|
Cricotus
''Cricotus'' is an extinct genus of Embolomeri. It was erected by Cope in 1875, on the basis of fragmentary, not clearly associated remains including caudal vertebrae, on which the name was established (in fact, based on a single intercentrum), as well as a few other postcranial bones. It was little-used in the subsequent literature, contrary to '' Archeria'', which appears to be a junior synonym of ''Cricotus''. However, given that the type species of ''Cricotus'' (''C. heteroclitus'') is a nomen dubium, the name ''Cricotus'' is unavailable. This is why Holmes Holmes R. 1989The skull and axial skeleton of the Lower Permian anthracosauroid amphibian''Archeria crassidisca'' Cope. Palaeontographica Abt. A Palaeozoologie – Stratigraphie 207: 161-206. suggested using the name '' Archeria'' for this taxon, though he provided no evidence that he made a formal appeal to the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature The International Commission on Zoological Nomenclat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embolomeri
Embolomeri is an order of tetrapods or stem-tetrapods, possibly members of Reptiliomorpha. Embolomeres first evolved in the Early Carboniferous (Mississippian) Period and were the largest and most successful predatory tetrapods of the Late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) Period. They were specialized semiaquatic predators with long bodies for eel-like undulatory swimming. Embolomeres are characterized by their vertebral centra, which are formed by two cylindrical segments, the pleurocentrum at the rear and intercentrum at the front. These segments are equal in size. Most other tetrapods have pleurocentra and intercentra which are drastically different in size and shape. Embolomeres were among the earliest large carnivorous tetrapods, with members such as the crocodilian-like '' Proterogyrinus'' appearing in the Visean stage of the Carboniferous. They declined in diversity during the Permian period, though at least one representative ('' Archeria)'' was common in the Early Permia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embolomeres
Embolomeri is an order of tetrapods or stem-tetrapods, possibly members of Reptiliomorpha. Embolomeres first evolved in the Early Carboniferous ( Mississippian) Period and were the largest and most successful predatory tetrapods of the Late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) Period. They were specialized semiaquatic predators with long bodies for eel-like undulatory swimming. Embolomeres are characterized by their vertebral centra, which are formed by two cylindrical segments, the pleurocentrum at the rear and intercentrum at the front. These segments are equal in size. Most other tetrapods have pleurocentra and intercentra which are drastically different in size and shape. Embolomeres were among the earliest large carnivorous tetrapods, with members such as the crocodilian-like ''Proterogyrinus'' appearing in the Visean stage of the Carboniferous. They declined in diversity during the Permian period, though at least one representative ('' Archeria)'' was common in the Early Permian. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archeriidae
Archeriidae is a family of embolomeres that lived in the Permian The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Pale ... period. '' Archeria'' is a well known genus of archeriid. Embolomeres Permian first appearances Permian extinctions {{paleo-amphibian-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
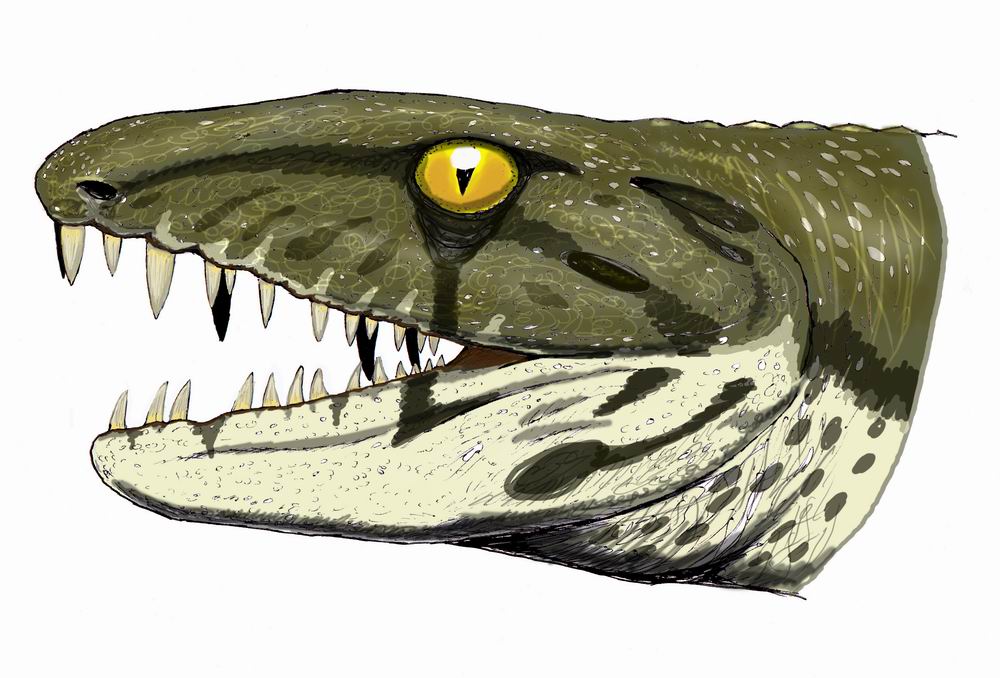
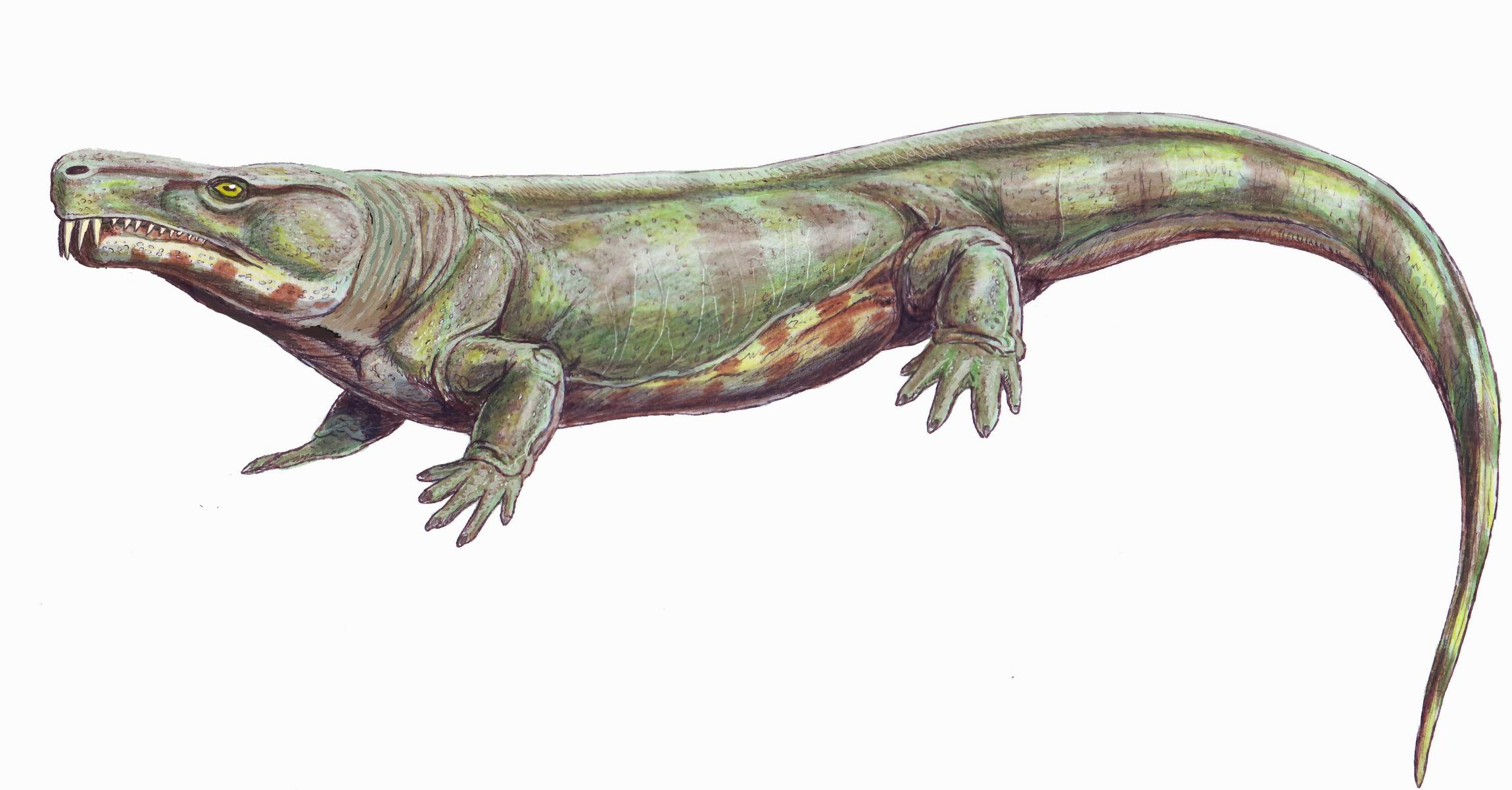
Archeria (animal)
''Archeria'' is a genus of embolomere which lived in the Early Permian of Texas and Oklahoma. It was a medium-sized aquatic predator, with an elongated body and tail. The limbs were proportionally small but well-developed, connected to robust limb girdles. The skull was moderately long and low, up to 30 cm (12 inches) in length. Unlike most embolomeres, ''Archeria'' had many small chisel-shaped teeth instead of large fangs. The anatomy of ''Archeria'' is well known compared to most embolomeres, as it is known from multiple complete skeletons discovered in 1939 by A.S. Romer. These specimens hailed from the Geraldine bonebed, a deposit of the coastal Admiral Formation in Archer County, Texas Archer County is a county located in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 8,560. Its county seat is Archer City. It is part of the Wichita Falls metropolitan statistical area. History In 1858, the Texas Legislat .... Other remains of the genus were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordata
A chordate () is an animal of the phylum Chordata (). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five synapomorphies, or primary physical characteristics, that distinguish them from all the other taxa. These five synapomorphies include a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. The name “chordate” comes from the first of these synapomorphies, the notochord, which plays a significant role in chordate structure and movement. Chordates are also bilaterally symmetric, have a coelom, possess a circulatory system, and exhibit metameric segmentation. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and mitochondrial inner membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cephalochordates. These CSIs provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiliomorpha
Reptiliomorpha (meaning reptile-shaped; in PhyloCode known as ''Pan-Amniota'') is a clade containing the amniotes and those tetrapods that share a more recent common ancestor with amniotes than with living amphibians (lissamphibians). It was defined by Michel Laurin (2001) and Vallin and Laurin (2004) as the largest clade that includes ''Homo sapiens'', but not '' Ascaphus truei'' (tailed frog). Laurin and Reisz (2020) defined Pan-Amniota as the largest total clade containing ''Homo sapiens'', but not '' Pipa pipa'', '' Caecilia tentaculata'', and ''Siren lacertina''. The informal variant of the name, "reptiliomorphs", is also occasionally used to refer to stem-amniotes, i.e. a grade of reptile-like tetrapods that are more closely related to amniotes than they are to lissamphibians, but are not amniotes themselves; the name is used in this meaning e.g. by Ruta, Coates and Quicke (2003). An alternative name, " Anthracosauria", is also commonly used for the group, but is confus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracosauria
Anthracosauria is an order of extinct reptile-like amphibians (in the broad sense) that flourished during the Carboniferous and early Permian periods, although precisely which species are included depends on one's definition of the taxon. "Anthracosauria" is sometimes used to refer to all tetrapods more closely related to amniotes such as reptiles, mammals, and birds, than to lissamphibians such as frogs and salamanders. An equivalent term to this definition would be Reptiliomorpha. Anthracosauria has also been used to refer to a smaller group of large, crocodilian-like aquatic tetrapods also known as embolomeres. Various definitions As originally defined by Säve-Söderbergh in 1934, the anthracosaurs are a group of usually large aquatic Amphibia from the Carboniferous and lower Permian. As defined by Alfred Sherwood Romer however, the anthracosaurs include all non-amniote "labyrinthodont" reptile-like amphibians, and Säve-Söderbergh's definition is more equivalent t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Commission On Zoological Nomenclature
The International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is an organization dedicated to "achieving stability and sense in the scientific naming of animals". Founded in 1895, it currently comprises 26 commissioners from 20 countries. Organization The ICZN is governed by the "Constitution of the ICZN", which is usually published together with the ICZN Code. Members are elected by the Section of Zoological Nomenclature, established by the International Union of Biological Sciences (IUBS). The regular term of service of a member of the Commission is six years. Members can be re-elected up to a total of three full six-year terms in a row. After 18 continuous years of elected service, a break of at least three years is prescribed before the member can stand again for election. Activities Since 2014, the work of the Commission is supported by a small secretariat based at the National University of Singapore, in Singapore. Previously, the secretariat was based in London and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |