|
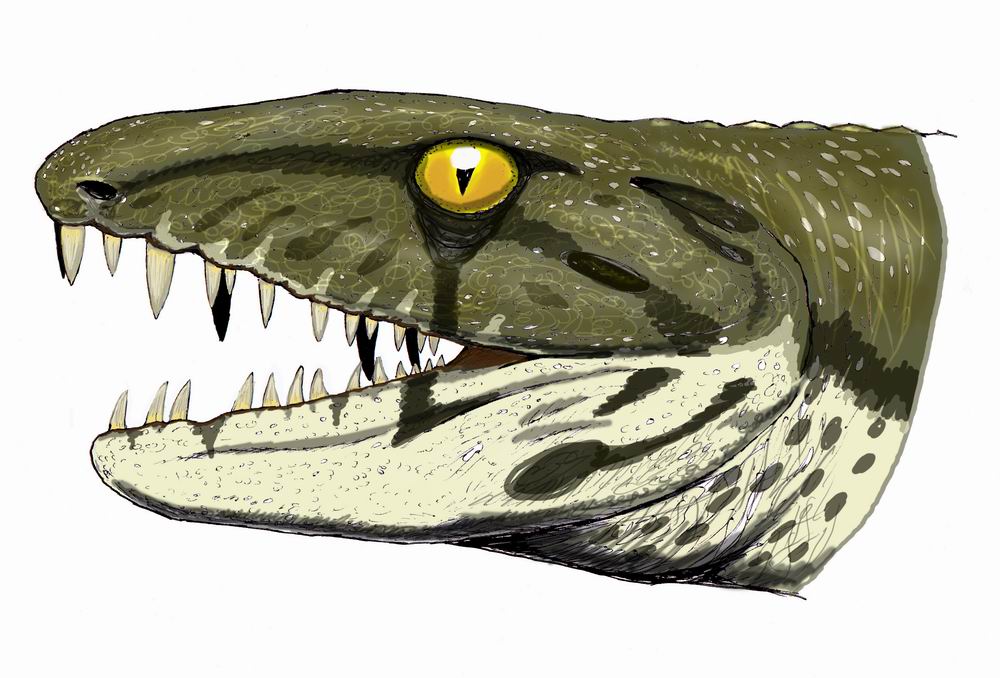
Embolomeri
Embolomeri is an Order (biology), order of Tetrapod, tetrapods or Stem-group, stem-tetrapods, possibly members of Reptiliomorpha. Embolomeres first evolution, evolved in the Early Carboniferous (Mississippian age, Mississippian) Period and were the largest and most successful predatory tetrapods of the Late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian) Period. They were specialized semiaquatic predators with long bodies for eel-like undulatory swimming. Embolomeres are characterized by their Vertebra, vertebral centra, which are formed by two cylindrical segments, the pleurocentrum at the rear and intercentrum at the front. These segments are equal in size. Most other tetrapods have pleurocentra and intercentra which are drastically different in size and shape. Embolomeres were among the earliest large carnivorous tetrapods, with members such as the crocodilian-like ''Proterogyrinus'' appearing in the Viséan, Visean stage of the Carboniferous. They declined in diversity d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiliomorpha
Reptiliomorpha (meaning reptile-shaped; in PhyloCode known as ''Pan-Amniota'') is a clade containing the amniotes and those tetrapods that share a more recent common ancestor with amniotes than with living amphibians (lissamphibians). It was defined by Michel Laurin (2001) and Vallin and Laurin (2004) as the largest clade that includes ''Homo sapiens'', but not ''Tailed frog, Ascaphus truei'' (tailed frog). Laurin and Reisz (2020) defined Pan-Amniota as the largest Total group, total clade containing ''Human, Homo sapiens'', but not ''Common Surinam toad, Pipa pipa'', ''Caecilia tentaculata'', and ''Greater siren, Siren lacertina''. The informal variant of the name, "reptiliomorphs", is also occasionally used to refer to Crown group#Stem groups, stem-amniotes, i.e. a Evolutionary grade, grade of reptile-like tetrapods that are more closely related to amniotes than they are to lissamphibians, but are not amniotes themselves; the name is used in this meaning e.g. by Ruta, Coates and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
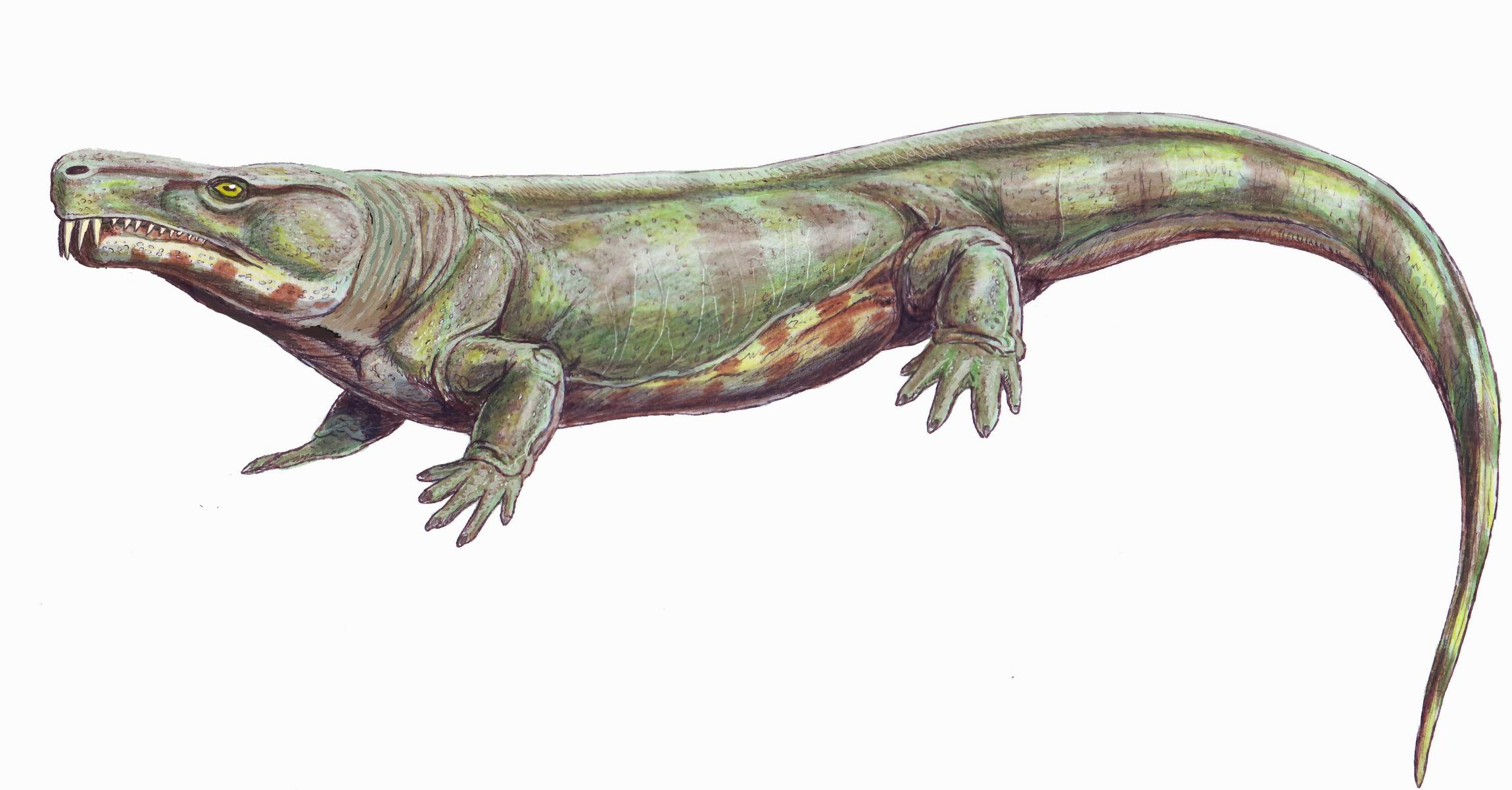
Proterogyrinus
''Proterogyrinus'' is an extinct genus of early tetrapods from the order Embolomeri. Fossil remains of ''Proterogyrinus'' have been found in Scotland, UK, and West Virginia, United States, and date back to the Serpukhovian (mid-Carboniferous period), which is from about 331 to 323 million years ago. The genus was originally named by renowned vertebrate paleontologist Alfred Sherwood Romer in 1970. A comprehensive redescription was later published by Canadian paleontologist Robert Holmes in 1984. The generic name "''Proterogyrinus''" is Greek for "earlier wanderer" or "earlier tadpole". This name was chosen by Romer in keeping with a trend of naming long-bodied early tetrapods (such as '' Eogyrinus'' and '' Crassigyrinus'') with the suffix "-''gyrinus''". Romer hesitated from designating ''Proterogyrinus'' as a true embolomere, because its intercentra (the forward portion of each vertebra) were smaller than its pleurocentra (the rear portion). He used the group Anthracosauria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eoherpeton
''Eoherpeton'' is the only genus of the family Eoherpetontidae in the extinct suborder Embolomeri. It is known from the Visean and Namurian (now Serpukhovian and lower Bashkirian) stages of the Carboniferous The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ... of Scotland. References Embolomeri Mississippian sarcopterygians of Europe Fossil taxa described in 1975 {{paleo-tetrapodomorph-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archeria (animal Genus)
''Archeria'' is a genus of embolomere which lived in the Early Permian of Texas and Oklahoma. It was a medium-sized aquatic predator, with an elongated body and tail. The limbs were proportionally small but well-developed, connected to robust limb girdles. The skull was moderately long and low, up to 30 cm (12 inches) in length. Unlike most embolomeres, ''Archeria'' had many small chisel-shaped teeth instead of large fangs. The anatomy of ''Archeria'' is well known compared to most embolomeres, as it is known from multiple complete skeletons discovered in 1939 by A.S. Romer. These specimens hail from the Geraldine bonebed, a deposit of the coastal Nocona Formation (formerly Admiral Formation) in Archer County, Texas. Other remains of the genus were previously referred to ''Cricotus ''Cricotus'' is an extinct genus of Embolomeri. It was erected by Cope in 1875, on the basis of fragmentary, not clearly associated remains including caudal vertebrae, on which the name w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cricotus
''Cricotus'' is an extinct genus of Embolomeri. It was erected by Cope in 1875, on the basis of fragmentary, not clearly associated remains including caudal vertebrae, on which the name was established (in fact, based on a single intercentrum), as well as a few other postcranial bones. It was little-used in the subsequent literature, contrary to '' Archeria'', which appears to be a junior synonym of ''Cricotus''. However, given that the type species of ''Cricotus'' (''C. heteroclitus'') is a ''nomen dubium'', the name ''Cricotus'' is unavailable. This led to HolmesHolmes R. 1989The skull and axial skeleton of the Lower Permian anthracosauroid amphibian''Archeria crassidisca'' Cope. Palaeontographica Abt. A Palaeozoologie – Stratigraphie 207: 161-206. suggesting using the name '' Archeria'' for this taxon, though he provided no evidence that he made a formal appeal to the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature The International Commission on Zoological Nomenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetrapoda (). Tetrapods include all Neontology#Extant taxa versus extinct taxa, extant and Extinction, extinct amphibians and amniotes, with the latter in turn Evolution, evolving into two major clades, the Sauropsida, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (extinct pelycosaur, "pelycosaurs", therapsids and all extant mammals, including Homo sapiens, humans). Hox gene mutations have resulted in some tetrapods becoming Limbless vertebrate, limbless (snakes, legless lizards, and caecilians) or two-limbed (cetaceans, sirenians, Bipedidae, some lizards, kiwi (bird), kiwis, and the extinct moa and elephant birds). Nevertheless, they still qualify as tetrapods through their ancestry, and some retain a pair of ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archeria (animal)
''Archeria'' is a genus of embolomere which lived in the Early Permian of Texas and Oklahoma. It was a medium-sized aquatic predator Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation ..., with an elongated body and tail. The limbs were proportionally small but well-developed, connected to robust limb girdles. The skull was moderately long and low, up to 30 cm (12 inches) in length. Unlike most embolomeres, ''Archeria'' had many small chisel-shaped teeth instead of large fangs. The anatomy of ''Archeria'' is well known compared to most embolomeres, as it is known from multiple complete skeletons discovered in 1939 by A.S. Romer. These specimens hail from the Geraldine bonebed, a deposit of the coastal Nocona Formation (formerly Admiral Formation) in Archer County, Texas. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepospondyli
Lepospondyli is a diverse clade of early tetrapods. With the exception of one late-surviving lepospondyl from the Late Permian of Morocco ('' Diplocaulus minimus''), lepospondyls lived from the Visean stage of the Early Carboniferous to the Early Permian and were geographically restricted to what is now Europe and North America. Five major groups of lepospondyls are known: Adelospondyli; Aïstopoda; Lysorophia; Microsauria; and Nectridea. Lepospondyls have a diverse range of body forms and include species with newt-like, eel- or snake-like, and lizard-like forms. Various species were aquatic, semiaquatic, or terrestrial. None were large (the biggest genus, the diplocaulid '' Diplocaulus'', reached a meter in length, but most were much smaller), and they are assumed to have lived in specialized ecological niches not taken by the more numerous temnospondyl amphibians that coexisted with them in the Paleozoic. Lepospondyli was named in 1888 by Karl Alfred von Zittel, who coi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracosaurus
''Anthracosaurus'' is an extinct genus of embolomere that lived during the Late Carboniferous (around 315 million years ago) in what is now Scotland, England, and Ohio. Measuring around long, it was a large, aquatic eel-like predator. It has a robust skull about in length with large teeth in the jaws and on the roof of the mouth. ''Anthracosaurus'' probably inhabited swamps, rivers and lakes. Its name is Greek for "coal lizard". Discovery and specimens Scotland The genus and type species ''Anthracosaurus russelli'' were named by Thomas Henry Huxley in 1863, based on fossils acquired by mining surveyor James Russell in 1861. Nearly all fossils were found near Airdrie, in the historic County Lanarkshire of Scotland. Geologically speaking, they hail from the Blackband Ironstone of the Scottish Middle Coal Measures. In traditional European stratigraphy, this layer would be dated to the Westphalian B, corresponding to the early-middle part of the Pennsylvanian (Late Carb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excluding the amniotes (tetrapods with an amniotic membrane, such as modern reptiles, birds and mammals). All extant taxon, extant (living) amphibians belong to the monophyletic subclass (biology), subclass Lissamphibia, with three living order (biology), orders: Anura (frogs and toads), Urodela (salamanders), and Gymnophiona (caecilians). Evolved to be mostly semiaquatic, amphibians have adapted to inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living in freshwater ecosystem, freshwater, wetland or terrestrial ecosystems (such as riparian woodland, fossorial and even arboreal habitats). Their biological life cycle, life cycle typically starts out as aquatic animal, aquatic larvae with gills known as tadpoles, but some species have devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Beds Of Texas And Oklahoma
The Red Beds of Texas and Oklahoma are a group of Early Permian-age geologic strata in the southwestern United States cropping out in north-central Texas and south-central Oklahoma. They comprise several stratigraphic groups, including the Clear Fork Group, the Wichita Group, and the Pease River Group.Nelson, John W., Robert W. Hook, and Dan S. Chaney (2013)Lithostratigraphy of the Lower Permian (Leonardian) Clear Fork Formation of North-Central Texasfrom The Carboniferous-Permian Transition: Bulletin 60, ed. Spencer G. Lucas et al. New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science, pg. 286-311. Retrieved December 28, 2017. The Red Beds were first explored by American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope starting in 1877.Cope, E.D. (1878)Descriptions of Batrachia and Reptilia from the Permian Formation of Texas.Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society, vol. 17, no. 101, pg. 505-30. Retrieved December 28, 2017. Fossil remains of many Permian tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian Age
The Mississippian ( ), also known as Lower Carboniferous or Early Carboniferous, is a subperiod in the geologic timescale or a subsystem of the geologic record. It is the earlier of two subperiods of the Carboniferous period lasting from roughly 358.9 to 323.2 million years ago. As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Mississippian are well identified, but the exact start and end dates are uncertain by a few million years. The Mississippian is so named because rocks with this age are exposed in the Mississippi Valley. The Mississippian was a period of marine transgression in the Northern Hemisphere: the sea level was so high that only the Fennoscandian Shield and the Laurentian Shield were dry land. The cratons were surrounded by extensive delta systems and lagoons, and carbonate sedimentation on the surrounding continental platforms, covered by shallow seas. In North America, where the interval consists primarily of marine limestones, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |