|
Dinitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colourless and odourless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant chemical species in air. Because of the volatility of nitrogen compounds, nitrogen is relatively rare in the solid parts of the Earth. It was first discovered and isolated by Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford in 1772 and independently by Carl Wilhelm Scheele and Henry Cavendish at about the same time. The name was suggested by French chemist Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal in 1790 when it was found that nitrogen was present in nitric acid and nitrates. Antoine Lavoisier suggested instea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% , it is referred to as ''fuming nitric acid''. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%. Nitric acid is the primary reagent used for nitration – the addition of a nitro group, typically to an organic molecule. While some resulting nitro compounds are shock- and thermally-sensitive explosives, a few are stable enough to be used in munitions and demolition, while others are still more stable and used as synthetic dyes and medicines (e.g. metronidazole). Nitric acid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly hazardous unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine hydrate (). Hydrazine is mainly used as a foaming agent in preparing Polymeric foam, polymer foams, but applications also include its uses as a precursor (chemistry), precursor to pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, as well as a long-term storable propellant for in-outer space, space spacecraft propulsion. Additionally, hydrazine is used in various rocket propellant, rocket fuels and to prepare the gas precursors used in airbags. Hydrazine is used within both nuclear and conventional electrical power plant steam cycles as an oxygen scavenger to control concentrations of dissolved oxygen in an effort to reduce corrosion. , approximately 120,000 tons of hydrazine hydrate (corresponding to a 64% solution of hydrazine in water by weight) we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pnictogen
, - ! colspan=2 style="text-align:left;" , ↓ Period , - ! 2 , , - ! 3 , , - ! 4 , , - ! 5 , , - ! 6 , , - ! 7 , , - , colspan="2", ---- ''Legend'' A pnictogen ( or ; from "to choke" and -gen, "generator") is any of the chemical elements in group 15 of the periodic table. Group 15 is also known as the nitrogen group or nitrogen family. Group 15 consists of the elements nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), bismuth (Bi), and moscovium (Mc). The IUPAC has called it Group 15 Since 1988. Before that, in America it was called Group VA, owing to a text by H. C. Deming and the Sargent-Welch Scientific Company, while in Europe it was called ecommended that in 1970. (Pronounced "group five A" and "group five B"; "V" is the Roman numeral 5). In semiconductor physics, it is still usually called Group V. The "five" ("V") in the historical names comes from the " pentavalency" of nitrogen, reflected by the stoichiometry of compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pungent smell. It is widely used in fertilizers, refrigerants, explosives, cleaning agents, and is a precursor for numeous chemicals. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to fertilisers. Around 70% of ammonia produced industrially is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many chemicals. In many countries, it is classified as an List of extremely hazardous substances, extremely hazardous substance. Ammonia is toxic, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pnictogen
, - ! colspan=2 style="text-align:left;" , ↓ Period , - ! 2 , , - ! 3 , , - ! 4 , , - ! 5 , , - ! 6 , , - ! 7 , , - , colspan="2", ---- ''Legend'' A pnictogen ( or ; from "to choke" and -gen, "generator") is any of the chemical elements in group 15 of the periodic table. Group 15 is also known as the nitrogen group or nitrogen family. Group 15 consists of the elements nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), bismuth (Bi), and moscovium (Mc). The IUPAC has called it Group 15 Since 1988. Before that, in America it was called Group VA, owing to a text by H. C. Deming and the Sargent-Welch Scientific Company, while in Europe it was called ecommended that in 1970. (Pronounced "group five A" and "group five B"; "V" is the Roman numeral 5). In semiconductor physics, it is still usually called Group V. The "five" ("V") in the historical names comes from the " pentavalency" of nitrogen, reflected by the stoichiometry of compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatomic Molecule
Diatomic molecules () are molecules composed of only two atoms, of the same or different chemical elements. If a diatomic molecule consists of two atoms of the same element, such as hydrogen () or oxygen (), then it is said to be homonuclear molecule, homonuclear. Otherwise, if a diatomic molecule consists of two different atoms, such as carbon monoxide () or nitric oxide (), the molecule is said to be heteronuclear molecule, heteronuclear. The bond in a homonuclear diatomic molecule is non-polar. The only chemical elements that form stable homonuclear diatomic molecules at standard temperature and pressure (STP) (or at typical laboratory conditions of 1 bar (pressure), bar and 25 °C) are the gases hydrogen (), nitrogen (), oxygen (), fluorine (), and chlorine (), and the liquid bromine (). The noble gases (helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon) are also gases at STP, but they are monatomic. The homonuclear diatomic gases and noble gases together are called "ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material, which may either be composed solely of one ingredient or be a mixture containing at least two substances. The potential energy stored in an explosive material may, for example, be: * chemical energy, such as nitroglycerin or grain dust * pressurized gas, such as a gas cylinder, aerosol can, or boiling liquid expanding vapor explosion * nuclear energy, such as in the fissile isotopes uranium-235 and plutonium-239 Explosive materials may be categorized by the speed at which they expand. Materials that detonate (the front of the chemical reaction moves faster through the material than the speed of sound) are said to be "high explosives" and materials that deflagrate ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen (LN2) is nitrogen in a liquid state at cryogenics, low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, mobile liquid whose viscosity is about one-tenth that of acetone (i.e. roughly one-thirtieth that of water at room temperature). Liquid nitrogen is widely used as a coolant. Physical properties The diatomic character of the N2 molecule is retained after liquefaction. The weak van der Waals interaction between the N2 molecules results in little interatomic attraction. This is the cause of nitrogen's unusually low boiling point. The temperature of liquid nitrogen can readily be reduced to its freezing point by placing it in a vacuum chamber pumped by a vacuum pump. Liquid nitrogen's efficiency as a coolant is limited by the fact that it boils immediately on contact with a warmer object, enveloping the object in an insulating layer of nitrogen gas bubbles. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal
Jean-Antoine Chaptal, comte de Chanteloup (; 5 June 1756 – 29 July 1832) was a French chemist, physician, agronomist, industrialist, statesman, educator and philanthropist. Chaptal was involved in early industrialization in France under Napoleon and during the Bourbon Restoration. He was a founder and the first president of the Society for the Encouragement of National Industry. He was an organizer of industrial expositions held in Paris. He compiled a study surveying the condition and needs of French industry in the early 1800s. Chaptal published practical essays on the uses of chemistry. He was an industrial producer of hydrochloric, nitric and sulfuric acids, and was sought after as a technical consultant for the manufacture of gunpowder. Chaptal published works which drew on Antoine Lavoisier's theoretical chemistry to make advances in wine-making.Chaptal, Jean-Antoine. 1801. ''L'Art de faire, de gouverner et de perfectionner les vins''Chaptal, Jean-Antoine. 1806. ''La Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
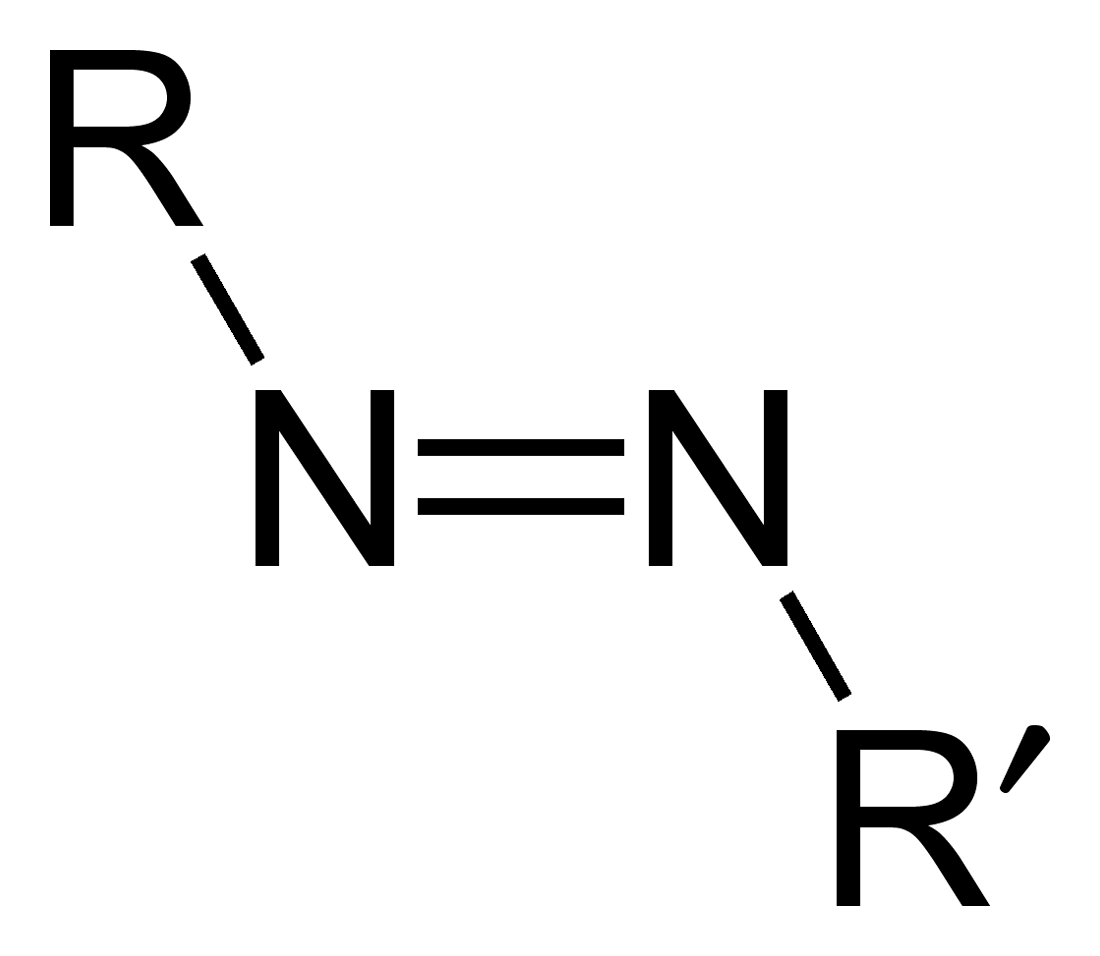
Azo Compound
Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl (, in which R and R′ can be either aryl or alkyl groups). IUPAC defines azo compounds as: "Derivatives of diazene (diimide), , wherein both hydrogens are substituted by hydrocarbyl groups, e.g. azobenzene or diphenyldiazene.", where Ph stands for phenyl group. The more stable derivatives contain two aryl groups. The group is called an ''azo group'' (, ). Many textile and leather articles are dyed with azo dyes and pigments. Aryl azo compounds urinary tract infections">Phenazopyridine, an aryl azo compound, is used to treat urinary tract infections">150px Aryl azo compounds are usually stable, crystalline species. Azobenzene is the prototypical aromatic azo compound. It exists mainly as the Cis-trans isomerism, ''trans'' isomer, but upon illumination, converts to the Cis-trans isomerism, ''cis'' isomer. Aromatic azo compounds can be synthesized by azo coupling, which entails an electrophilic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azide
In chemistry, azide (, ) is a linear, polyatomic anion with the formula and structure . It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid . Organic azides are organic compounds with the formula , containing the azide functional group. The dominant application of azides is as a propellant in air bags. Preparation Sodium azide is made industrially by the reaction of nitrous oxide, with sodium amide in liquid ammonia as solvent: : Many inorganic azides can be prepared directly or indirectly from sodium azide. For example, lead azide, used in detonators, may be prepared from the metathesis reaction between lead nitrate and sodium azide. An alternative route is direct reaction of the metal with silver azide dissolved in liquid ammonia. Some azides are produced by treating the carbonate salts with hydrazoic acid. Bonding Azide is isoelectronic with carbon dioxide , cyanate , nitrous oxide , nitronium ion , molecular beryllium fluoride and cyanogen fluoride FCN. Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures. The 13th International Institute of Refrigeration's (IIR) International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington, DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of "cryogenics" and "cryogenic" by accepting a threshold of to distinguish these terms from conventional refrigeration. This is a logical dividing line, since the normal boiling points of the so-called permanent gases (such as helium, hydrogen, neon, nitrogen, oxygen, and normal air) lie below 120 K, while the Freon refrigerants, hydrocarbons, and other common refrigerants have boiling points above 120 K. Discovery of superconducting materials with critical temperatures significantly above the boiling point of nitrogen has provided new interest in reliable, low-cost methods of producing high-temperature cryogenic refrigeration. The term "high temperature cryogenic" describes temperatures ranging from above the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |