|
Enamel-dentine Fracture
Enamel-dentine fracture is a complete fracture of the tooth enamel and dentine without the exposure of the pulp. Pulp sensibility testing is recommended to confirm pulpal health. Treatment depends on how close the fracture is in relation to the pulp. If a tooth fragment is available, it can be bonded to the tooth. Otherwise, provisional treatment can be done, which the exposed dentine can be covered using glass ionomer cement or a more permanent treatment restoration using dental composite resin or other accepted restorative dental materials. If the exposed dentine is within 0.5mm of the pulp, clinically a pink appearance can be seen. This shows close proximity to the pulp. In this case, calcium hydroxide is used to place at the base and then covered with a material such as ionomer An ionomer () ('' iono-'' + ''-mer'') is a polymer composed of repeat units of both electrically neutral repeating units and ionized units covalently bonded to the polymer backbone as pendant group moie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
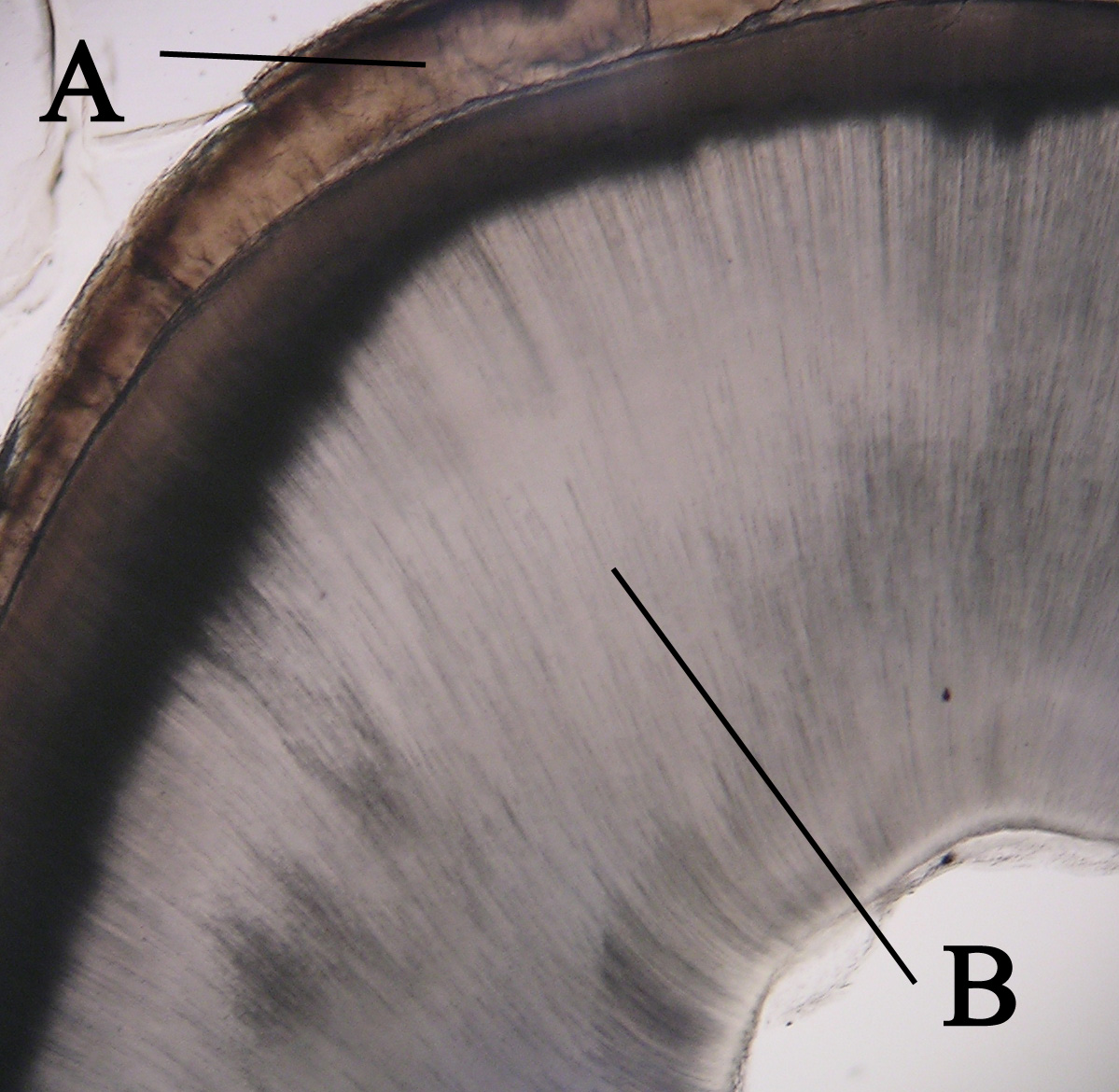
Tooth Enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the four major tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many other animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the crown. The other major tissues are dentin, cementum, and dental pulp. It is a very hard, white to off-white, highly mineralised substance that acts as a barrier to protect the tooth but can become susceptible to degradation, especially by acids from food and drink. Calcium hardens the tooth enamel. In rare circumstances enamel fails to form, leaving the underlying dentin exposed on the surface. Features Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and contains the highest percentage of minerals (at 96%),Ross ''et al.'', p. 485 with water and organic material composing the rest.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nancy, Elsevier, pp. 70–94 The primary mineral is hydroxyapatite, which is a crystalline calcium phosphate. Enamel is formed on the tooth while the tooth develops wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentine
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes and dentin channels b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulp (tooth)
The pulp is the connective tissue, nerves, blood vessels, and odontoblasts that comprise the innermost layer of a tooth. The pulp's activity and signalling processes regulate its behaviour. Anatomy The pulp is the neurovascular bundle central to each tooth, permanent or primary. It is composed of a central pulp chamber, pulp horns, and radicular canals. The large mass of the pulp is contained within the pulp chamber, which is contained in and mimics the overall shape of the crown of the tooth.Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 164. Because of the continuous deposition of the dentine, the pulp chamber becomes smaller with the age. This is not uniform throughout the coronal pulp but progresses faster on the floor than on the roof or sidewalls. Radicular pulp canals extend down from the cervical region of the crown to the root apex. They are not always straight but vary in shape, size, and number. They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulp Sensibility Test
Dental pulpal testing is a clinical and diagnostic aid used in dentistry to help establish the health of the dental pulp within the pulp chamber and root canals of a tooth. Such investigations are important in aiding dentists in devising a treatment plan for the tooth being tested. There are two major types of dental pulp tests. Vitality testing assesses the blood supply to the tooth, whilst sensitivity testing tests the sensory supply. Clinical application Dental pulp tests are valuable techniques used to establish the pulpal health status of a tooth in dentistry. The diagnostic information obtained from pulpal testing is then used alongside a patient's history, clinical and radiographic findings to determine a diagnosis and prognosis of the tooth. Pulp tests are useful for the following procedures in dentistry: * diagnosis of endodontic pathology, * localisation of tooth pain, * differentiating between odontogenic and non-odontogenic pain, * assessing pulpal status following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Ionomer Cement
A glass ionomer cement (GIC) is a dental restorative material used in dentistry as a filling material and luting cement, including for orthodontic bracket attachment. Glass-ionomer cements are based on the reaction of silicate glass-powder (calciumaluminofluorosilicate glass) and polyacrylic acid, an ionomer. Occasionally water is used instead of an acid, altering the properties of the material and its uses. This reaction produces a powdered cement of glass particles surrounded by matrix of fluoride elements and is known chemically as glass polyalkenoate. There are other forms of similar reactions which can take place, for example, when using an aqueous solution of acrylic/ itaconic copolymer with tartaric acid, this results in a glass-ionomer in liquid form. An aqueous solution of maleic acid polymer or maleic/acrylic copolymer with tartaric acid can also be used to form a glass-ionomer in liquid form. Tartaric acid plays a significant part in controlling the setting characteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Composite
Dental composite resins (better referred to as "resin-based composites" or simply "filled resins") are dental cements made of synthetic resins. Synthetic resins evolved as restorative materials since they were insoluble, of good tooth-like appearance, insensitive to dehydration, easy to manipulate and inexpensive. Composite resins are most commonly composed of Bis-GMA and other dimethacrylate monomers (TEGMA, UDMA, HDDMA), a filler material such as silica and in most applications, a photoinitiator. Dimethylglyoxime is also commonly added to achieve certain physical properties such as flow-ability. Further tailoring of physical properties is achieved by formulating unique concentrations of each constituent. Many studies have compared the lesser longevity of resin-based composite restorations to the longevity of silver- mercury amalgam restorations. Depending on the skill of the dentist, patient characteristics and the type and location of damage, composite restorations can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime ( calcium oxide) is mixed or slaked with water. It has many names including hydrated lime, caustic lime, builders' lime, slaked lime, cal, and pickling lime. Calcium hydroxide is used in many applications, including food preparation, where it has been identified as E number E526. Limewater, also called milk of lime, is the common name for a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide. Properties Calcium hydroxide is poorly soluble in water, with a retrograde solubility increasing from 0.66 g/L at 100 °C to 1.89 g/L at 0 °C. With a solubility product ''K''sp of 5.02 at 25 °C, its dissociation in water is large enough that its solutions are basic according to the following dissolution reaction: : Ca(OH)2 → Ca2+ + 2 OH− At ambient temperature, calcium hydroxide ( portlandite) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionomer
An ionomer () ('' iono-'' + '' -mer'') is a polymer composed of repeat units of both electrically neutral repeating units and ionized units covalently bonded to the polymer backbone as pendant group moieties. Usually no more than 15 mole percent are ionized. The ionized units are often carboxylic acid groups. The classification of a polymer as an ionomer depends on the level of substitution of ionic groups as well as how the ionic groups are incorporated into the polymer structure. For example, polyelectrolytes also have ionic groups covalently bonded to the polymer backbone, but have a much higher ionic group molar substitution level (usually greater than 80%); ionenes are polymers where ionic groups are part of the actual polymer backbone. These two classes of ionic-group-containing polymers have vastly different morphological and physical properties and are therefore not considered ionomers. Ionomers have unique physical properties including electrical conductivity and v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergency Medicine
Emergency medicine is the medical speciality concerned with the care of illnesses or injuries requiring immediate medical attention. Emergency physicians (often called “ER doctors” in the United States) continuously learn to care for unscheduled and undifferentiated patients of all ages. As first-line providers, in coordination with Emergency Medical Services, they are primarily responsible for initiating resuscitation and stabilization and performing the initial investigations and interventions necessary to diagnose and treat illnesses or injuries in the acute phase. Emergency physicians generally practise in hospital emergency departments, pre-hospital settings via emergency medical services, and intensive care units. Still, they may also work in primary care settings such as urgent care clinics. Sub-specializations of emergency medicine include; disaster medicine, medical toxicology, point-of-care ultrasonography, critical care medicine, emergency medical service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |