Schatzki and Gary was of a ring of fibrous tissue seen on autopsy; this is the less common type of Schatzki ring. More commonly, the ring consists of the same mucosal tissue that lines the entire esophagus.
Treatment
Asymptomatic Schatzki rings seldom worsen over time, and need no treatment. Symptomatic Schatzki rings may be treated withesophageal dilatation
Esophageal dilatation is a therapeutic endoscopic procedure that enlarges the lumen of the esophagus.
Indications
It can be used to treat a number of medical conditions that result in narrowing of the esophageal lumen, or decrease motility in t ...
, using bougie or balloon dilators. These have been found to be equally effective. Bougie dilatation involves passage of long dilating tubes of increasing size down the esophagus to stretch the area of narrowing, either over a guidewire passed into the stomach by endoscopy (the ''Savary-Gillard'' system) or using mercury-weighted dilators (the ''Maloney'' system). This is usually done with intravenous sedation
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure. Examples of drugs which can be used for sedation include isoflurane, diethyl ethe ...
to reduce discomfort. Dilatation can produce some temporary irritation. A short course of proton pump inhibitor
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase proton pump.
They are the most potent inhibitor ...
therapy may decrease aggravation by stomach acid reflux into the esophagus. The duration of the benefit of dilation varies, but may be from months to years. Dilation may be repeated if narrowing recurs.
Epidemiology
About 6 to 14 percent of patients who receive a routinebarium swallow
An upper gastrointestinal series, also called a barium swallow, barium study, or barium meal, is a series of radiographs used to examine the gastrointestinal tract for abnormalities. A contrast medium, usually a radiocontrast agent such as bariu ...
test of the esophagus are found to have a Schatzki ring.
See also
*Dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liqu ...
* Esophageal web
* Esophageal dilatation
Esophageal dilatation is a therapeutic endoscopic procedure that enlarges the lumen of the esophagus.
Indications
It can be used to treat a number of medical conditions that result in narrowing of the esophageal lumen, or decrease motility in t ...
References
External links
{{Congenital malformations and deformations of digestive system Esophagus disorders Congenital disorders of digestive system