|
Endophytic Fungi
An endophyte is an endosymbiont, often a bacterium or fungus, that lives within a plant for at least part of its life cycle without causing apparent disease. Endophytes are ubiquitous and have been found in all species of plants studied to date; however, most of the endophyte/plant relationships are not well understood. Some endophytes may enhance host growth and nutrient acquisition and improve the plant's ability to tolerate abiotic stresses, such as drought, and decrease biotic stresses by enhancing plant resistance to insects, pathogens and herbivores. Although endophytic bacteria and fungi are frequently studied, endophytic archaea are increasingly being considered for their role in plant growth promotion as part of the core microbiome of a plant. History Endophytes were first described by the German botanist Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link in 1809. They were thought to be plant parasitic fungi and they were later termed as "microzymas" by the French scientist Béchamp. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senescence
Senescence () or biological aging is the gradual deterioration of Function (biology), functional characteristics in living organisms. Whole organism senescence involves an increase in mortality rate, death rates or a decrease in fecundity with increasing age, at least in the later part of an organism's biological life cycle, life cycle. However, the resulting effects of senescence can be delayed. The 1934 discovery that calorie restriction can Life extension, extend lifespans by 50% in rats, the existence of species having negligible senescence, and the existence of potentially immortal organisms such as members of the genus ''Hydra (genus), Hydra'' have motivated research into Life extension, delaying senescence and thus age-related diseases. Rare human mutations can cause accelerated aging diseases. Environmental Gerontogens, factors may affect aging – for example, overexposure to ultraviolet radiation accelerates skin aging. Different parts of the body may age at different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbaspirillum Frisingense
''Herbaspirillum frisingense'' is a nitrogen-fixing bacterium which was found in C4-fibre plants like prairie cordgrass ('' Spartina pectinata''), Chinese silver grass, (''Miscanthus sinensis''), Amur silver-grass ('' Miscanthus sacchariflorus''), and Napier grass (''Pennisetum purpureum ''Cenchrus purpureus'', Synonym (taxonomy), synonym ''Pennisetum purpureum'', also known as Napier grass, elephant grass or Uganda grass, is a species of perennial tropical grass native to African grasslands. arrell, G., Simons, S. A., & Hillock ...''). The specific name '' frisingense'' comes from Freising, a town in Germany where '' H. frisingense'' was first isolated from prairie cordgrass and ''Miscanthus'' plants. References External linksType strain of ''Herbaspirillum frisingense'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase Burkholderiales Bacteria described in 2001 {{betaproteobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miscanthus Sinensis
''Miscanthus sinensis'', the eulalia or Chinese silver grass, is a species of flowering plant in the grass family Poaceae, native to most of East Asia (China, Japan, Taiwan and Korea) and Southeast Asia (the Philippines, eastern Indonesia, Malaysia, Vietnam, Thailand, and Laos). Description It is an herbaceous perennial grass, growing to tall, rarely , forming dense clumps from an underground rhizome. The leaves are tall and 0.3–2 cm broad. The flowers are purplish, held above the foliage. This plant is the preferred structure for the nesting of some species of paper wasps, such as '' Ropalidia fasciata''. Nomenclature The Latin specific epithet ''sinensis'' means "from China", though the plant is found elsewhere in eastern Asia. Forms and varieties *''M. sinensis'' f. ''glaber'' Honda *''M. sinensis'' var. ''gracillimus'' Hitchc. *''M. sinensis'' var. ''variegatus'' Beal *''M. sinensis'' var. ''zebrinus'' Beal Cultivation It is widely cultivated as an ornamental pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abscisic Acid
Abscisic acid (ABA or abscisin II) is a plant hormone. ABA functions in many plant developmental processes, including seed and bud dormancy, the control of organ size and stomatal closure. It is especially important for plants in the response to environmental stresses, including drought, soil salinity, cold tolerance, freezing tolerance, heat stress and heavy metal ion tolerance. Discovery In the 1940s, Torsten Hemberg, while working at the University of Stockholm, found evidence that a positive correlation exists between the rest period and the occurrence of an acidic ether soluble growth inhibitor in potato tubers. In 1963, abscisic acid was first identified and characterized as a plant hormone by Frederick T. Addicott and Larry A. Davis. They were studying compounds that cause abscission (shedding) of cotton fruits (bolls). Two compounds were isolated and called abscisin I and abscisin II. Abscisin II is presently called abscisic acid (ABA). In plants Function ABA was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
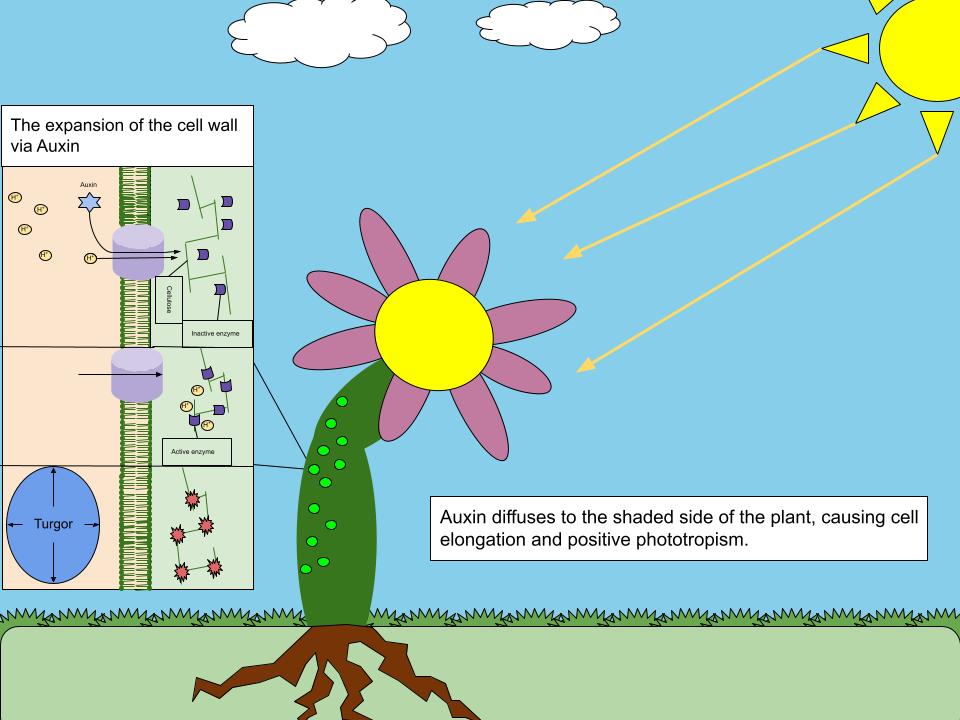
Auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, ''Phytohormones'', in 1937. Overview Auxins were the first of the major plant hormones to be discovered. They derive their name from the Greek word ( – 'to grow/increase'). Auxin is present in all parts of a plant, although in very different concentrations. The concentration in each position is crucial developmental information, so it is subject to tight regulation through both metabolism and transp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Fir
The Douglas fir (''Pseudotsuga menziesii'') is an evergreen conifer species in the pine family, Pinaceae. It is the tallest tree in the Pinaceae family. It is native to western North America and is also known as Douglas-fir, Douglas spruce, Oregon pine, and Columbian pine. There are three varieties: coast Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''menziesii''), Rocky Mountain Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''glauca'') and Mexican Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''lindleyana''). Despite its common names, it is not a true fir (genus '' Abies''), spruce (genus '' Picea''), or pine (genus ''Pinus''). It is also not a hemlock; the genus name ''Pseudotsuga'' means "false hemlock". Description Douglas-firs are medium-sized to extremely large evergreen trees, tall (although only coast Douglas-firs reach heights near 100 m) and commonly reach in diameter, although trees with diameters of almost exist. The largest coast Douglas-firs regularly live over 500 years, with the ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ergoline
Ergoline is a core structure in many alkaloids and their synthetic derivatives. Ergoline alkaloids were first characterized in ergot. Some of these are implicated in the condition of ergotism, which can take a convulsive form or a gangrenous form. Even so, many ergoline alkaloids have been found to be clinically useful. Annual world production of ergot alkaloids has been estimated at 5,000–8,000 kg of all ergopeptines and 10,000–15,000 kg of lysergic acid, used primarily in the manufacture of semi-synthetic derivatives. Others, such as lysergic acid diethylamide, better known as LSD, a Semisynthesis, semi-synthetic derivative, and ergine, a natural derivative found in ''Argyreia nervosa'', ''Ipomoea tricolor'' and related species, are known Psychedelic drug, psychedelic substances. Natural occurrence Ergoline alkaloids are found in fungi such as Claviceps purpurea, Claviceps paspali, and the related Periglandula, which have a permanent, symbiotic bond with numerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clavicipitaceae
The Clavicipitaceae are a family (biology), family of fungi within the order Hypocreales. A 2008 estimate placed 43 genus, genera in the family, but a study in 2020 has increased this number to 50. Phylogeny Molecular phylogeny, phylogenetic analysis of multigene DNA sequence data indicates the taxon Clavicipitaceae (as circumscribed by 2007) is paraphyletic, and consists of three well-defined cladistics, clades, at least one of which is shared with members of another fungal family (Hypocreaceae). The most recent common ancestor of the three clades also include Hypocreaceae as a descendant. The issue seems to have been resolved in Sung ''et al.'' (2007b). Clavicipitaceae becomes restricted to "clade A". Cordycipitaceae is resurrected to hold "clade C". Ophiocordycipitaceae is created to hold "clade B". Evolution The evolution within the Clavicipitaceae (as circumscribed by 2007) is marked by interkingdom host jumping, and the range of this large and heterogeneous fungal grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convolvulaceae
Convolvulaceae (), commonly called the bindweed, bindweeds or morning glory, morning glories, is a Family (biology), family of about 60 genera and more than 1,650 species. These species are primarily herbaceous vines, but also include trees, shrubs and herbs. The Tuber, tubers of several species are edible, the best known of which is the sweet potato. Description Convolvulaceae can be recognized by their funnel-shaped, radially symmetrical corolla (flower), corolla; the floral formula for the family has five sepals, five fused petals, five epipetalous stamens (stamens fused to the petals), and a two-part syncarpous and superior gynoecium. The stems of these plants are usually winding, hence their Latin name (from ''convolvere'', "to wind"). The leaves are simple and alternate, without stipules. In parasitic Cuscuta (dodder) they are reduced to scales. The fruit can be a capsule, berry, or nut, all containing only two seeds per one locule (one ovule/ovary (botany), ovary). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicotyledonous
The dicotyledons, also known as dicots (or, more rarely, dicotyls), are one of the two groups into which all the flowering plants (angiosperms) were formerly divided. The name refers to one of the typical characteristics of the group: namely, that the seed has two embryonic leaves or cotyledons. There are around 200,000 species within this group. The other group of flowering plants were called monocotyledons (or monocots), typically each having one cotyledon. Historically, these two groups formed the two divisions of the flowering plants. Largely from the 1990s onwards, molecular phylogenetic research confirmed what had already been suspected: that dicotyledons are not a group made up of all the descendants of a common ancestor (i.e., they are not a monophyletic group). Rather, a number of lineages, such as the magnoliids and groups now collectively known as the basal angiosperms, diverged earlier than the monocots did; in other words, monocots evolved from within the dico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Metabolite
Secondary metabolites, also called ''specialised metabolites'', ''secondary products'', or ''natural products'', are organic compounds produced by any lifeform, e.g. bacteria, archaea, fungi, animals, or plants, which are not directly involved in the normal cell growth, growth, Biological development, development, or reproduction of the organism. Instead, they generally mediate ecological biological interaction, interactions, which may produce a Natural selection, selective advantage for the organism by increasing its survivability or fecundity. Specific secondary metabolites are often restricted to a narrow set of species within a phylogenetic group. Secondary metabolites often play an important role in plant defense against herbivory and other interspecies defenses. Humans use secondary metabolites as medicines, flavourings, pigments, and recreational drugs. The term secondary metabolite was first coined by Albrecht Kossel, the 1910 Nobel Prize laureate for medicine and physio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |