|
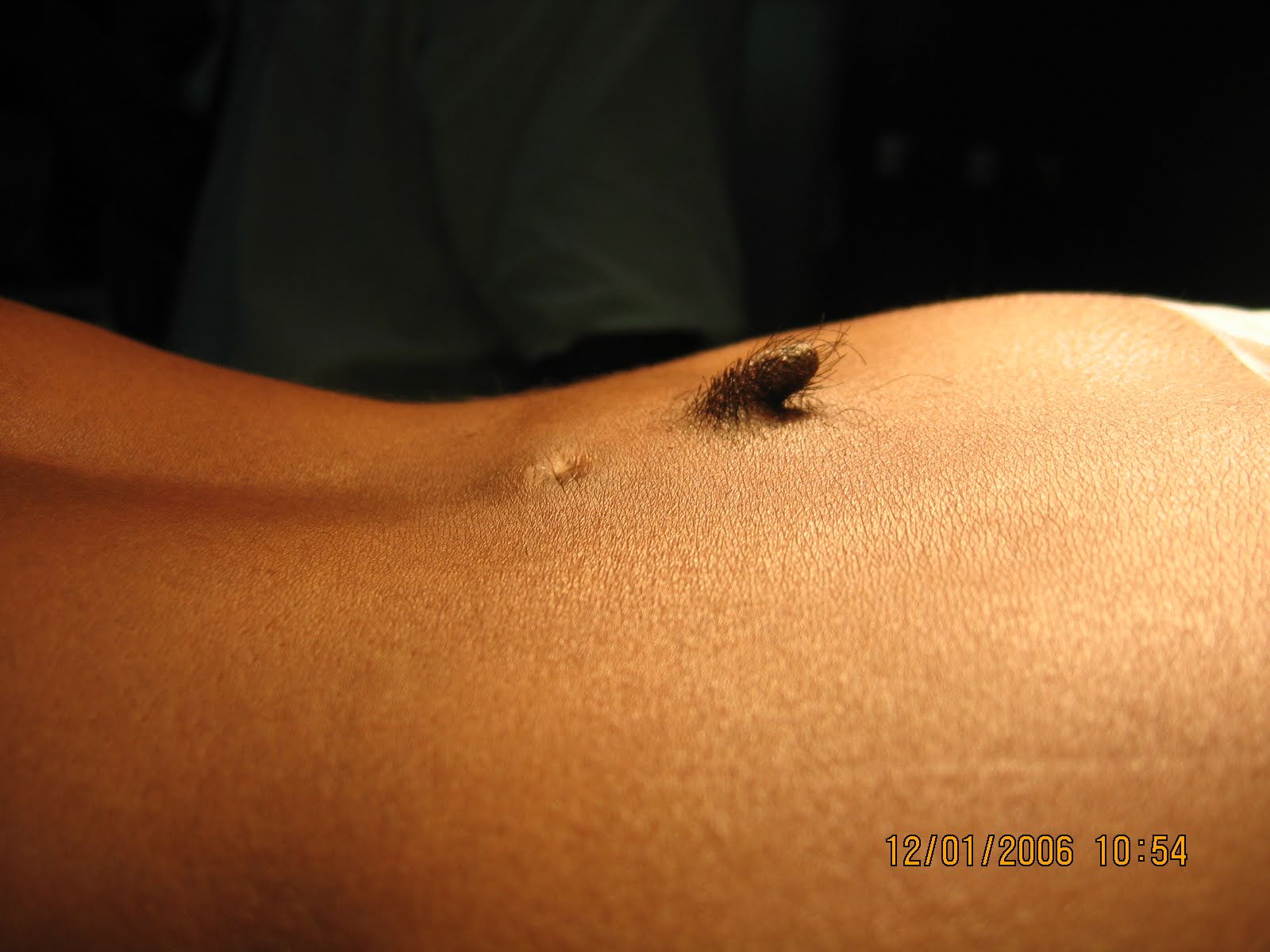
Diastematomyelia
In neurology, diastematomyelia (occasionally diastomyelia) is a congenital disorder in which a part of the spinal cord is split, usually at the level of the upper lumbar vertebra in the longitudinal (sagittal) direction. Females are affected much more commonly than males. This condition occurs in the presence of an osseous, cartilaginous or fibrous septum in the central portion of the spinal canal which then produces a complete or incomplete sagittal division of the spinal cord into two hemicords. When the split does not reunite distally to the spur, the condition is referred to as diplomyelia, which is true duplication of the spinal cord. Signs and symptoms The signs and symptoms of diastematomyelia may appear at any time of life, although the diagnosis is usually made in childhood. Cutaneous lesions (or stigmata), such as a hairy patch, dimple, Hemangioma, subcutaneous mass, Lipoma or Teratoma over the affected area of the spine is found in more than half of cases. Neurolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system. In humans, the spinal cord is a continuation of the brainstem and anatomically begins at the occipital bone, passing out of the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it tapers to become the cauda equina. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tethered Spinal Cord Syndrome
Tethered cord syndrome (TCS) refers to a group of neurological disorders that relate to malformations of the spinal cord.Tethered Spinal Cord , Columbia University Department of Neurosurgery. Various forms include tight , lipomeningomyelocele, split cord malformations ( diastematomyelia), occult, dermal sinus tracts, and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurology
Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suffix wikt:-logia, -logia, "study of") is the branch of specialty (medicine) , medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the Human brain, brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system , peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system, using various techniques of neurotherapy. IEEE Brain (2019). "Neurotherapy: Treating Disorders by Retraining the Brain". ''The Future Neural Therapeutics White Paper''. Retrieved 23.01.2025 from: https://brain.ieee.org/topics/neurotherapy-treating-disorders-by-retraining-the-brain/#:~:text=Neurotherapy%20trains%20a%20patient's%20brain,wave%20activity%20through%20positive%20reinforcement International Neuromodulation Society, Retrieved 23 January 2025 from: https://www.neuromodulation.com/ Val Danilov I (2023). "The O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Tissue
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, or superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macrophages. The subcutaneous tissue is derived from the mesoderm, but unlike the dermis, it is not derived from the mesoderm's Dermatome (anatomy), dermatome region. It consists primarily of loose connective tissue and contains larger blood vessels and nerves than those found in the dermis. It is a major site of fat storage in the body. In arthropods, a hypodermis can refer to an epidermal layer of cells that secretes the chitinous cuticle. The term also refers to a layer of cells lying immediately below the Epidermis (botany), epidermis of plants. Structure * Fibrous bands anchoring the skin to the deep fascia * Collagen and elastin fibers attaching it to the dermis * Fat is absent from the eyelids, clitoris, penis, much of Pinna (anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Trauma
{{disambiguation ...
Acute may refer to: Language * Acute accent, a diacritic used in many modern written languages * Acute (phonetic), a perceptual classification Science and mathematics * Acute angle ** Acute triangle ** Acute, a leaf shape in the glossary of leaf morphology * Acute (medicine), a disease that it is of short duration and of recent onset. ** Acute toxicity, the adverse effects of a substance from a single exposure or in a short period of time See also * Acutance, in photography, subjective perception of sharpness related to the edge contrast of an image * Acuity (other) Acuity may refer to: Biology and medicine *Visual acuity, the behavioral ability to resolve fine image detail *Tactile acuity, resolving fine spatial details with the sense of touch * Acute Catheterization and Urgent Intervention Triage Strategy ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates viscera, internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, its Myocardial contractility, force of contraction, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary dilation, pupillary response, Micturition, urination, and Animal sexual behaviour, sexual arousal. The fight-or-flight response, also known as the acute stress response, is set into action by the autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is regulated by integrated reflexes through the brainstem to the spinal cord and organ (anatomy), organs. Autonomic functions include control of respiration, heart rate, cardiac regulation (the cardiac control center), vasomotor activity (the vasomotor center), and certain reflex, reflex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syringomyelia
Syringomyelia is a generic term referring to a disorder in which a cyst or cavity forms within the spinal cord. Often, syringomyelia is used as a generic term before an etiology is determined. This cyst, called a syrinx, can expand and elongate over time, destroying the spinal cord. The damage may result in loss of feeling, paralysis, weakness, and stiffness in the back, shoulders, and extremities. Syringomyelia may also cause a loss of the ability to feel extremes of hot or cold, especially in the hands. It may also lead to a cape-like bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensation along the upper chest and arms. The combination of symptoms varies from one patient to another depending on the location of the syrinx within the spinal cord, as well as its extent. Syringomyelia has a prevalence estimated at 8.4 cases per 100,000 people, with symptoms usually beginning in young adulthood. Signs of the disorder tend to develop slowly, although sudden onset may occur with coughing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysts
A cyst is a closed Wikt:sac, sac, having a distinct Cell envelope, envelope and cell division, division compared with the nearby Biological tissue, tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of Cell (biology), cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble); however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal (in both appearance and behaviour) when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location. Cancer-related cysts are formed as a defense mechanism for the body following the development of mutations that lead to an uncontrolled cellular division. Once that mutation has o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spina Bifida
Spina bifida (SB; ; Latin for 'split spine') is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the vertebral column, spine and the meninges, membranes around the spinal cord during embryonic development, early development in pregnancy. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, meningocele and myelomeningocele. Meningocele and myelomeningocele may be grouped as spina bifida cystica. The most common location is the Lumbar vertebrae, lower back, but in rare cases it may be in the Thoracic vertebrae, middle back or Cervical vertebrae, neck. Occulta has no or only mild signs, which may include a hairy patch, dimple, dark spot or swelling on the back at the site of the gap in the spine. Meningocele typically causes mild problems, with a sac of fluid present at the gap in the spine. Myelomeningocele, also known as open spina bifida, is the most severe form. Problems associated with this form include poor ability to walk, impaired Neurogenic bladder dysfunction, bladder o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a significant effect on quality of life. Urinary incontinence is common in older women and has been identified as an important issue in geriatric health care. The term enuresis is often used to refer to urinary incontinence primarily in children, such as nocturnal enuresis (bed wetting). UI is an example of a stigmatized medical condition, which creates barriers to successful management and makes the problem worse. People may be too embarrassed to seek medical help, and attempt to self-manage the symptom in secrecy from others. Pelvic surgery, pregnancy, childbirth, attention deficit disorder (ADHD), and menopause are major risk factors. Urinary incontinence is often a result of an underlying medical condition but is under-reported to medical practitioners. There are four main types of incontinence: * Urge incontinence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scoliosis
Scoliosis (: scolioses) is a condition in which a person's Vertebral column, spine has an irregular curve in the coronal plane. The curve is usually S- or C-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others, it increases over time. Mild scoliosis does not typically cause problems, but more severe cases can affect breathing and movement. Pain is usually present in adults, and can worsen with age. As the condition progresses, it may alter a person's life, and hence can also be considered a disability. It can be compared to kyphosis and lordosis, other abnormal curvatures of the spine which are in the sagittal plane (front-back) rather than the coronal (left-right). The cause of most cases is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of Genetics, genetic and environmental factors. Scoliosis most often occurs during growth spurts right before puberty. Risk factors include other affected family members. It can also occur due to anoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Back Pain
Low back pain or wiktionary:lumbago#Etymology, lumbago is a common musculoskeletal disorders, disorder involving the muscles, nerves, and bones of the back, in between the lower edge of the ribs and the lower fold of the buttocks. Pain can vary from a dull constant ache to a sudden sharp feeling. Low back pain may be classified by Pain#Chronic versus acute, duration as acute (pain lasting less than 6 weeks), sub-chronic (6 to 12 weeks), or chronic (more than 12 weeks). The condition may be further classified by the underlying cause as either mechanical, non-mechanical, or referred pain. The symptoms of low back pain usually improve within a few weeks from the time they start, with 40–90% of people recovered by six weeks. In most episodes of low back pain a specific underlying cause is not identified or even looked for, with the pain believed to be due to mechanical problems such as muscle strain, muscle or joint strain. If the pain does not go away with conservative treatmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |